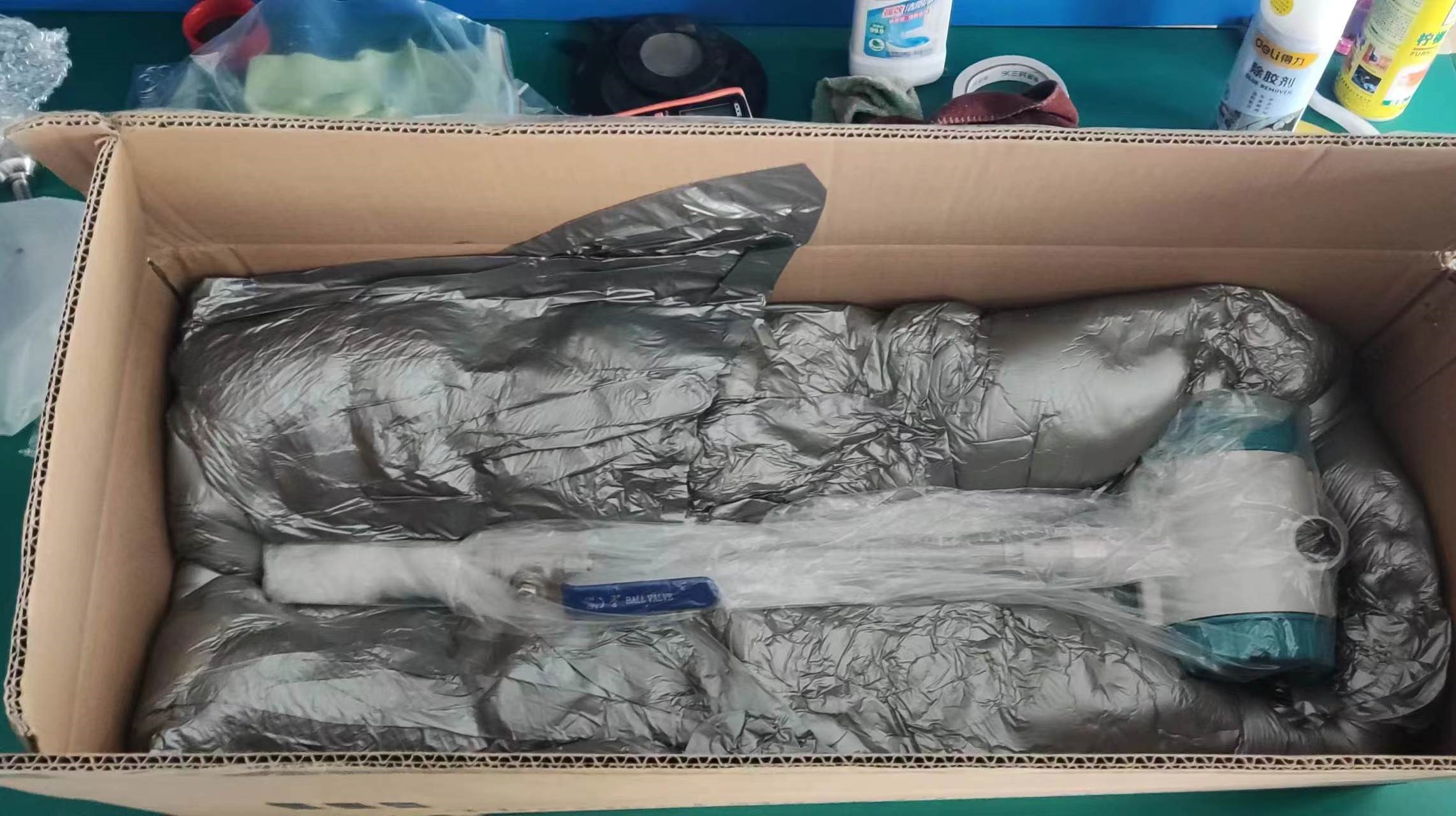
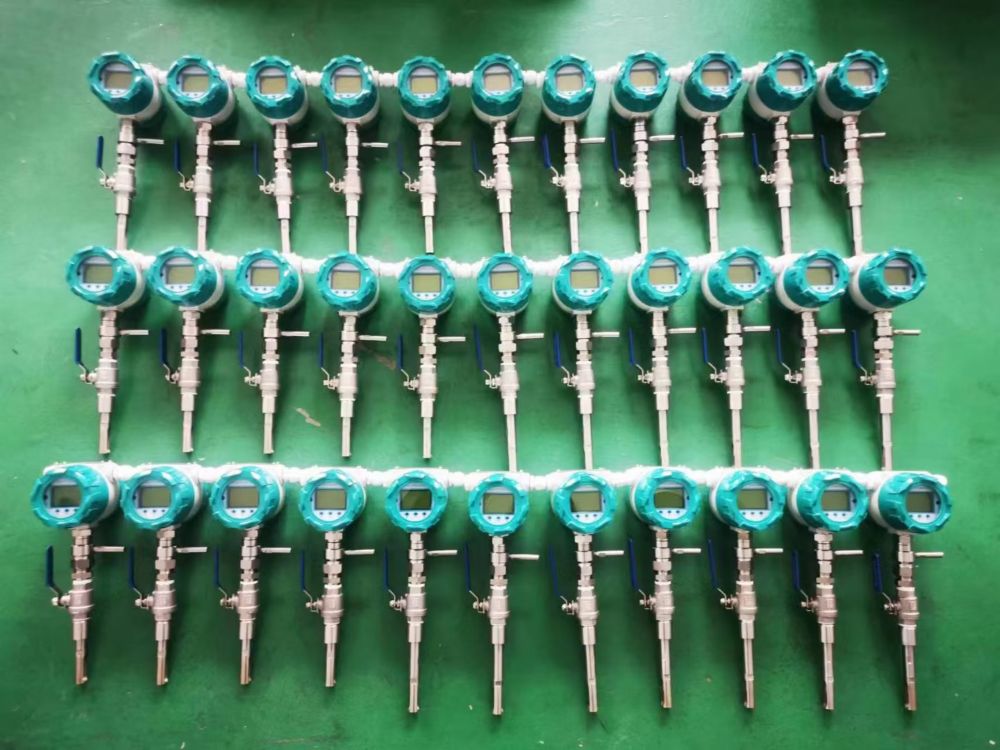
Analysis of the Advantages and Disadvantages of Thermal Gas Mass flowmeters: The choice for precise gas measurement
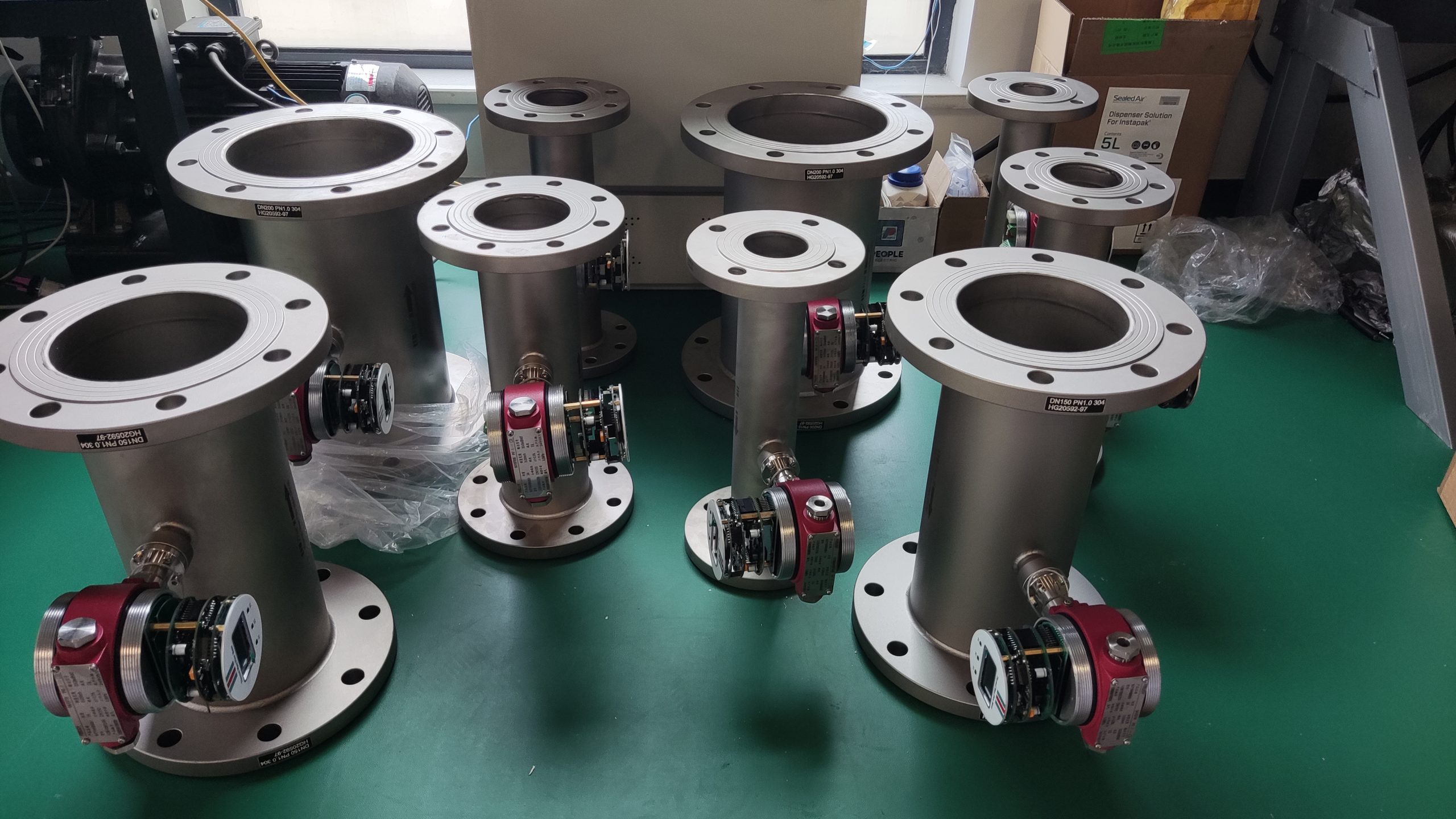
In the field of industrial gas flow measurement, thermal gas mass flowmeters have become the preferred equipment in many industries due to their feature of directly measuring mass