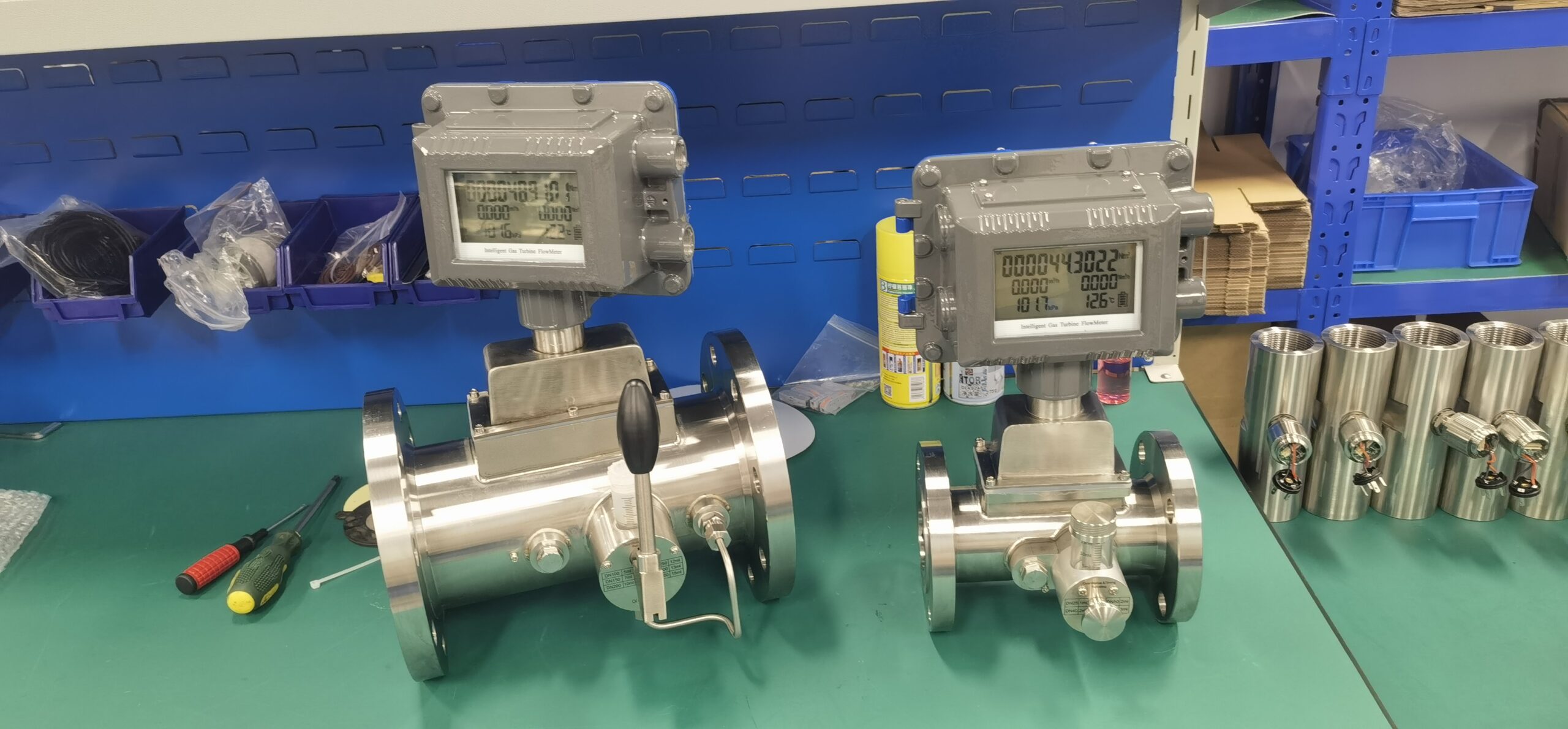
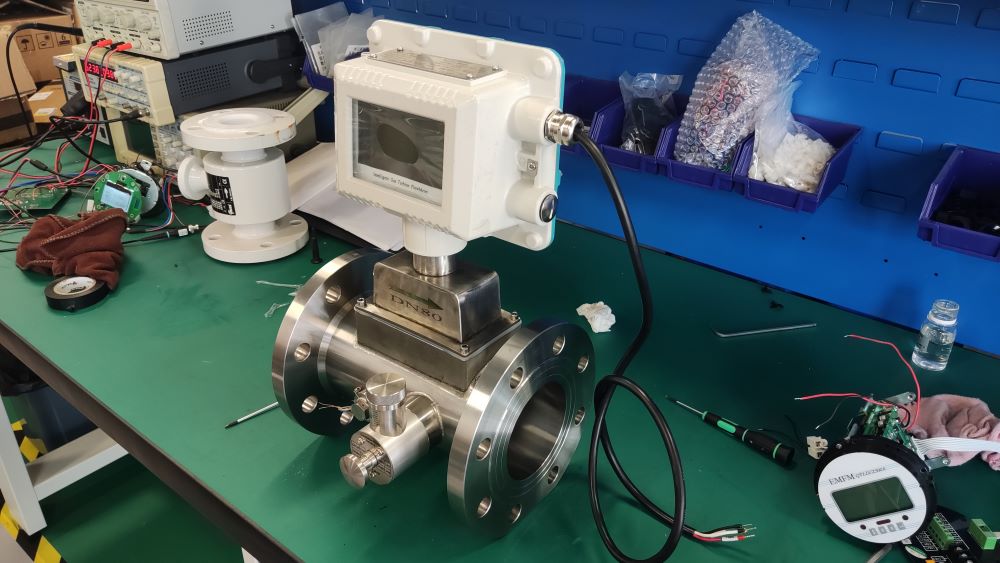
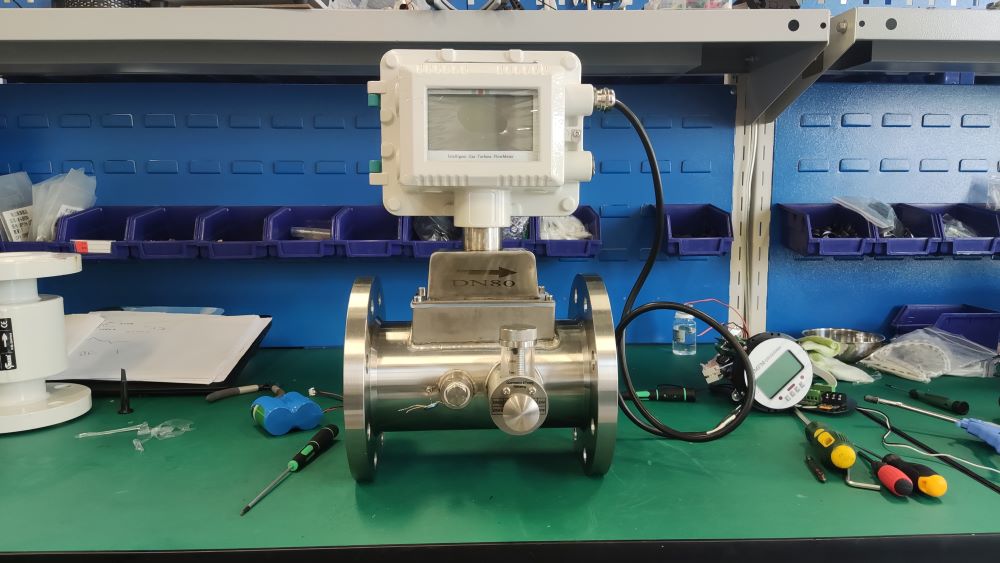
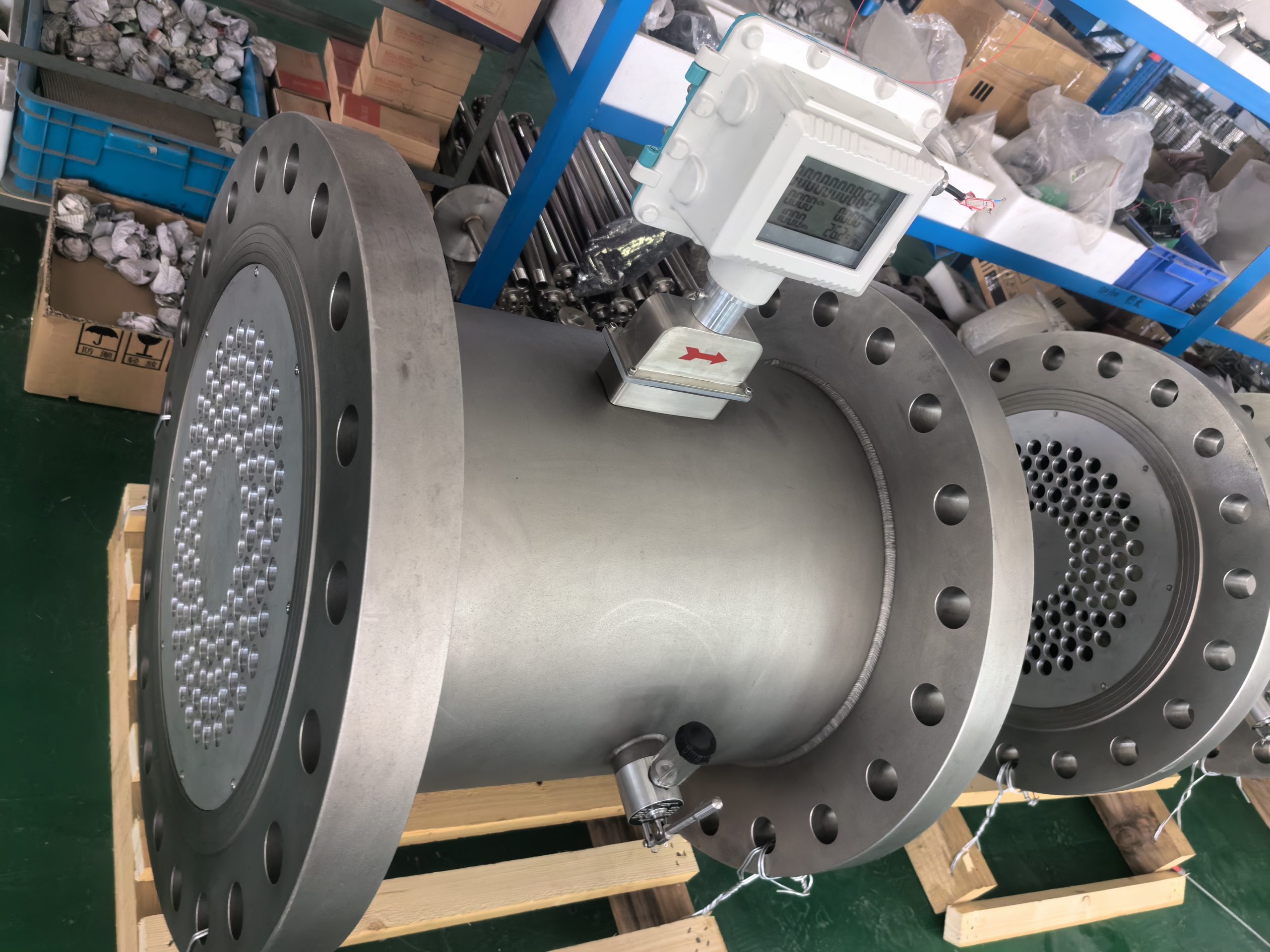
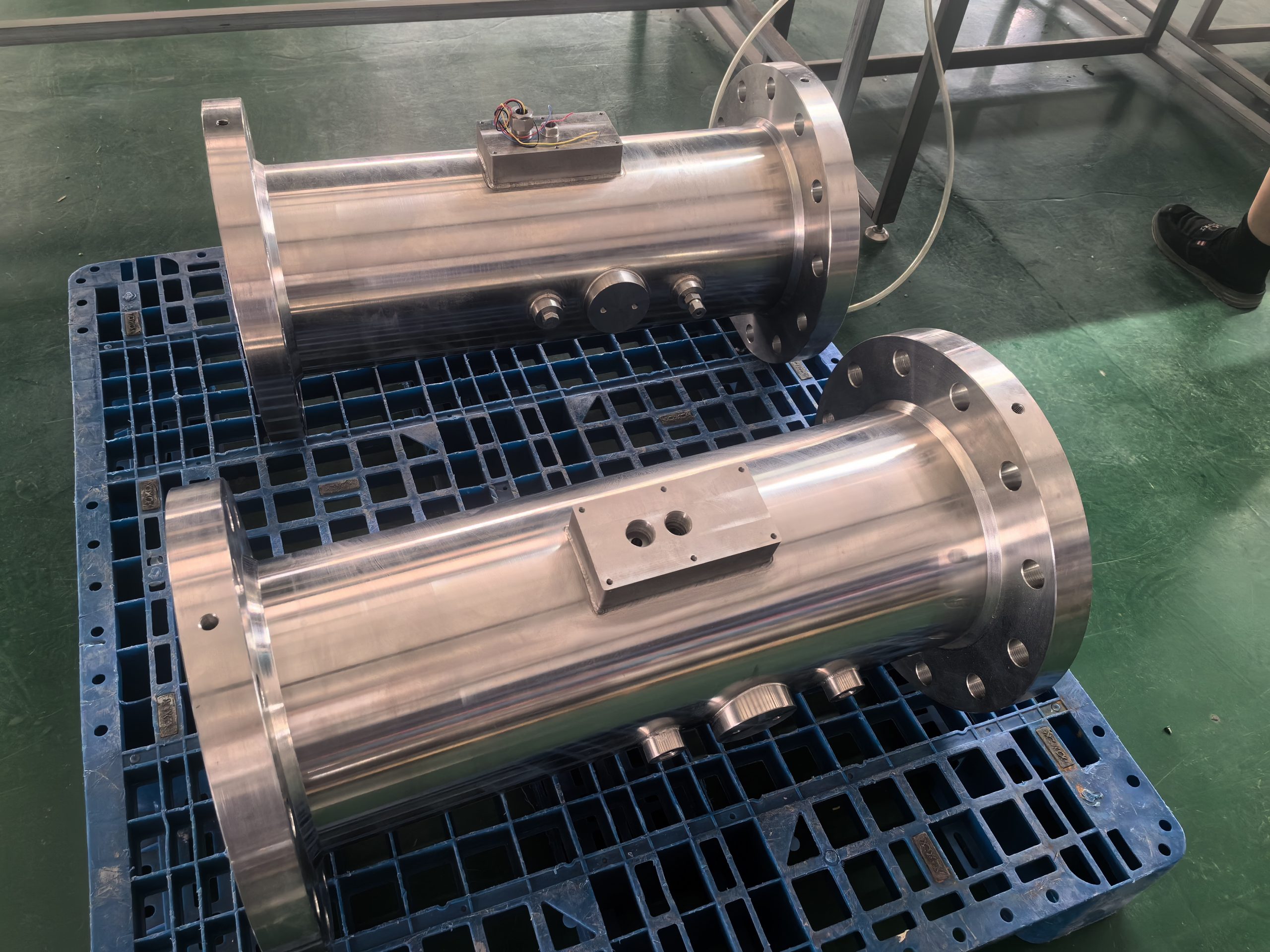
Application Analysis of Gas Turbine Flowmeter
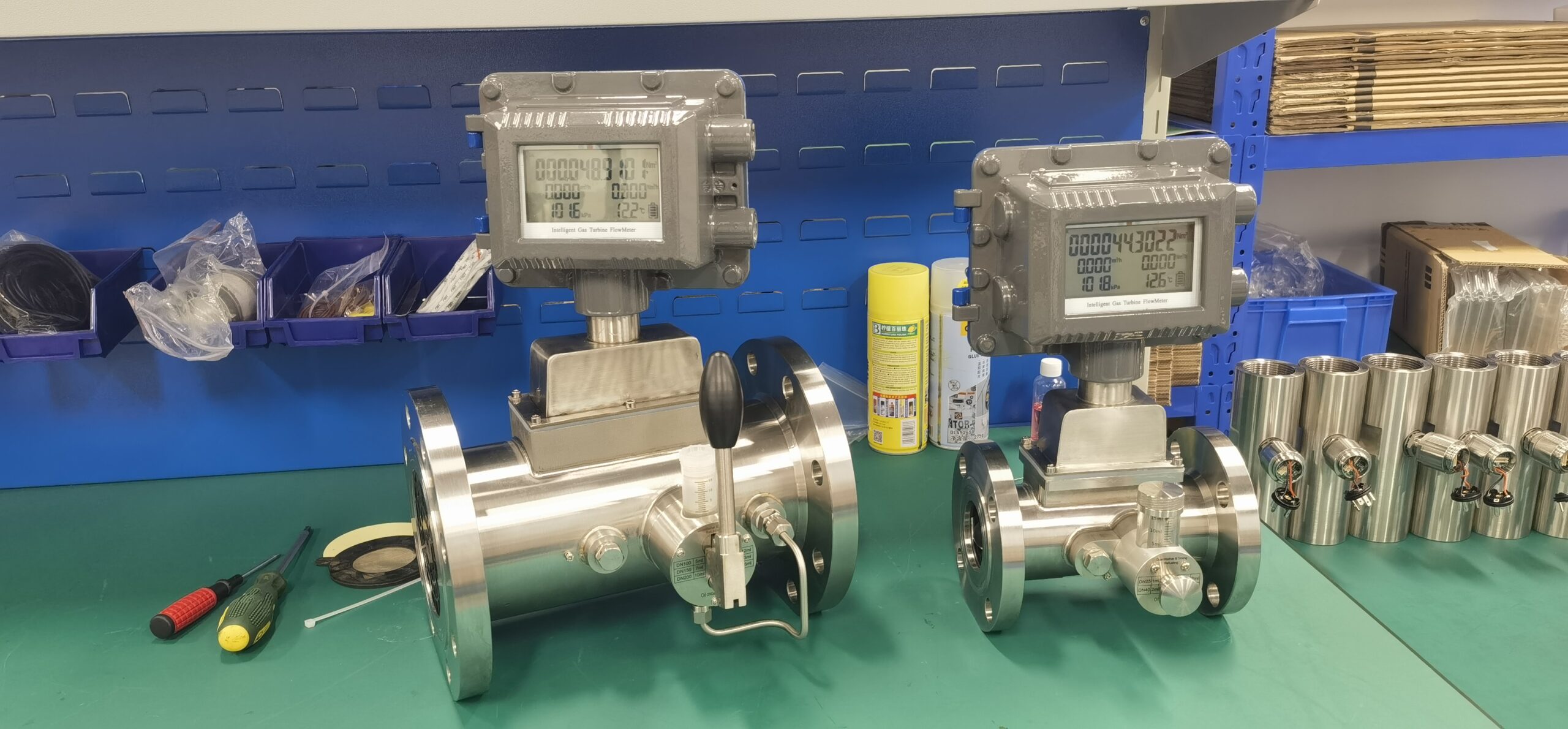
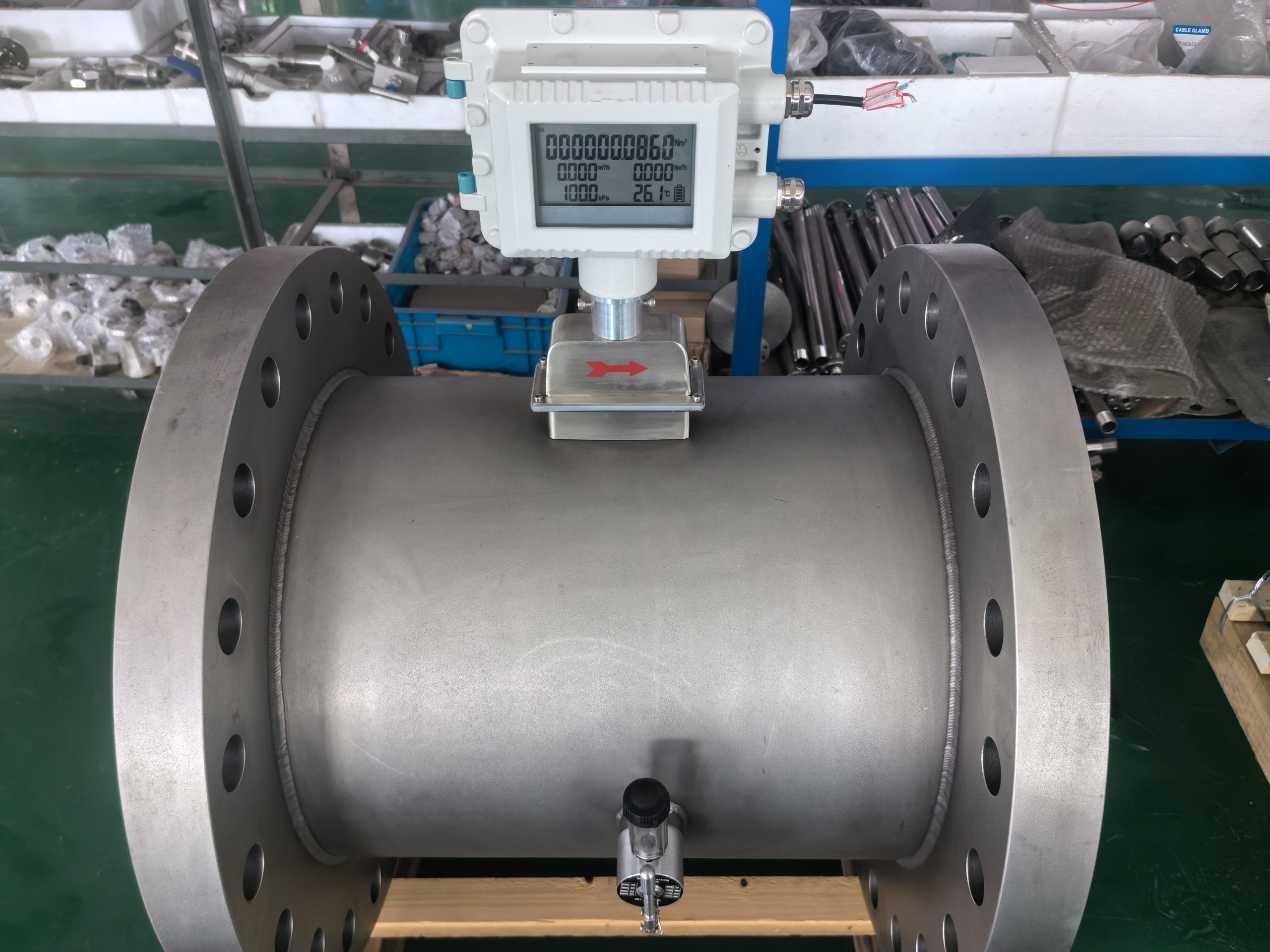
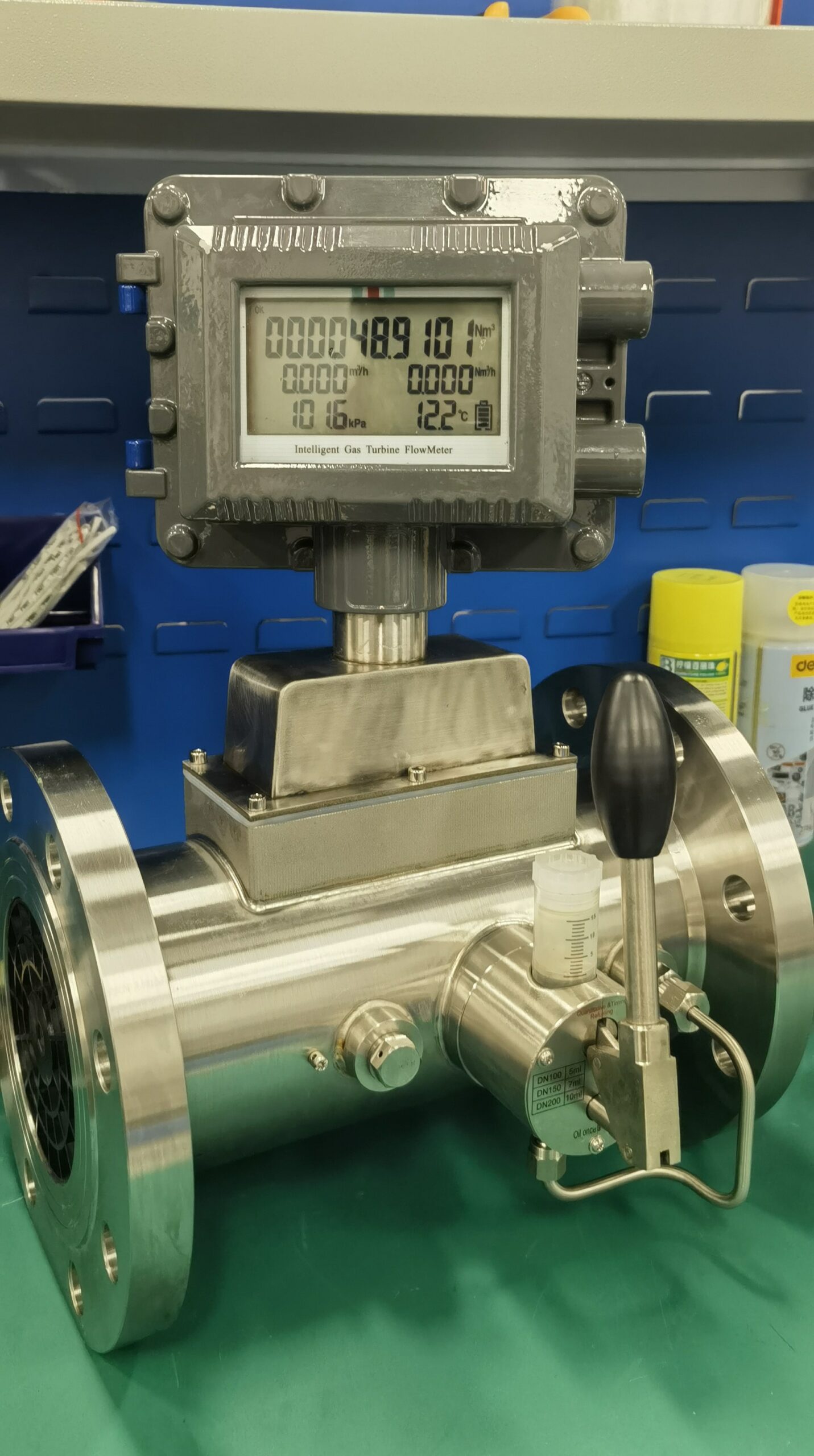
