Application Analysis of Thermal Gas Mass Flowmeter: Precise Measurement, Efficient Control
In the field of industrial gas flow measurement, thermal gas mass flowmeters have become the preferred equipment for scenarios such as natural gas, compressed air, and flue gas monitoring, thanks to their advantages of high precision, low pressure loss, and direct measurement of mass flow. This article will analyze the core value of thermal gas mass flowmeters from three aspects: principle, advantages and typical applications.
I. Working Principle: Based on thermal diffusion technology
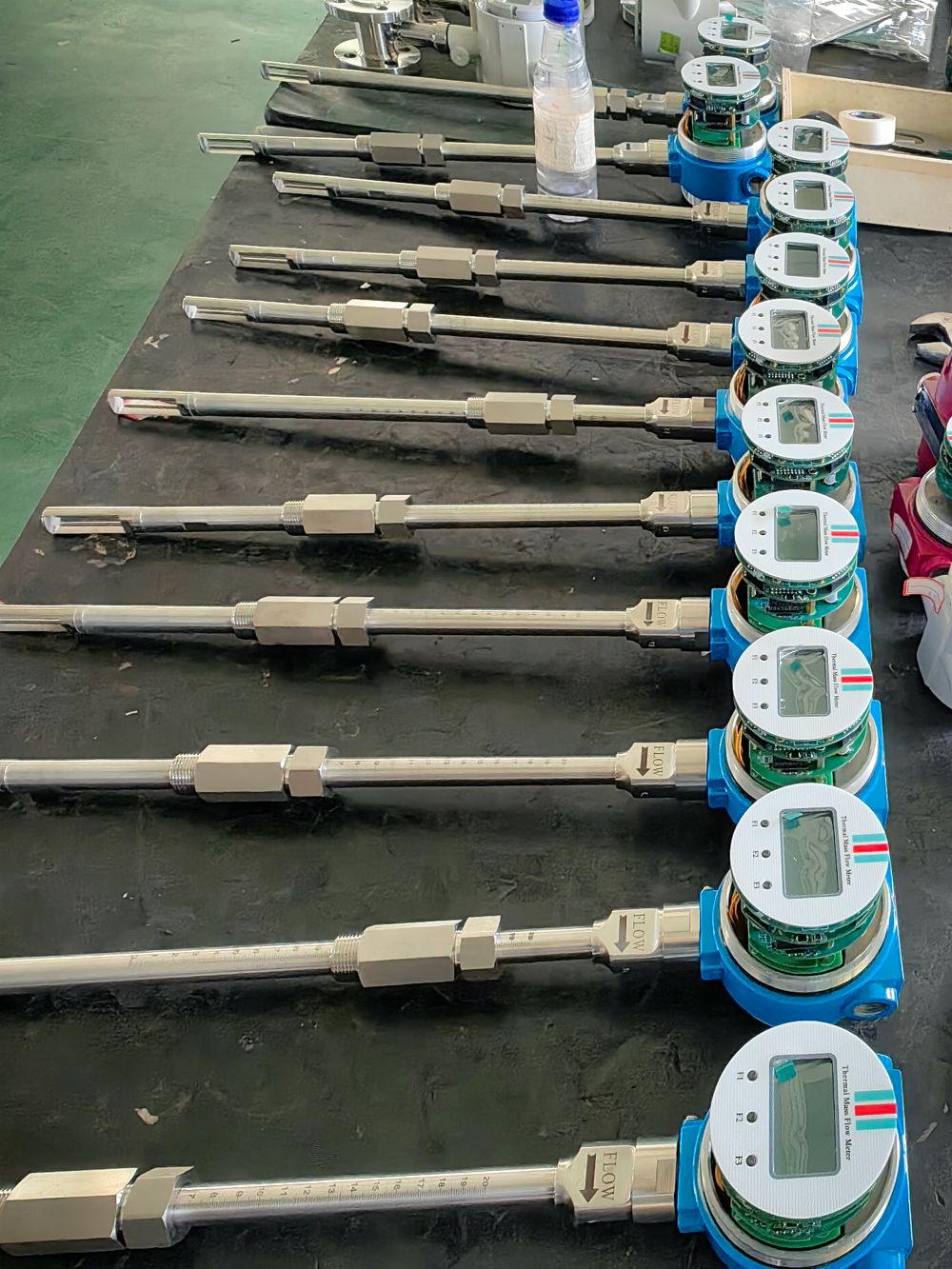
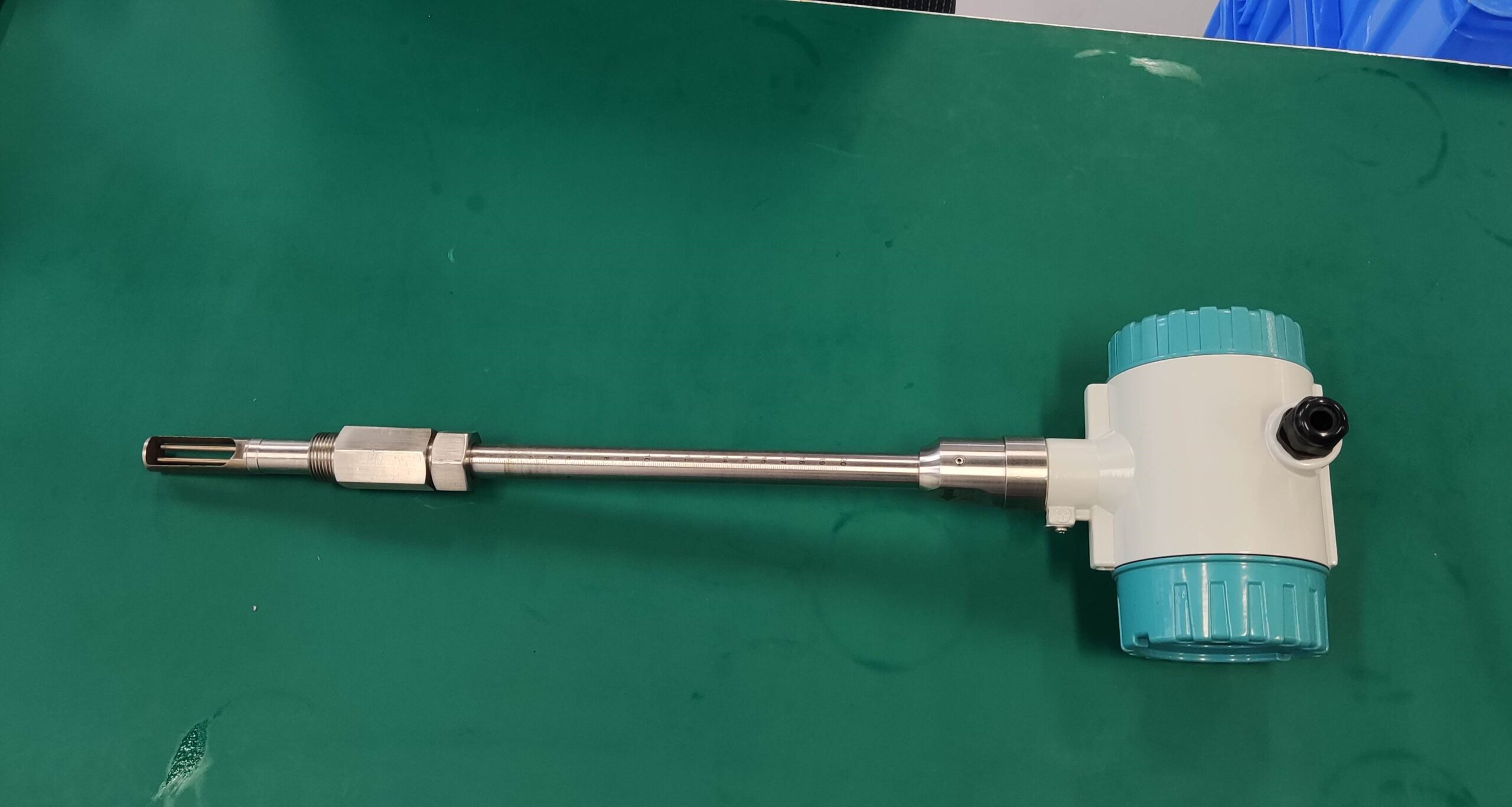
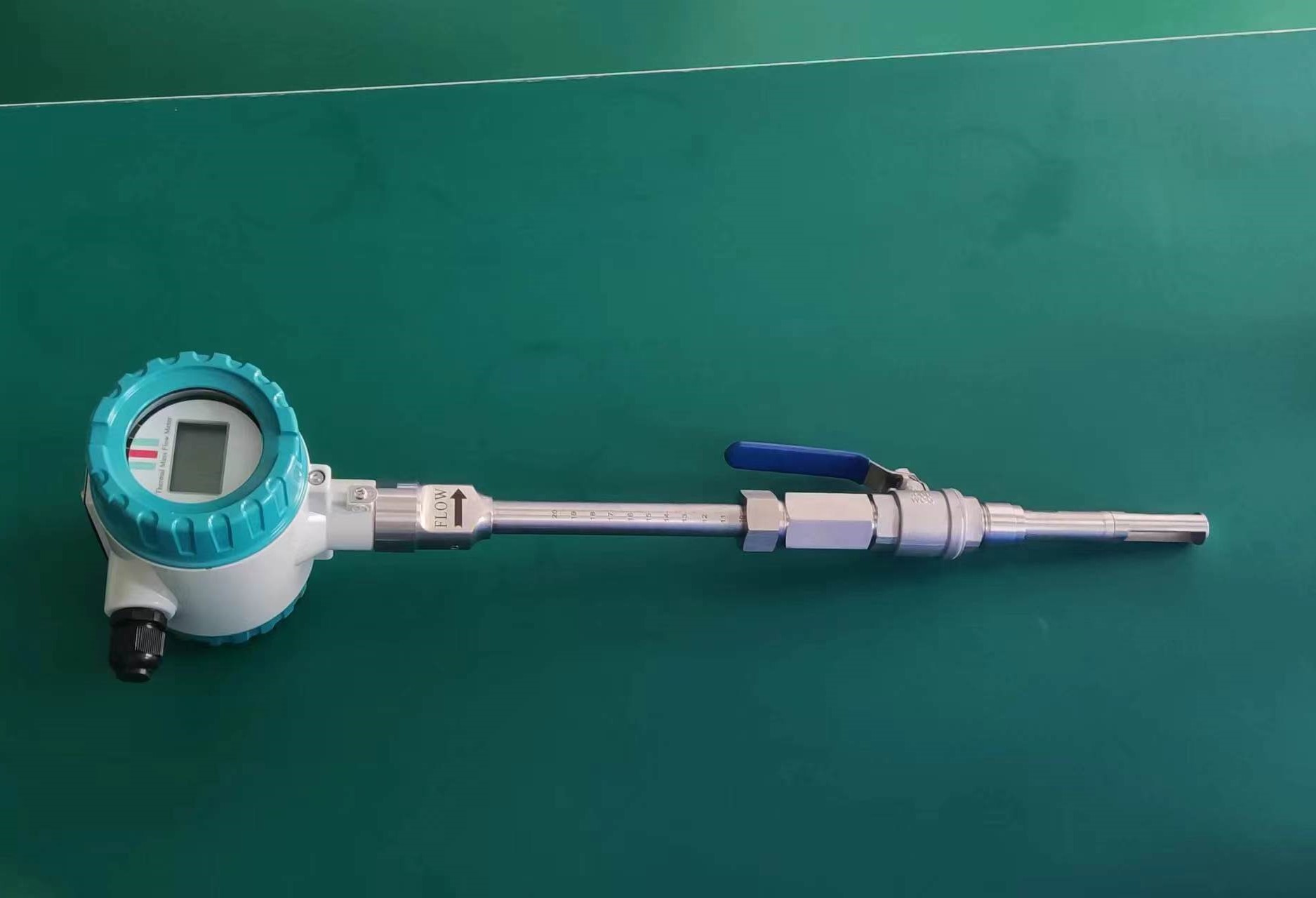