flow. However, is it suitable for your working conditions? This article will deeply analyze its advantages and disadvantages to help you make a scientific selection decision.
The core advantages of thermal gas mass flowmeters
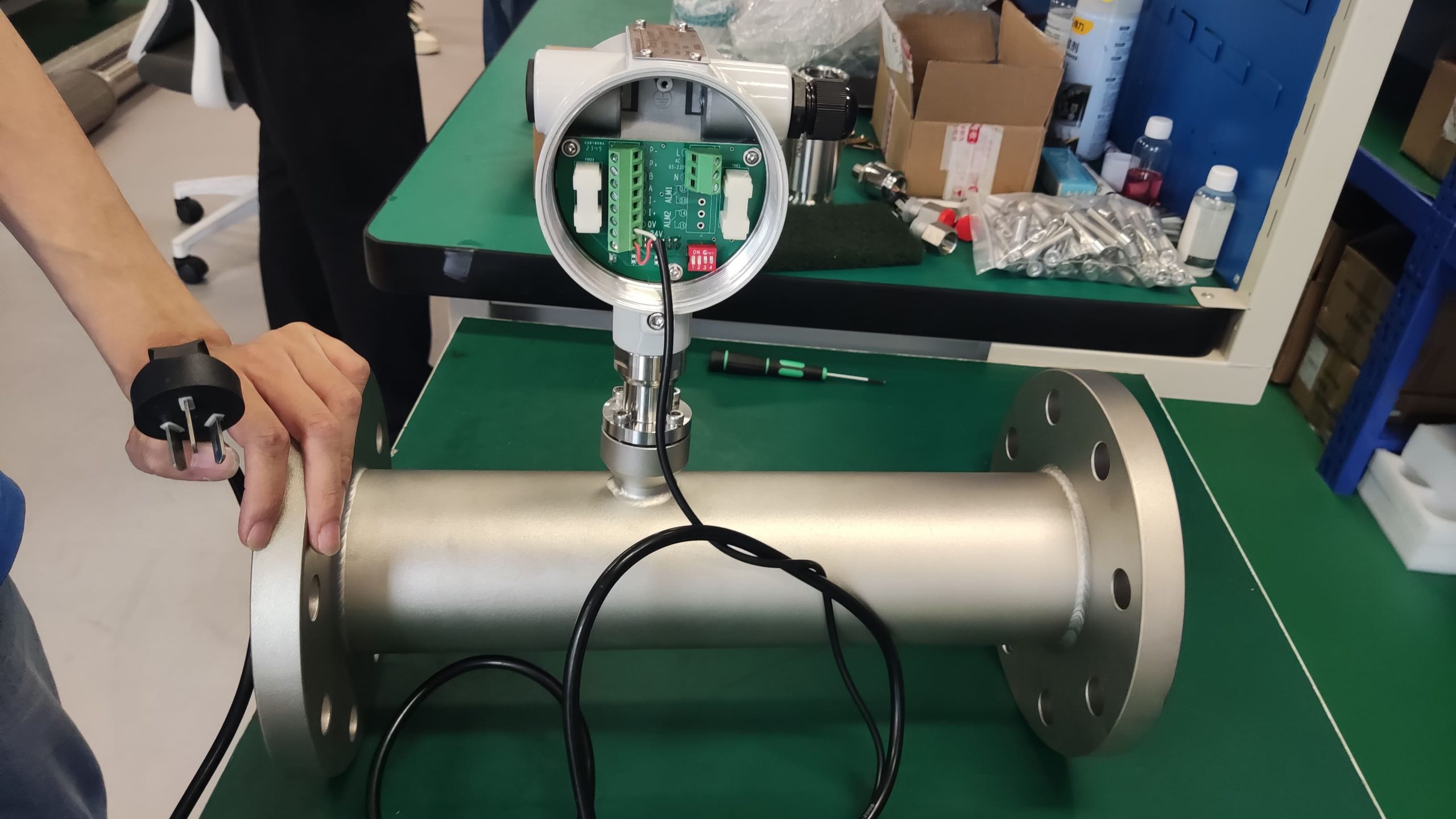
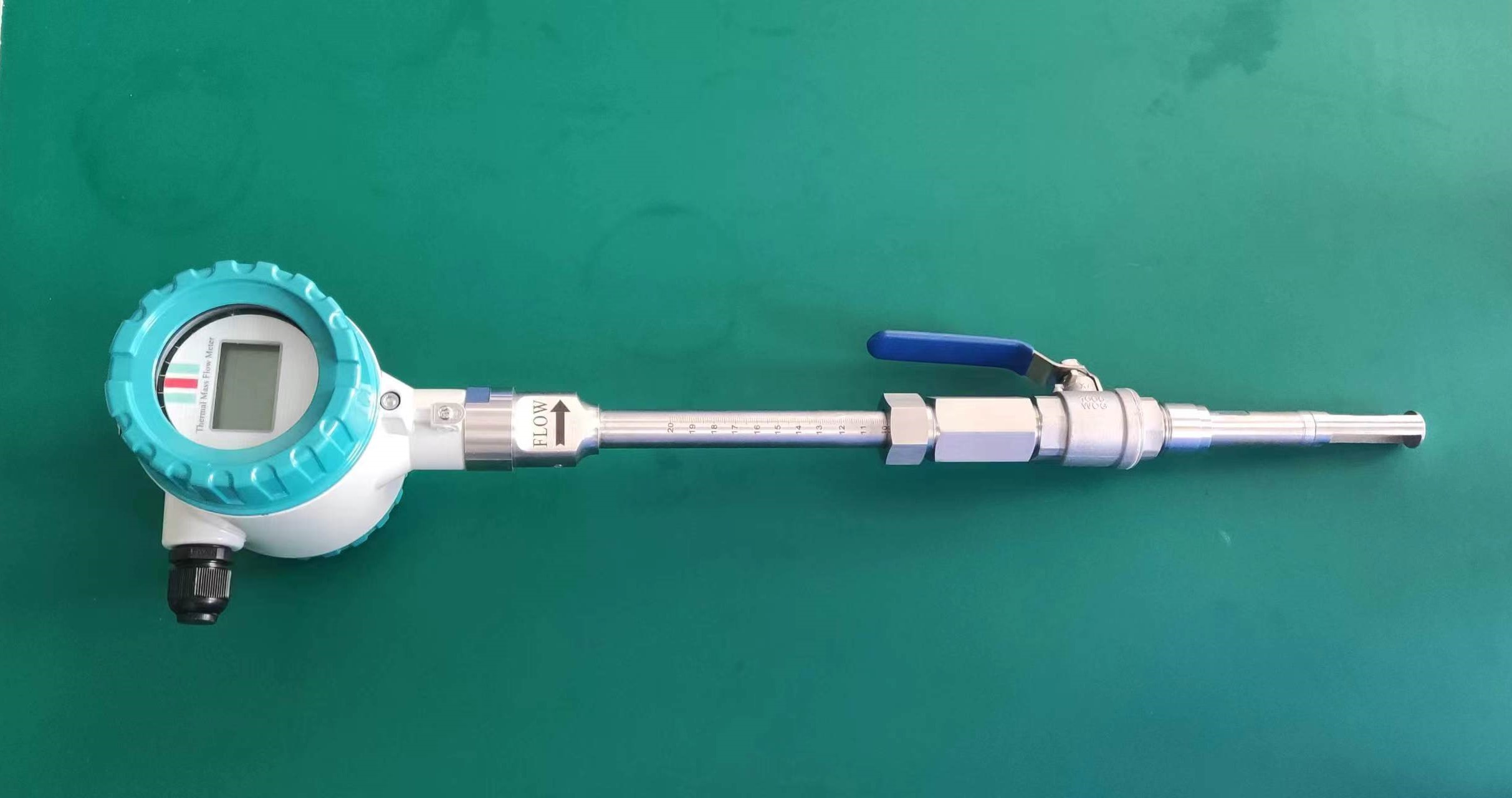
Directly measure the mass flow rate without the need for temperature and pressure compensation
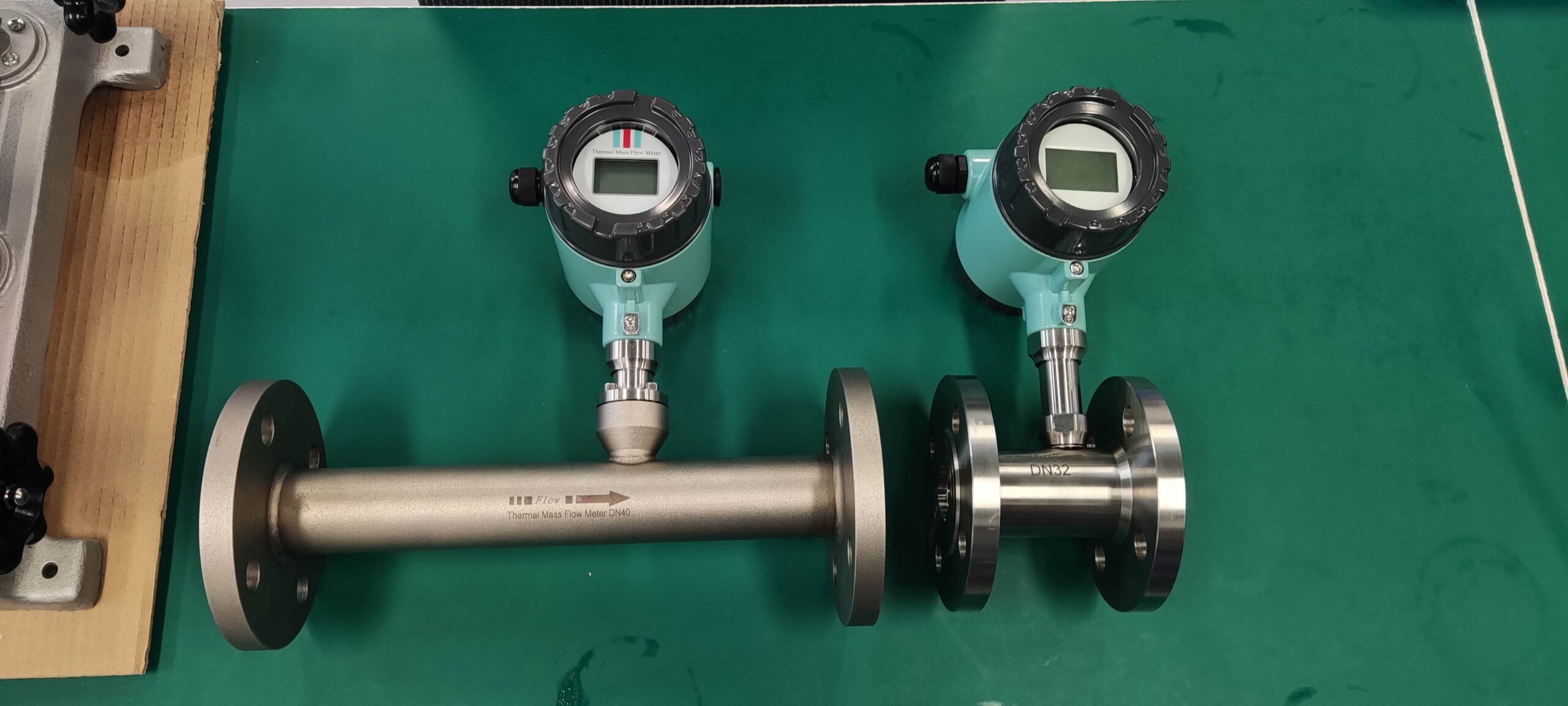