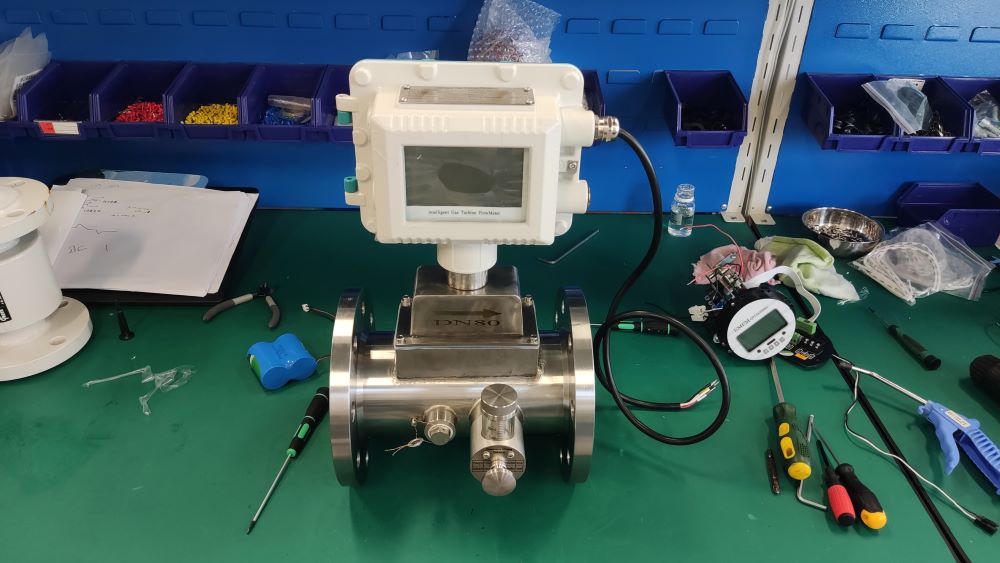
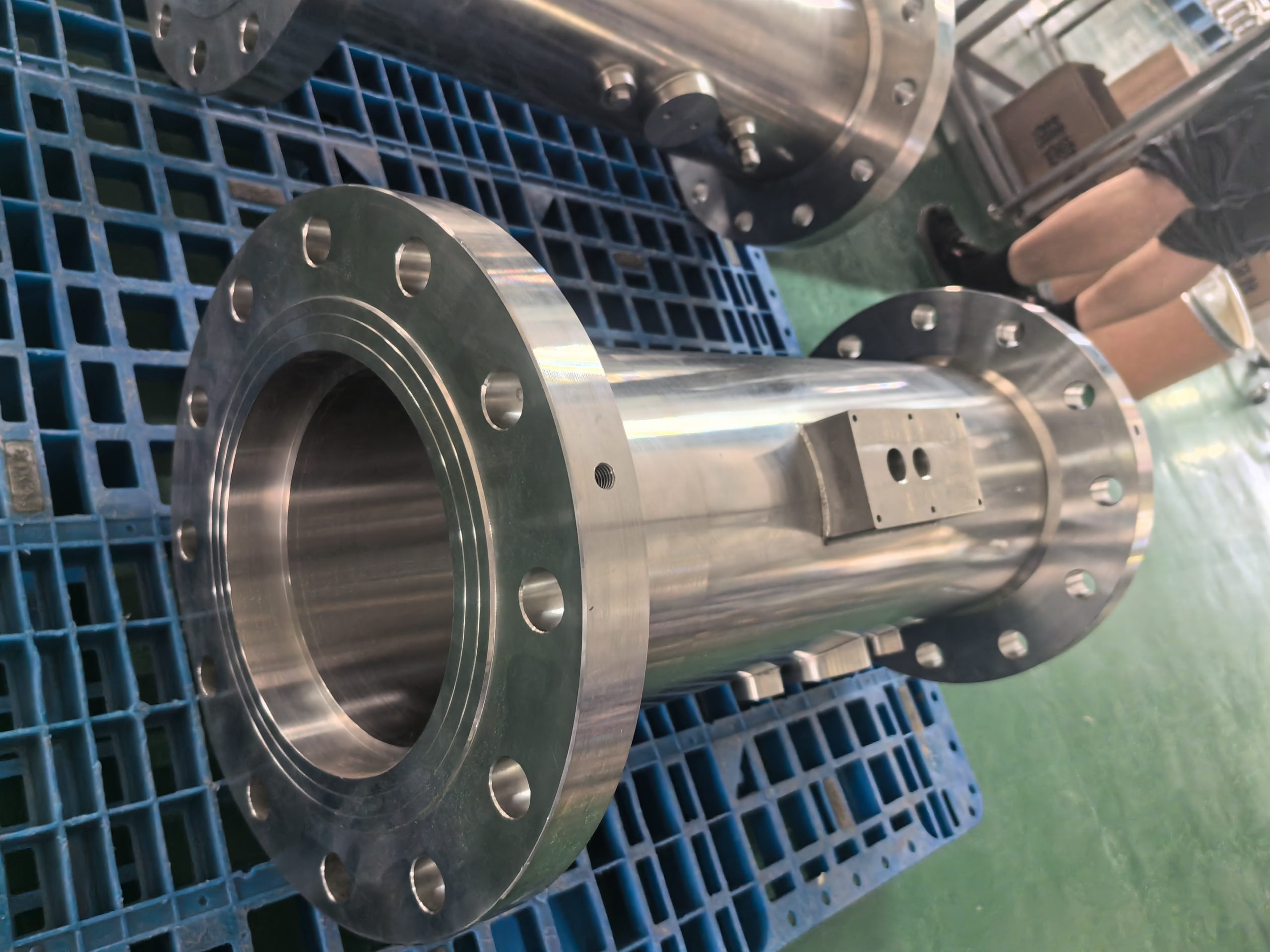
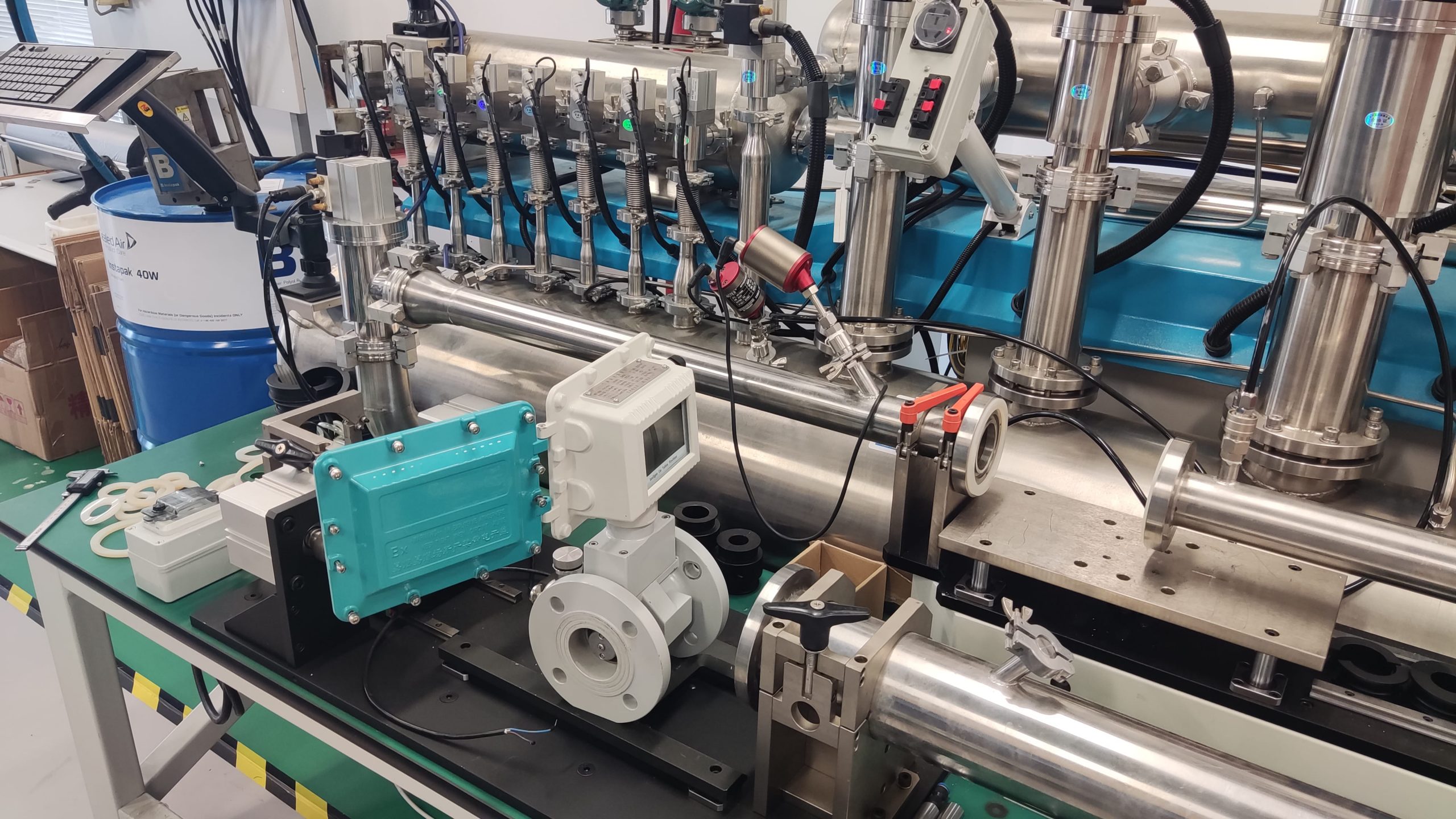
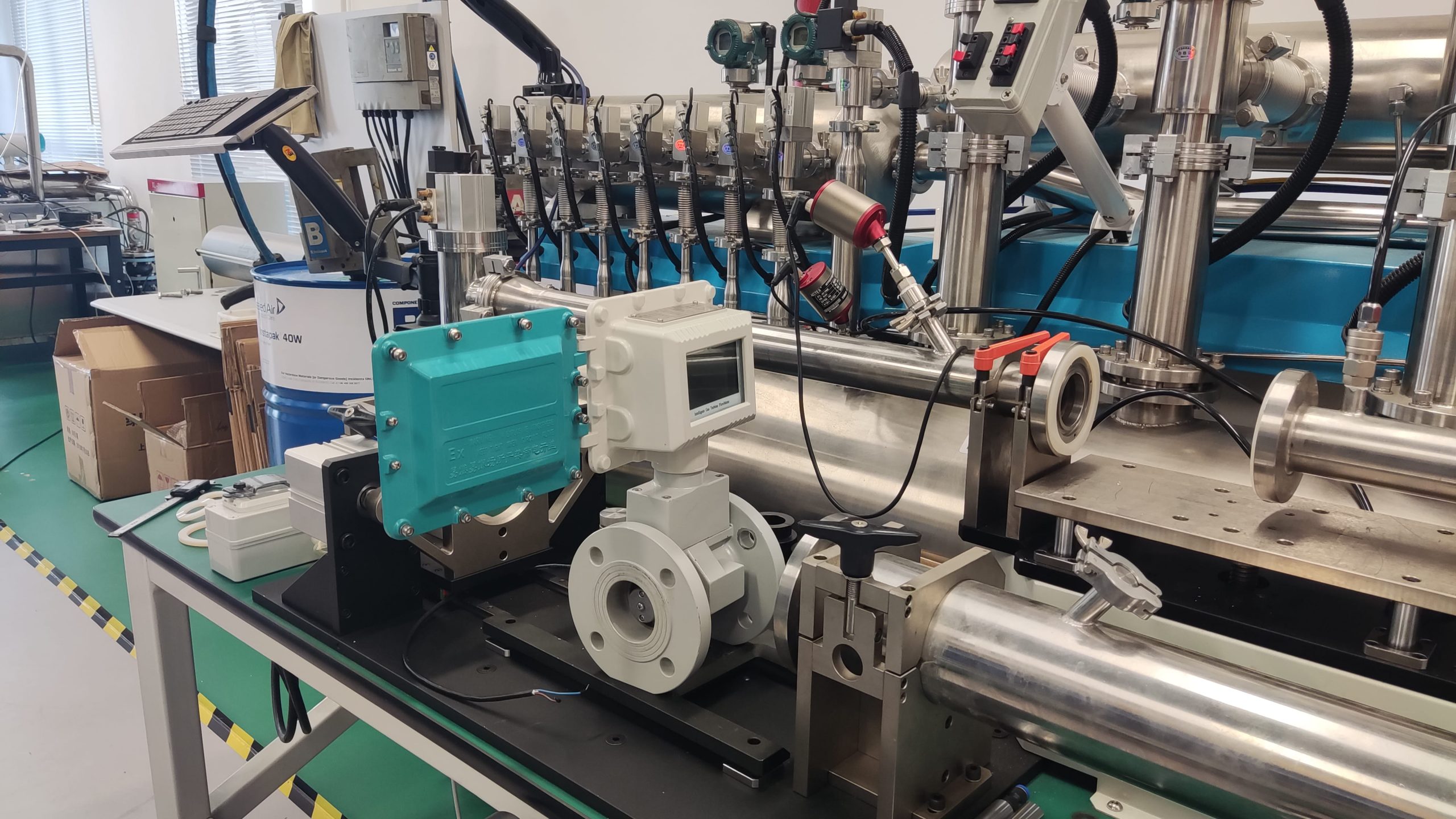
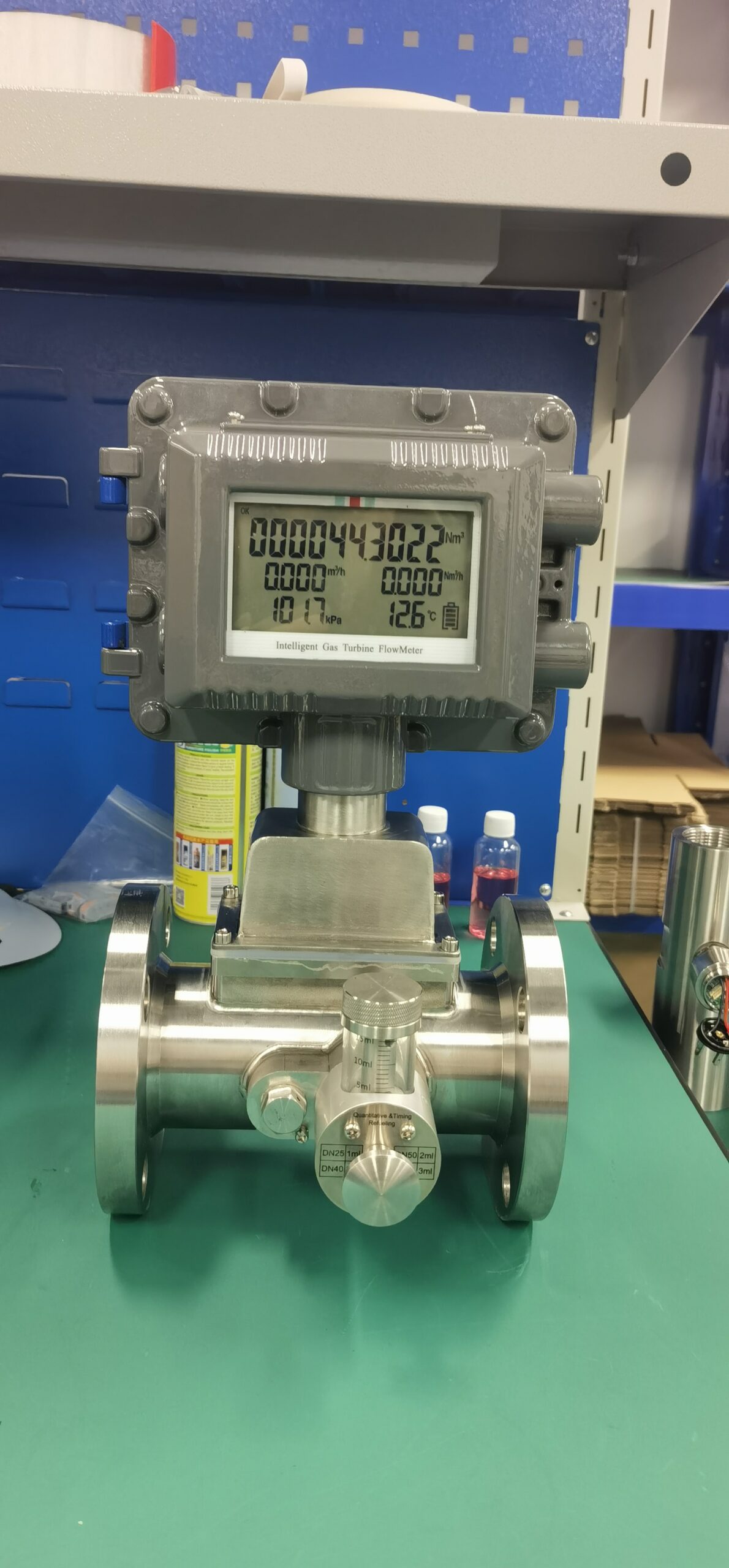
The gas turbine flowmeter is a flow measurement instrument designed based on the principle that the turbine speed is proportional to the fluid