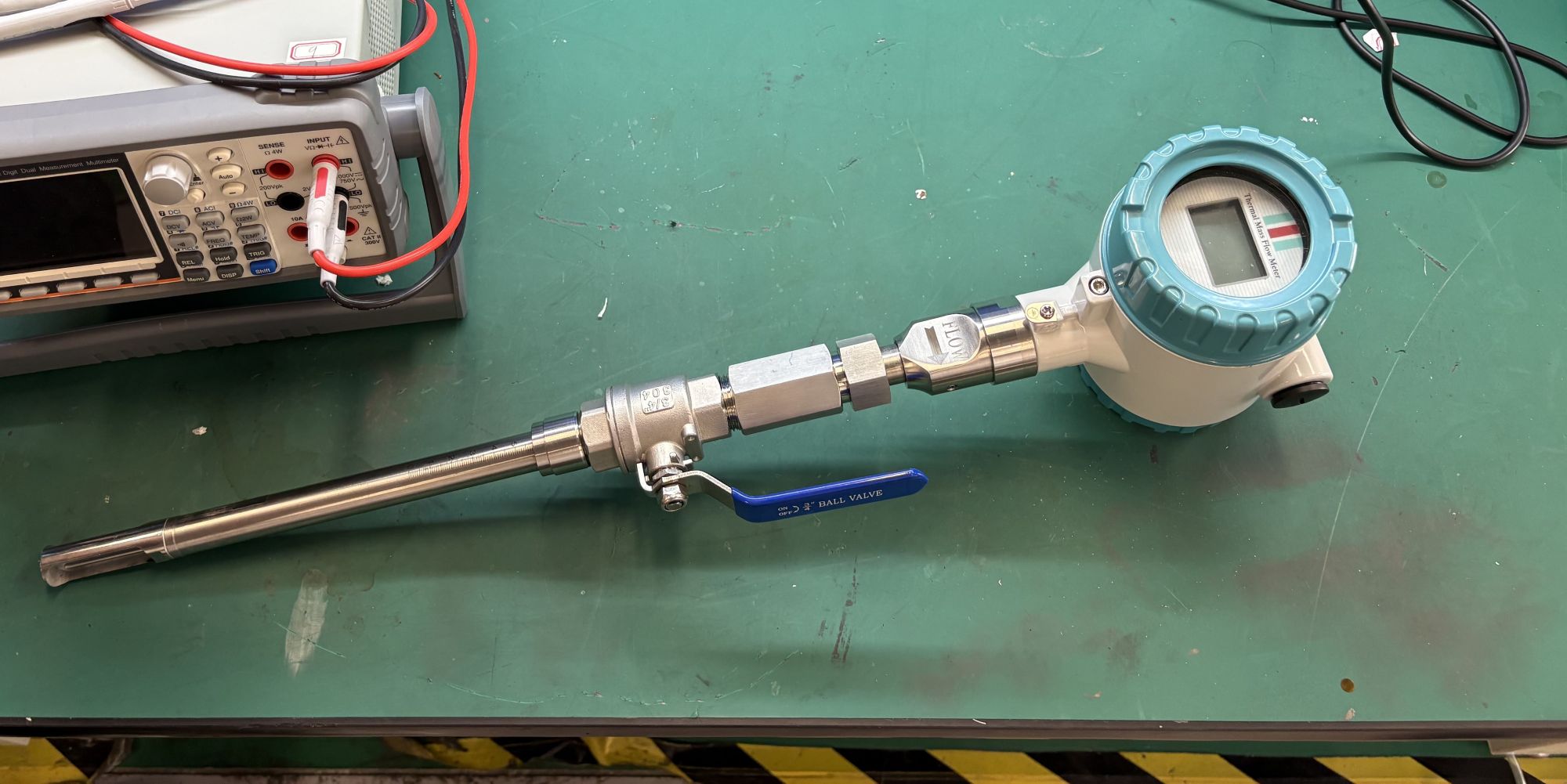
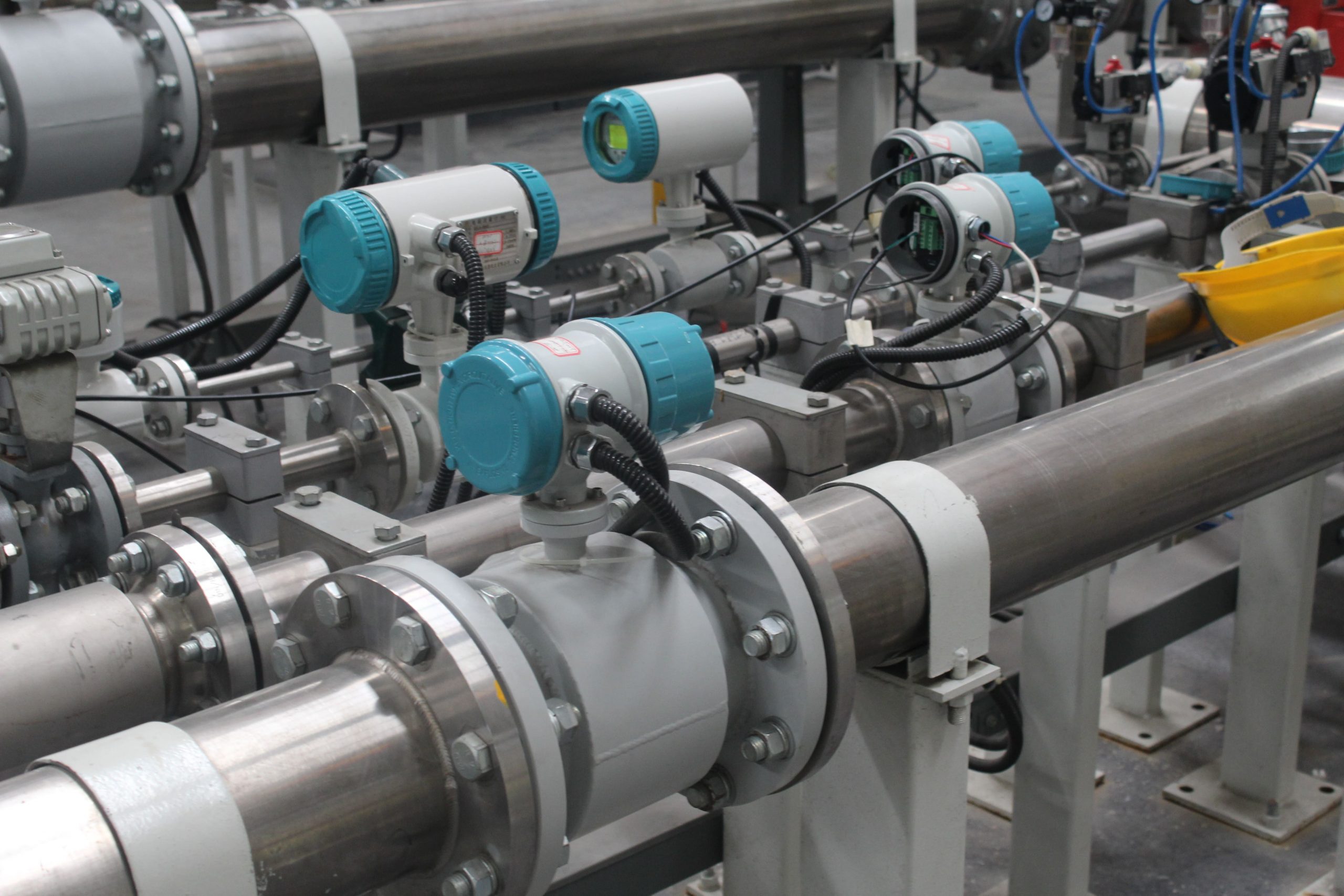
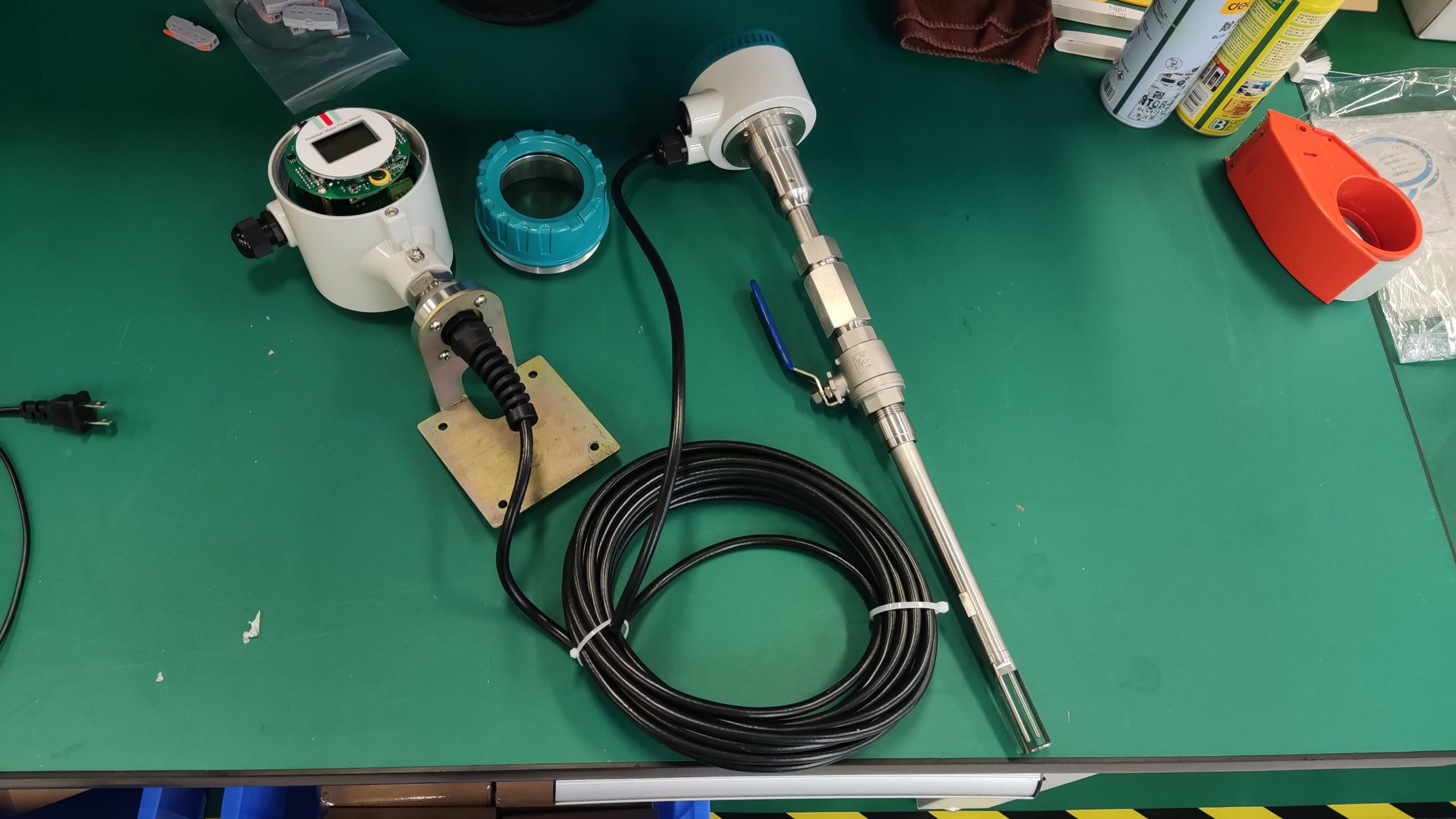
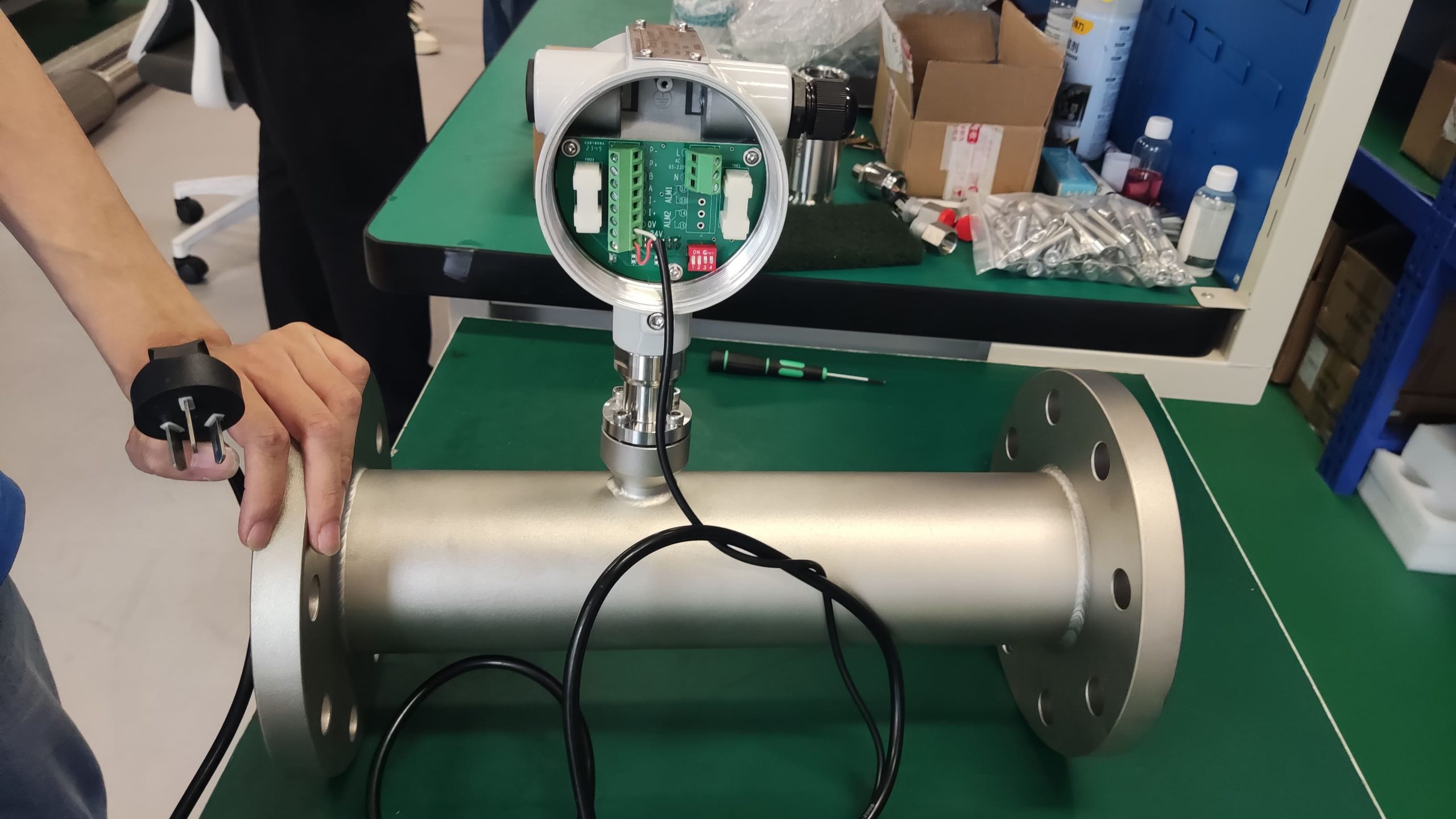
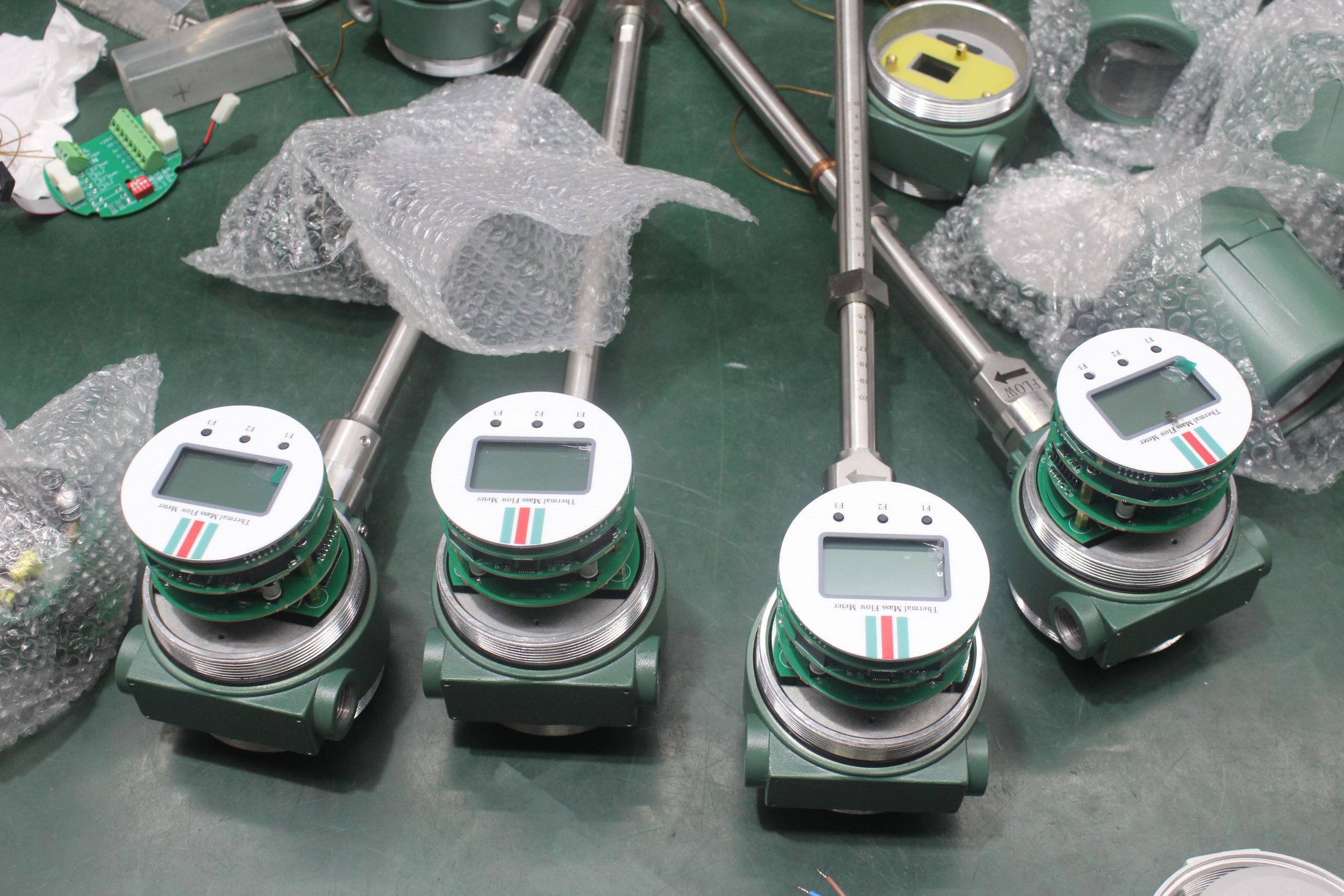
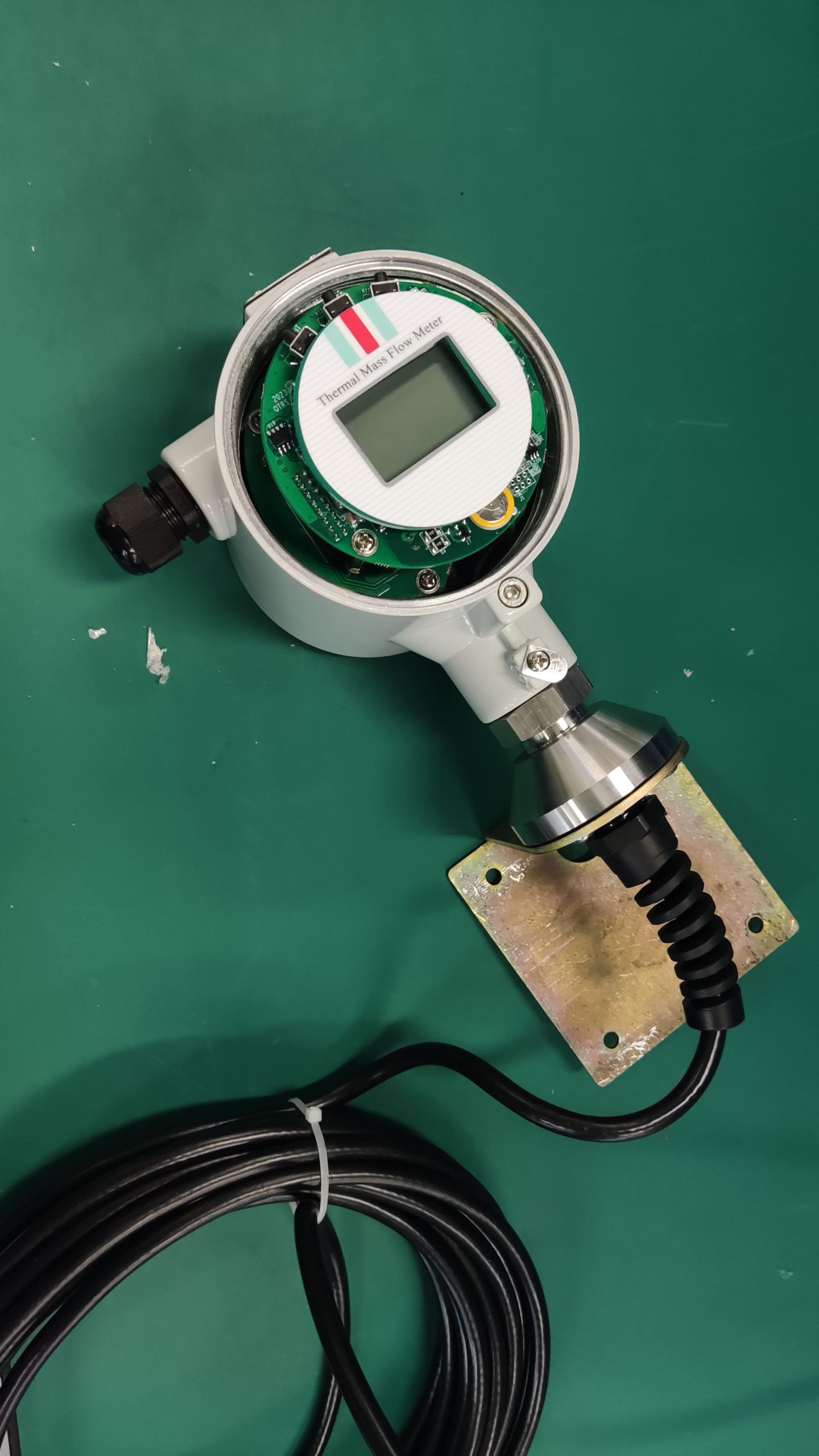