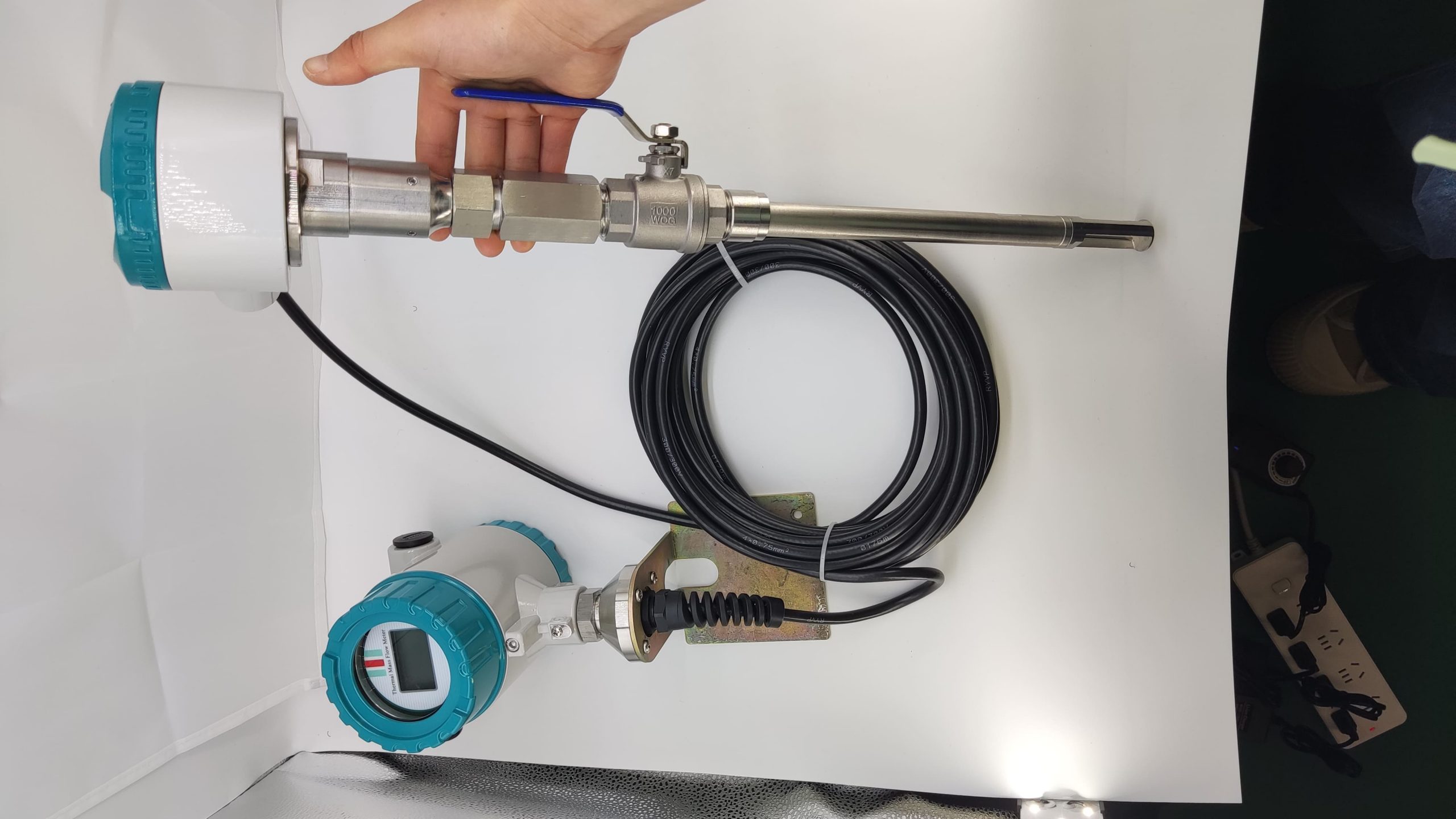
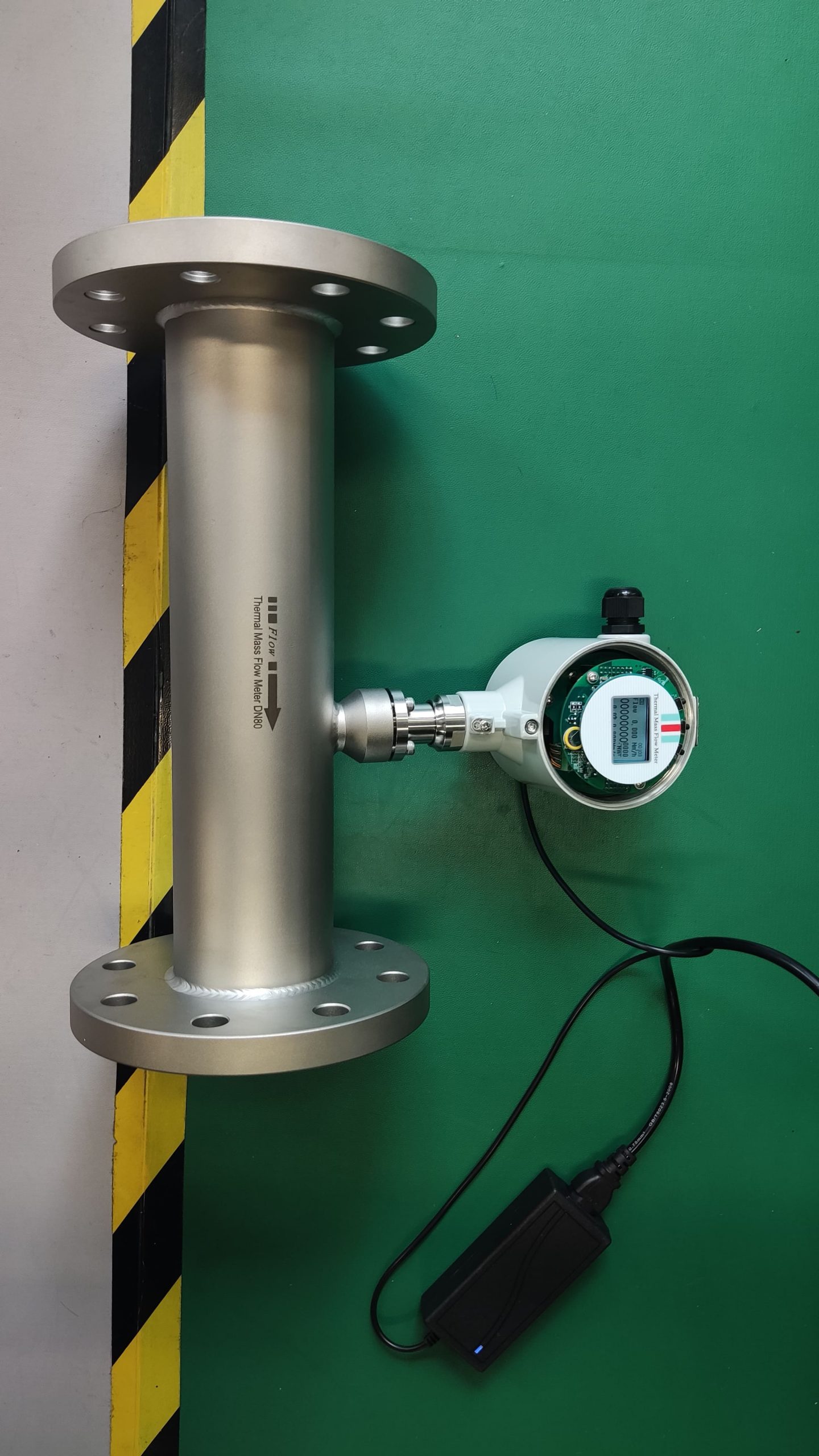
Unlike volumetric flowmeters such as vortex and orifice plate flowmeters, thermal flowmeters are based on the principle of thermal diffusion and directly measure the mass flow of gas. They are not affected by changes in temperature and pressure, eliminating the need for complex compensation calculations and providing more accurate and reliable data.