flow velocity. It features high measurement accuracy, fast response speed and wide range ratio. It calculates the gas flow rate by detecting the rotation frequency of turbine blades and is widely used in fields such as industrial process control, energy measurement and environmental protection.
1. Overview of Gas Turbine Flowmeter
The gas turbine flowmeter is a flow measurement instrument designed based on the principle that the turbine speed is proportional to the fluid flow velocity. It features high measurement accuracy, fast response speed and wide range ratio. It calculates the gas flow rate by detecting the rotation frequency of turbine blades and is widely used in fields such as industrial process control, energy measurement and environmental protection.
2. Main application fields
Natural gas measurement: In the natural gas transmission and distribution system, turbine flowmeters have become the preferred instrument for trade settlement due to their high precision, especially suitable for large industrial and commercial users and urban gate stations.
Industrial process control: It is used in industries such as chemical engineering and metallurgy to monitor the flow of reaction gases and ensure the stability of the production process.
Compressed air measurement: Monitoring energy consumption in air compressor stations and compressed air pipelines to enhance energy utilization efficiency.
Environmental protection monitoring: It is used for monitoring flue gas emissions and helps environmental protection departments supervise the emission situation of enterprises.
3. Analysis of Technical Advantages
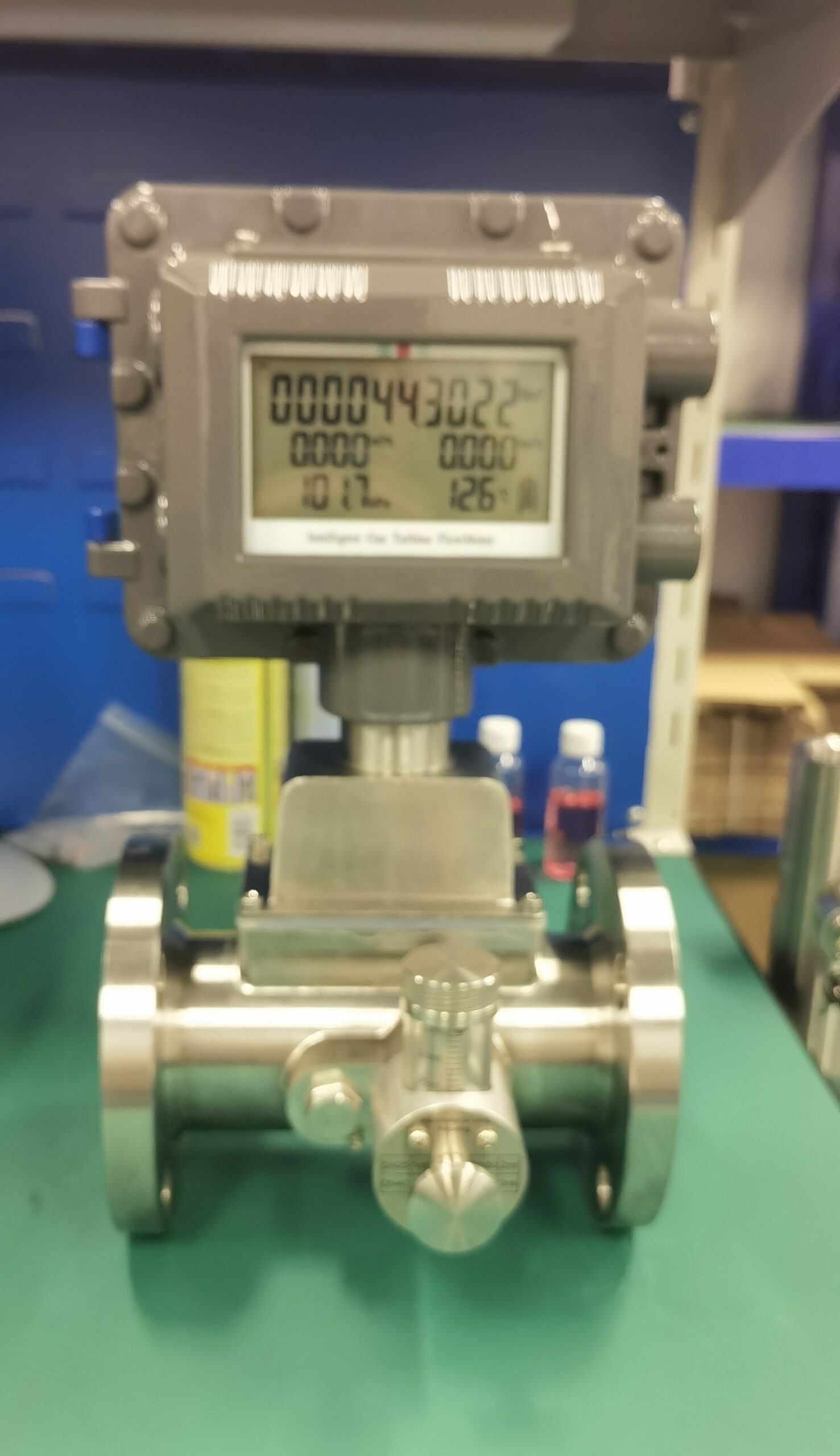
High-precision measurement: The accuracy of high-quality turbine flowmeters can reach ±1.0%, meeting the requirements of trade measurement.