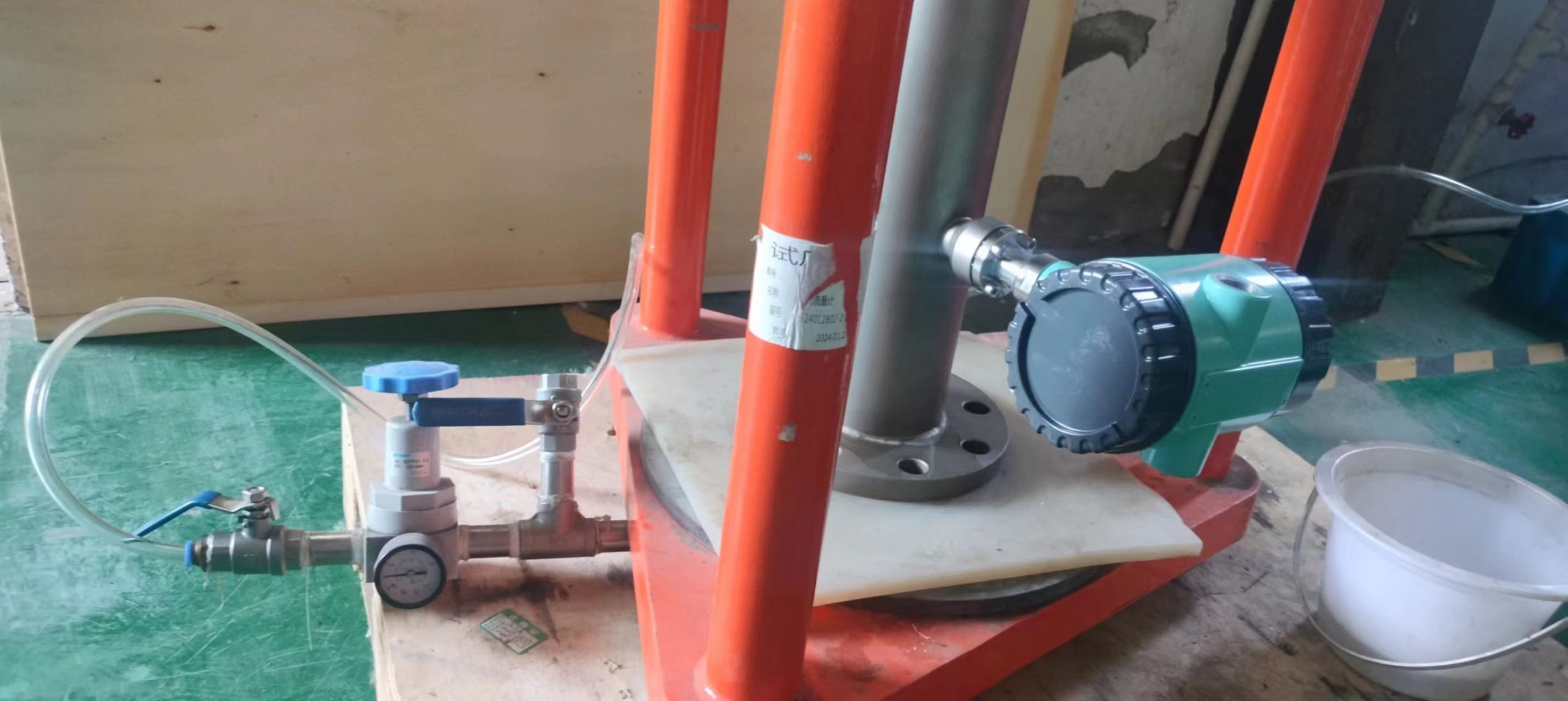
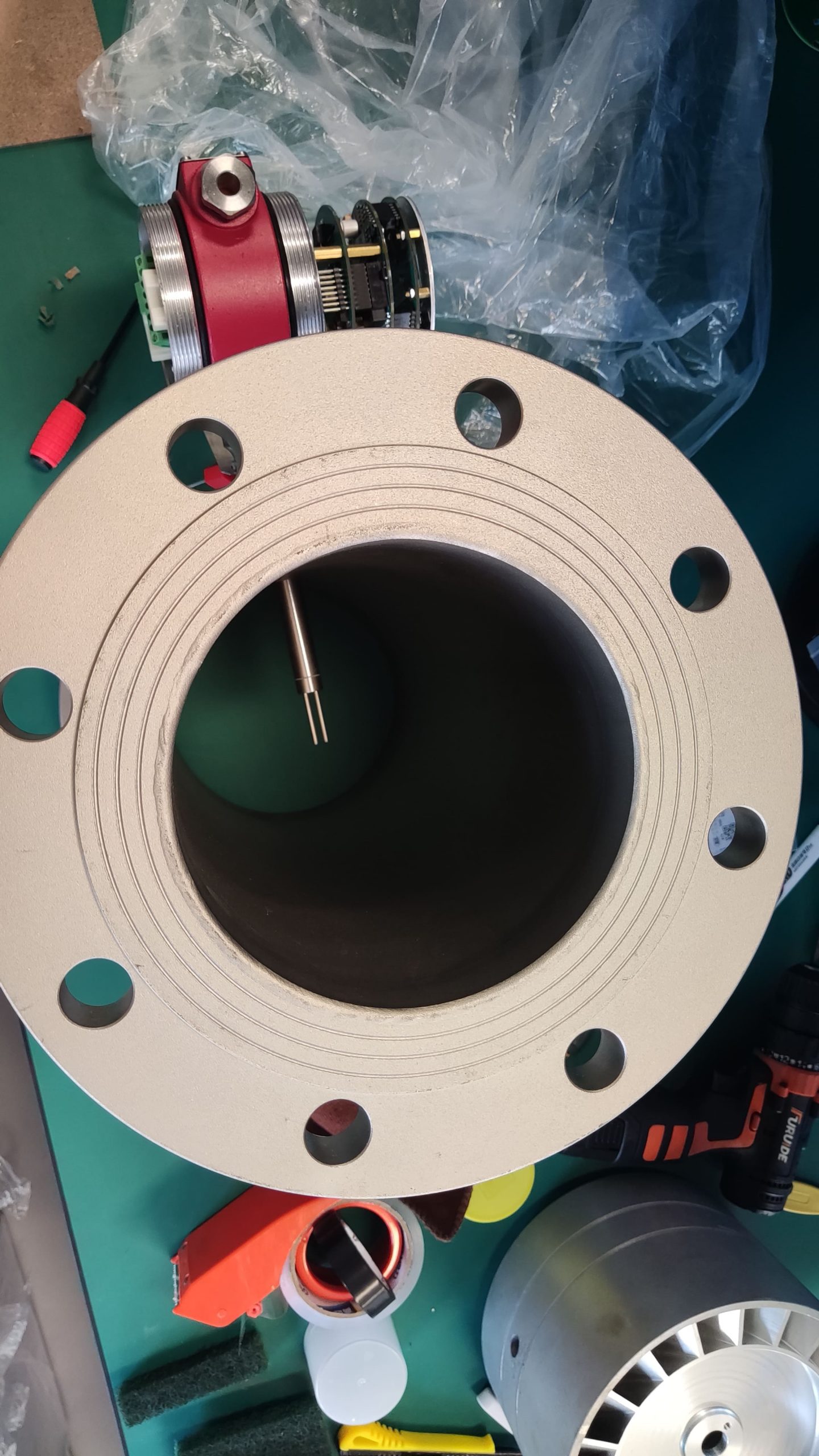
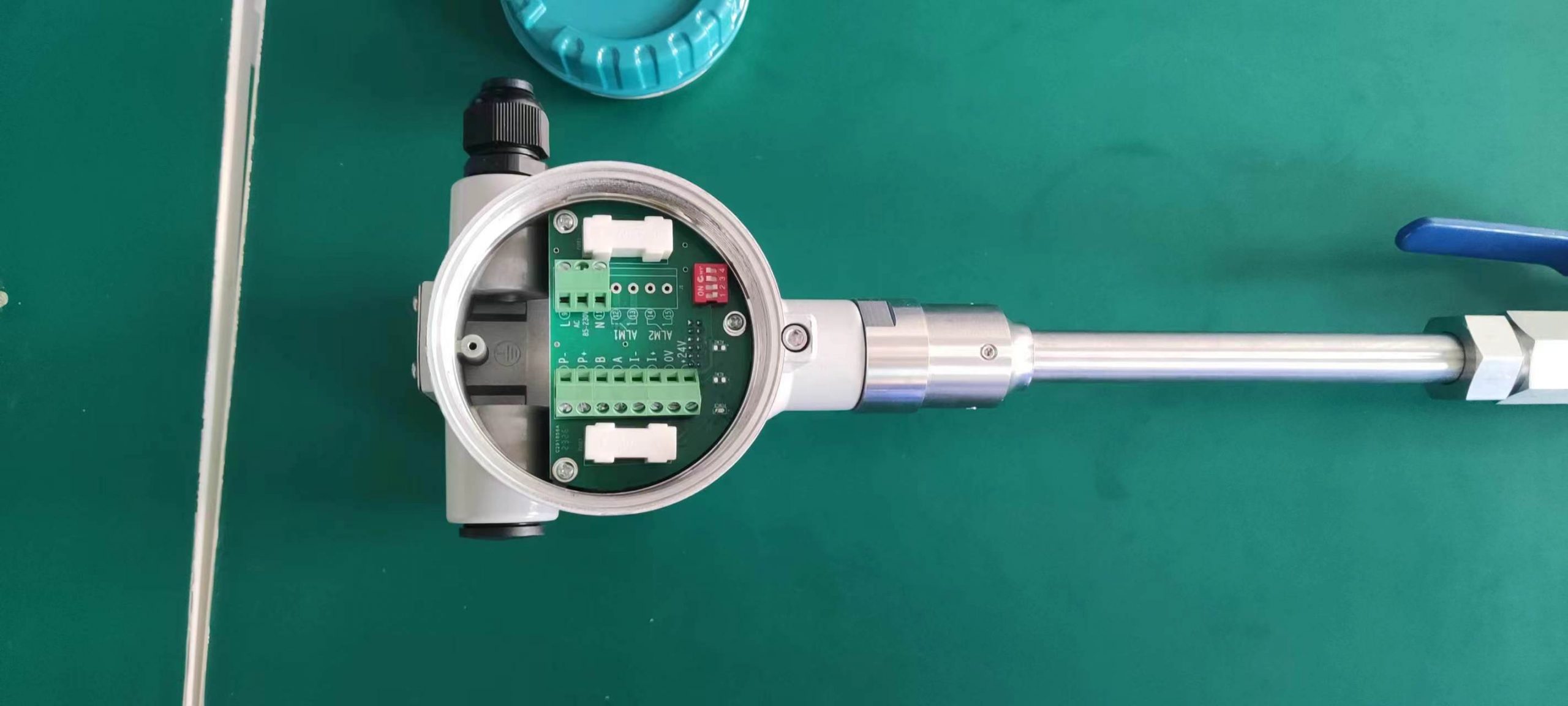
The thermal gas mass flowmeter adopts the principle of heat conduction and calculates the flow rate by measuring the heat carried away by the gas as it passes through the sensor. Its core components include:
Heating element: It heats the gas at a constant temperature or power.
Temperature sensor: Detects the temperature difference caused by changes in gas flow rate.