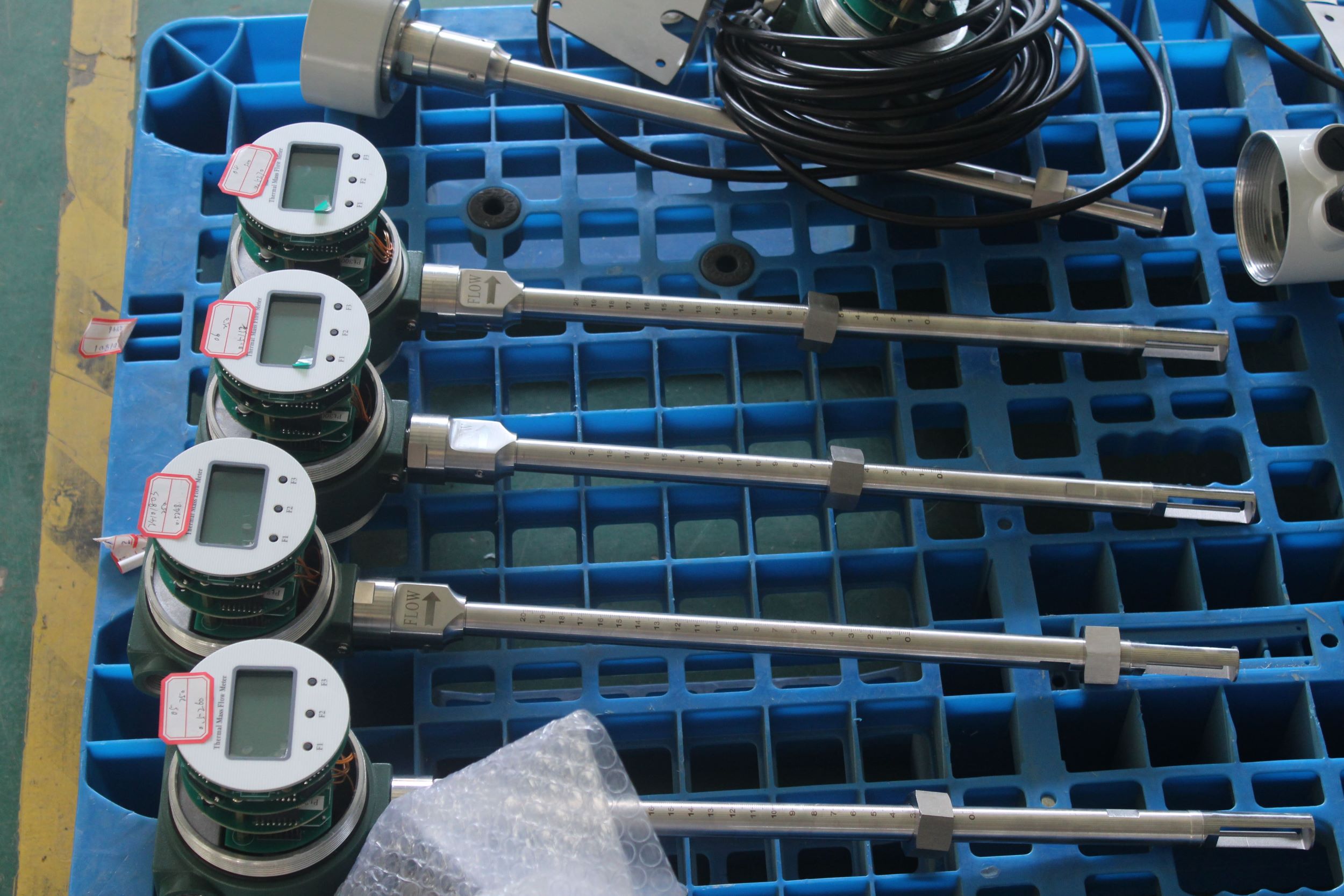
2. Wide range ratio, suitable for high and low flow rates
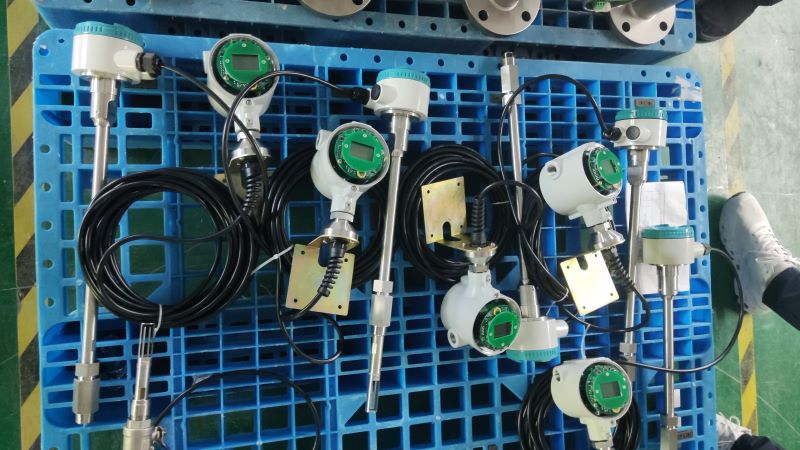
The range ratio can reach 100:1, capable of detecting both extremely low flow rates (such as 0.1m /s) and high flow rates. It is suitable for measuring various gases including compressed air, gas, and biogas.
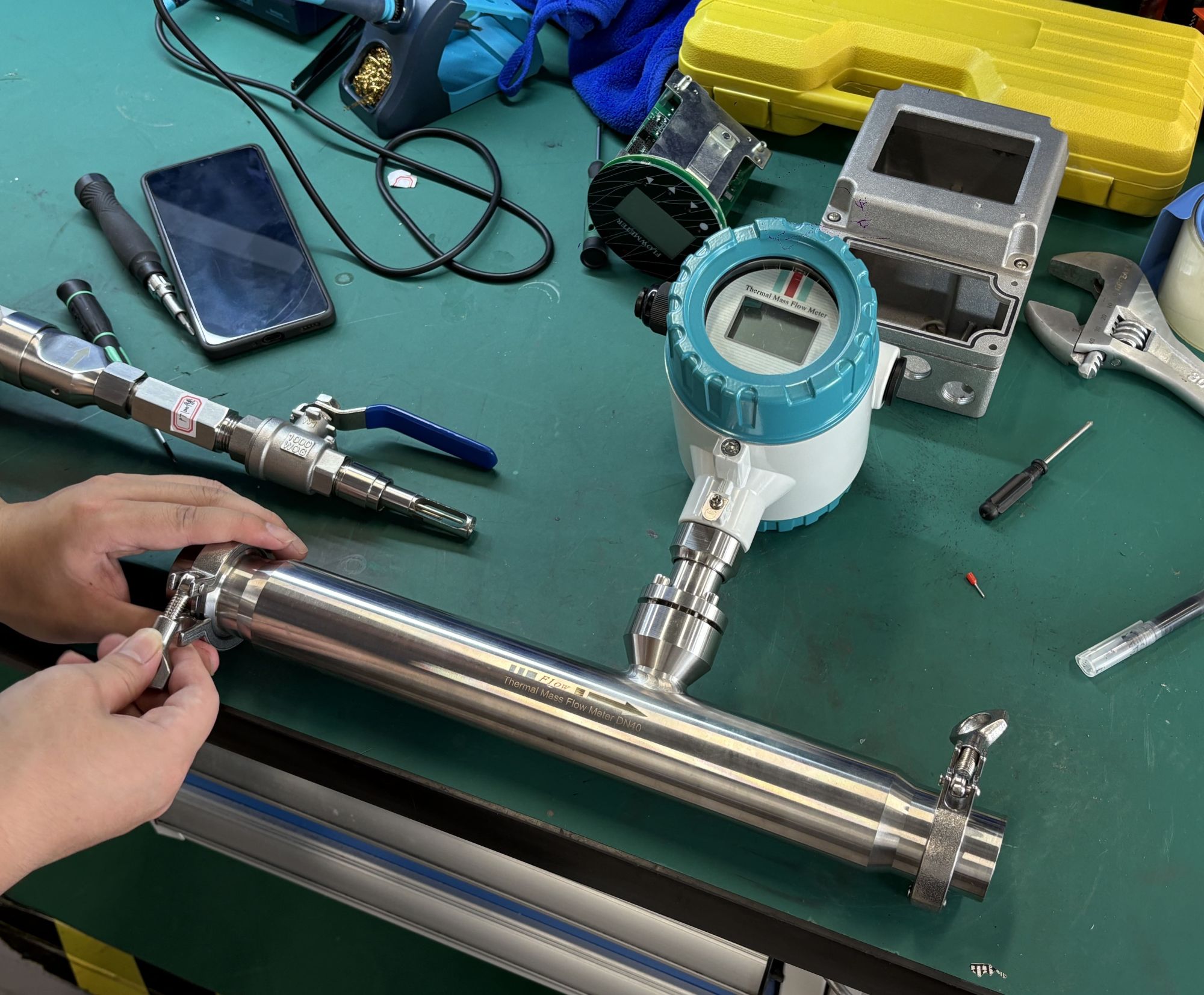
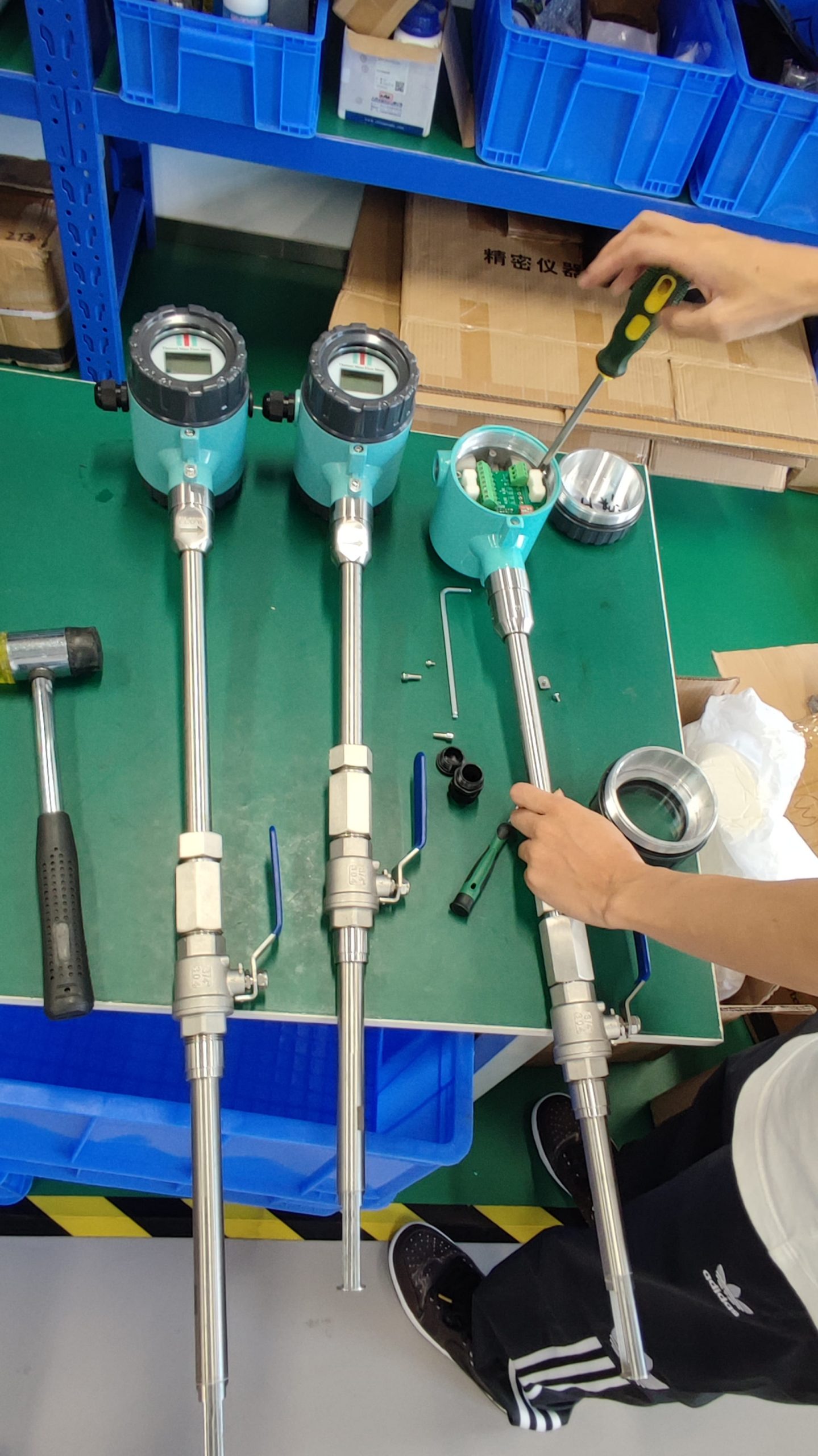