Wide range ratio: It can usually reach 10:1 or even higher, suitable for working conditions with large flow fluctuations.
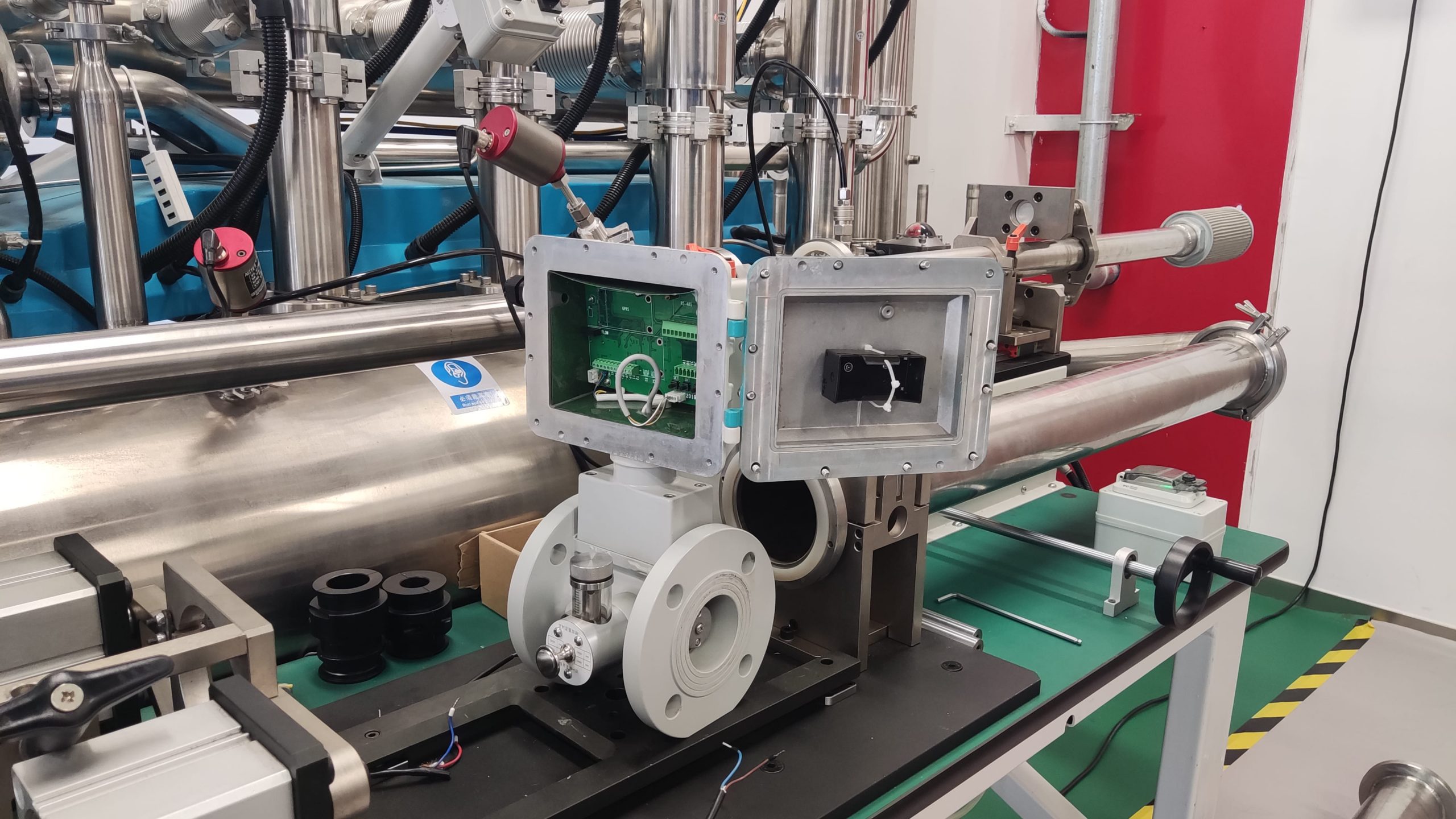
Digital signal output: Facilitates integration with systems such as DCS and SCADA to achieve remote monitoring.
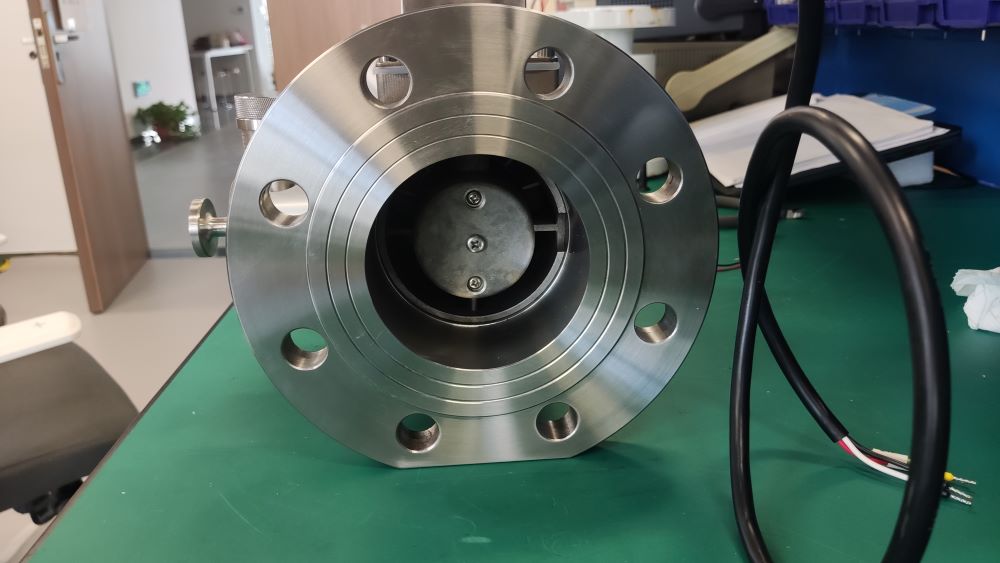
Sturdy structure: No moving mechanical parts come into contact with the airflow, requiring less maintenance and having a long service life.
4. Precautions for Use
Installation requirements: It is necessary to ensure sufficient straight pipe sections before and after (usually 10D before and 5D after) to avoid flow field disturbance.
Regular calibration: It is recommended to conduct calibration every 1-2 years to ensure measurement accuracy.
Filtration protection: A filter should be installed to prevent impurities from damaging the turbine blades.
Pressure and temperature compensation: It is necessary to be equipped with a pressure transmitter and a temperature sensor for working condition conversion.
5. Development Trends
With the development of Internet of Things (iot) technology, intelligent turbine flowmeters have gradually become popular, featuring functions such as self-diagnosis and wireless transmission. Meanwhile, the application of new materials (such as tungsten carbide bearings) has further enhanced the reliability and service life of the instrument. In the future, turbine flowmeters will play a more significant role in smart energy systems.