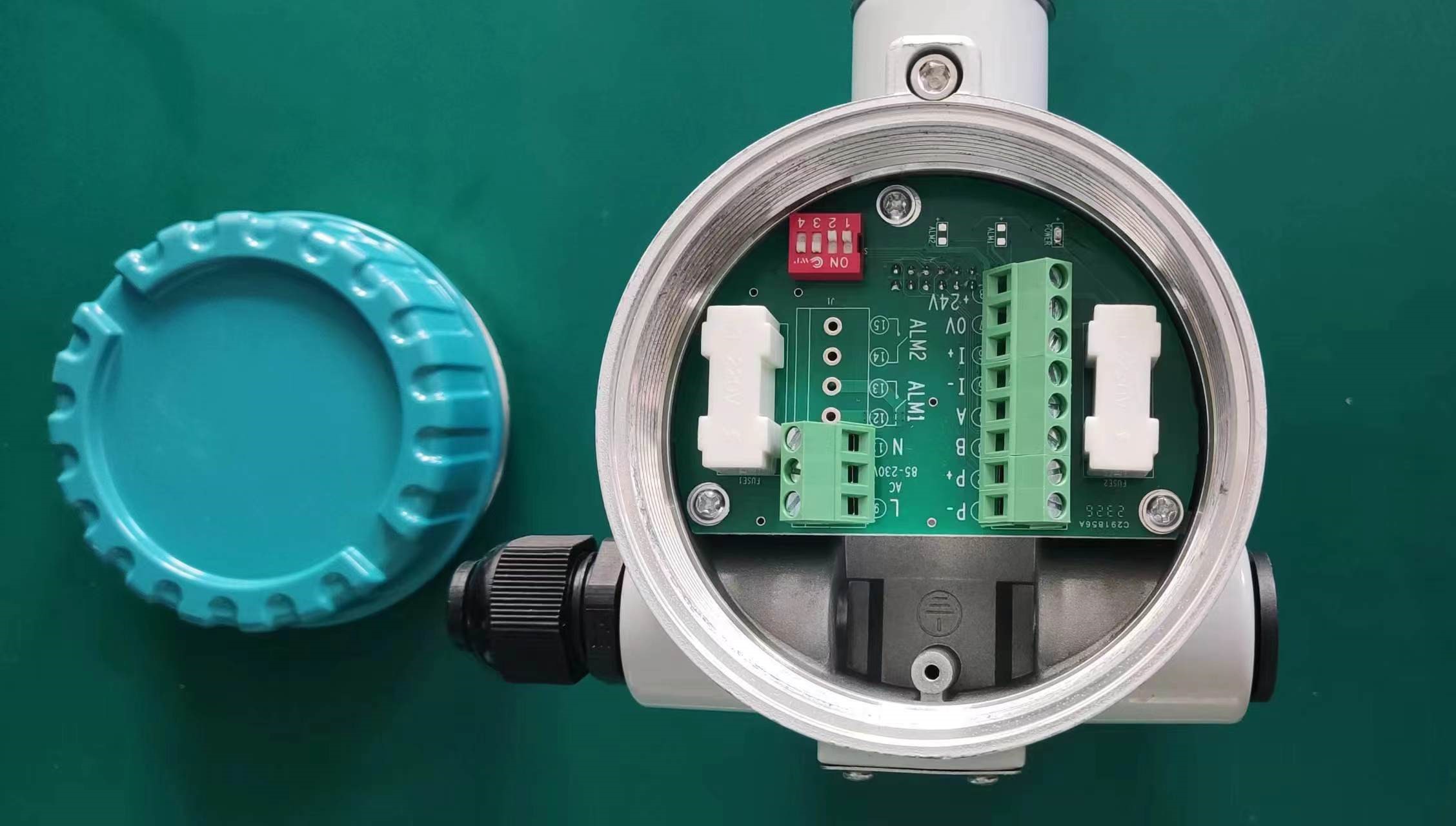
Signal processor: Converts temperature difference signals into standard flow signals (such as 4-20mA).
Because it directly measures the mass flow rate (rather than the volumetric flow rate), no additional temperature and pressure compensation is required, making it particularly suitable for working conditions with large fluctuations in pressure and temperature.
Ii. Core Advantages: Why Choose Thermal Flowmeters?
High-precision measurement: Suitable for low flow rates (starting from 0.1m/s) and micro-flow detection, with an accuracy of ±1%FS.
No moving parts: Maintenance-free, with long-term stability superior to mechanical flowmeters (such as turbines, orifice plates).
Wide range ratio (usually 100:1) : The same instrument can measure extremely low and high flow rates, reducing the need for equipment replacement.
Compatible with multiple gases: air, oxygen, nitrogen, biogas, etc. Some models support corrosive gases (special coating required).
Iii. Typical Application Scenarios
1. Industrial gas monitoring