3. No moving parts, low maintenance cost
The sensor has no mechanical moving parts, is not prone to wear and tear, and has high long-term stability. It is particularly suitable for dirty and corrosive gas conditions (such as smoke and exhaust gas), reducing maintenance frequency.
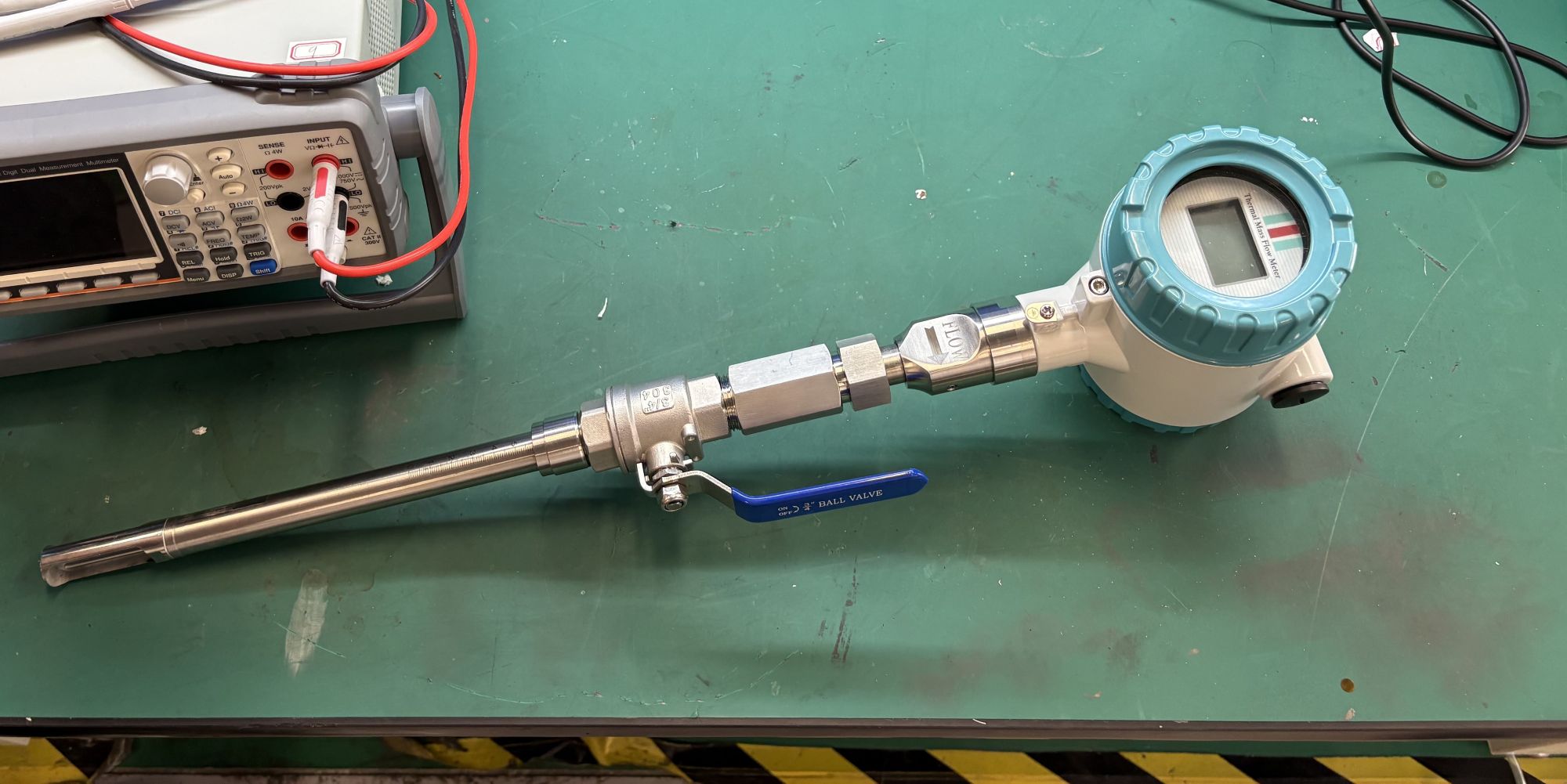
4. Low voltage loss, energy-saving and highly efficient
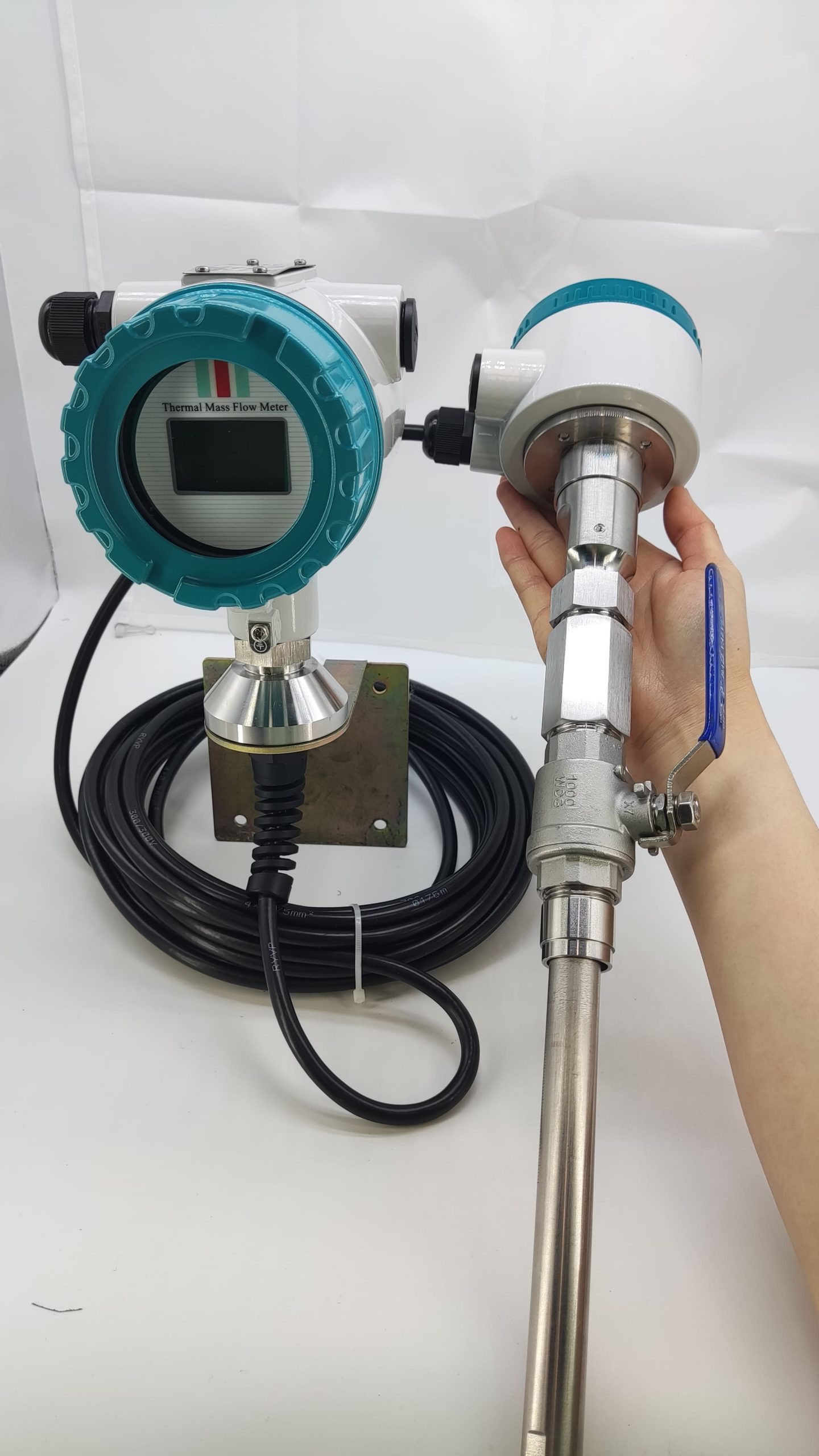
It adopts an insertable or pipeline design, generating almost no pressure loss and is suitable for applications with high energy-saving requirements, such as air compressors and HVAC systems.
The limitations of thermal gas mass flowmeters
1. Not suitable for liquids or high-humidity gases
The thermal principle is only applicable to gas measurement. If the medium contains liquid droplets (such as saturated moist air) or is prone to condensation, it may affect the accuracy of the sensor and even cause damage.
2. Sensitive to gas components
The thermal conductivity of different gases varies. If the composition of the working gas fluctuates greatly (such as mixed gas, biogas), recalibration is required; otherwise, errors may be introduced.
3. Not suitable for high-pressure or ultra-high-temperature gases
It usually has a pressure resistance of no more than 4MPa and a temperature range of approximately -40℃ to 200℃. Beyond this range, special customization is required and the cost is relatively high.
4. Relatively high initial investment
Compared with differential pressure flowmeters (such as orifice plates), thermal flowmeters are more expensive. However, in the long run, their advantages of low maintenance and high precision can reduce the overall cost.