Compressed air system: Detect pipeline leaks and optimize energy consumption management.
Natural gas distribution: Trade settlement to ensure fair measurement.
2. Environmental Protection and Emission Control
Flue Gas Emission monitoring (CEMS) : Real-time measurement of the flow of gases such as SO₂ and NOx, in compliance with environmental protection regulations.
Biogas recovery and utilization: Precise measurement of methane production at landfills or sewage treatment plants.
3. Laboratories and the semiconductor industry
High-purity gas control: such as argon and hydrogen, to ensure process stability.
Fume hood exhaust volume monitoring: Ensuring laboratory safety.
Iv. Key Factors for Selection
Gas composition: For corrosive gases, Hastelloy or coated probes should be selected.
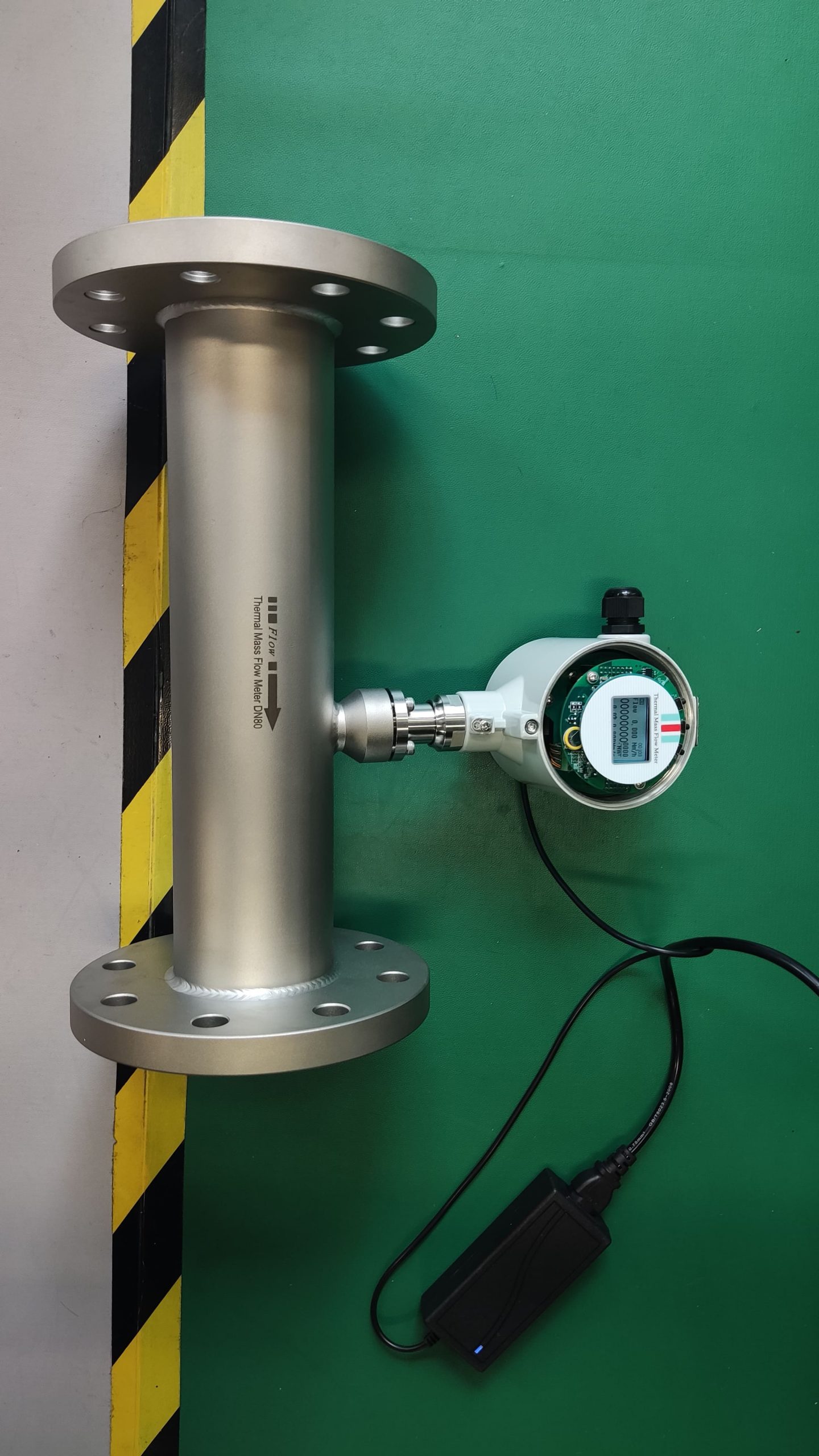
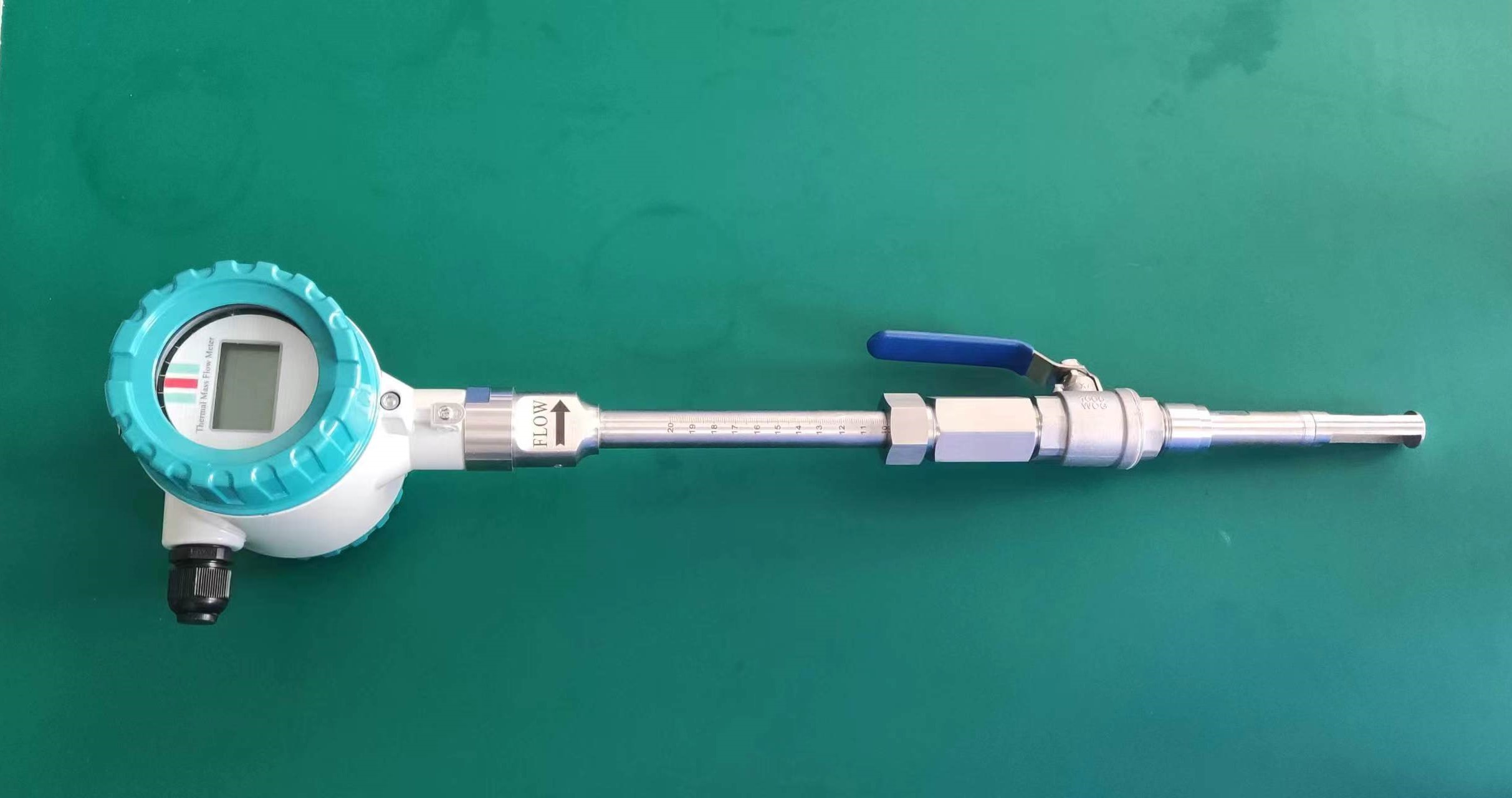
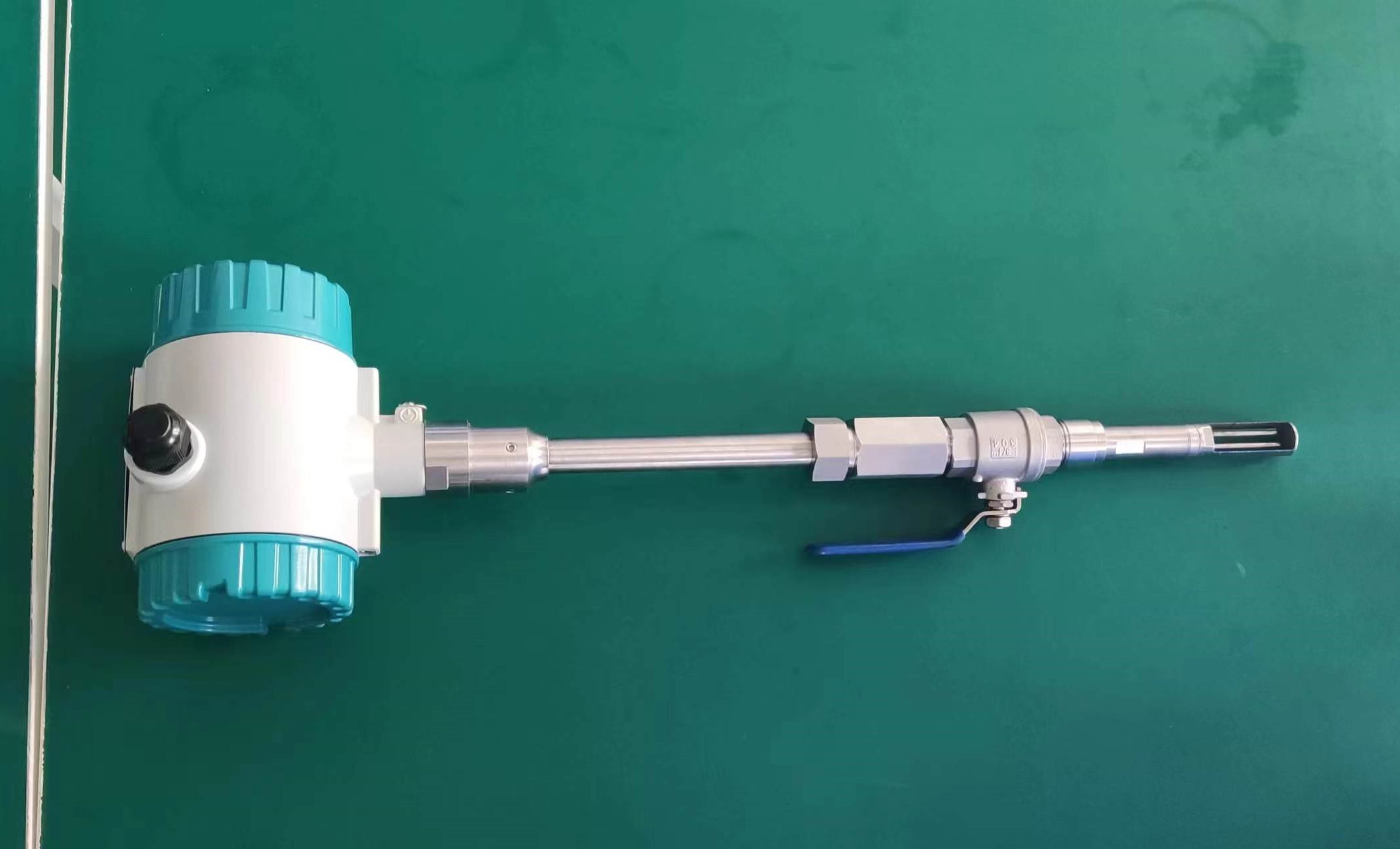
Pipe size: Small diameters (DN15-DN50) are suitable for insertion type, while large diameters require flange installation.
Explosion-proof requirements: In the chemical and gas fields, ATEX or IECEx certification must be met.