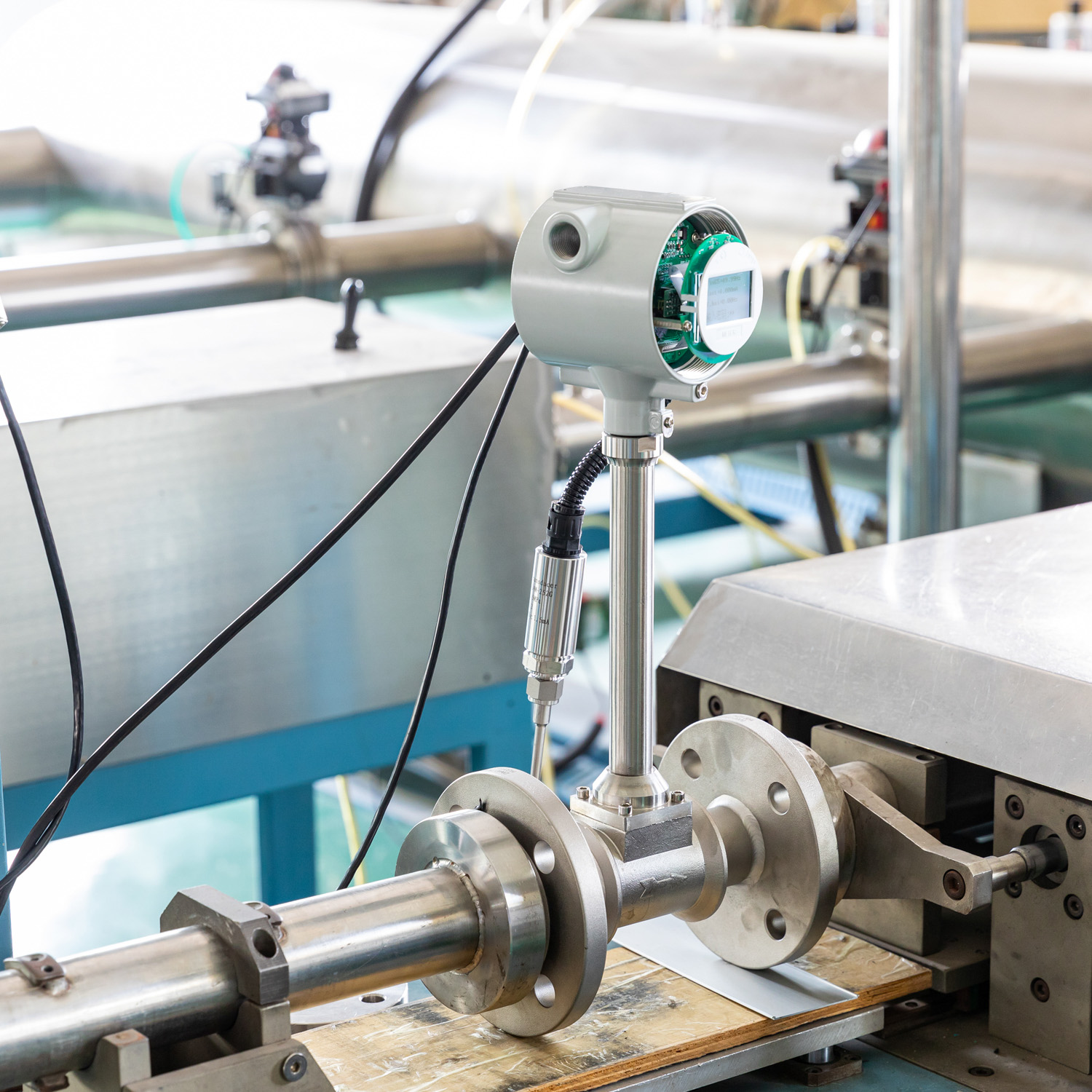
Key points of Application of vortex flowmeters in hot water measurement
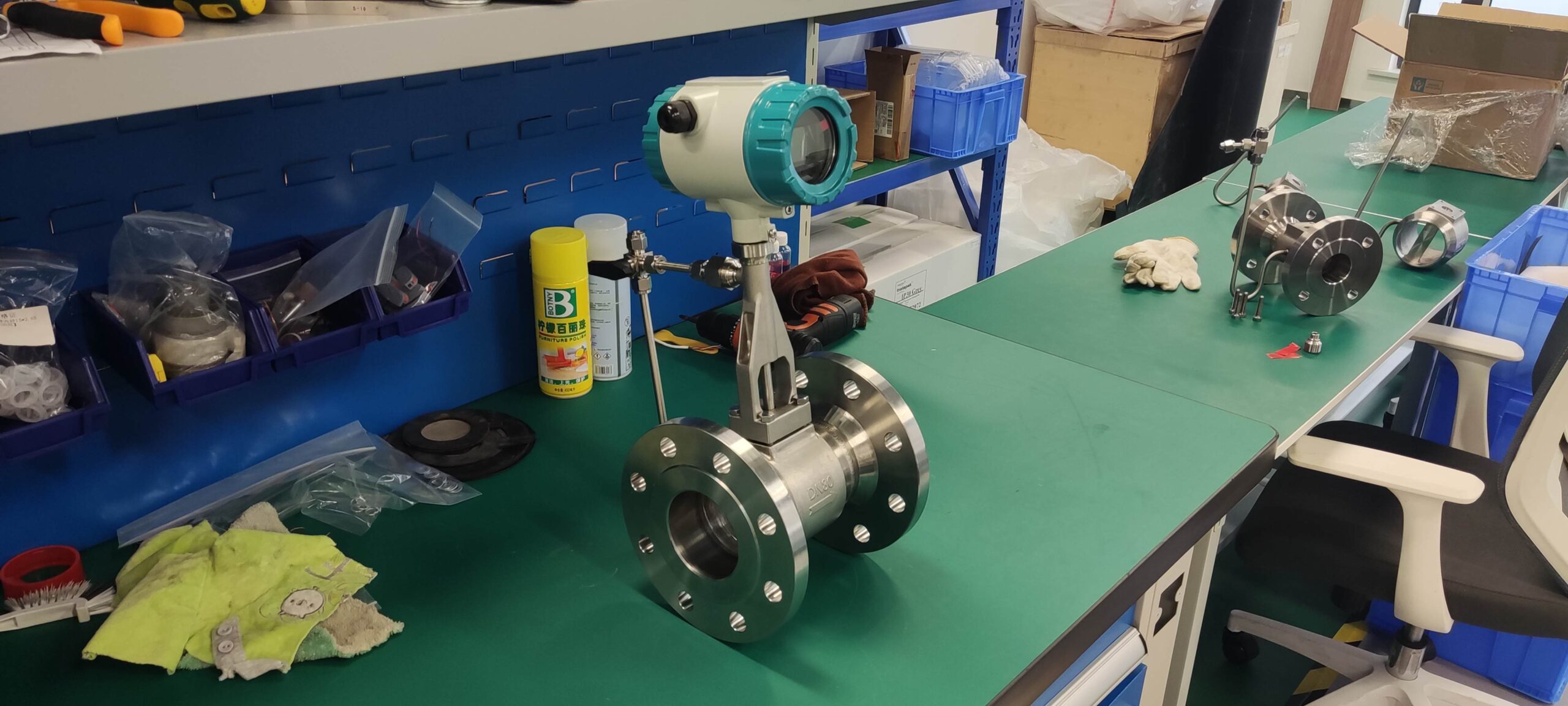
The vortex flowmeter is based on the Karman vortex street principle. It is mainly characterized by setting up a non-streamlined vortex generator (blocking the fluid) in the flowing fluid, and alternately generating two regular vortices on both sides of the vortex generator. It is widely applicable to industries such as petroleum, chemical engineering, metallurgy, thermal power, textile, and papermaking, for the measurement and control of superheated steam, saturated steam, compressed air, and general gases, water, and liquids. What issues should be noted when using a vortex flowmeter for hot water measurement
1. Single-phase medium remains unchanged: Due to different temperatures and transmission distances, the states of steam media include superheated steam, saturated steam, wet saturated steam, steam-water mixture and water. When measuring single-phase hot water media, vortex flow can better maintain the accuracy of the meter.
2. Measurement range: Compared with steam, the medium density of hot water is greater, the force acting on the probe body is stronger, the amplitude of the generated signal is larger, and the signal processing range is very wide. The measurement range ratio of a good sensor can reach 1:6 to 1:30, which makes the measurement and selection range wider and can adapt to more users.
3. Loss: The water supply network mainly controls the amount of water lost, which is a major indicator of loss. The magnitude of loss can be reflected through water replenishment. It is necessary to prevent leakage in one’s own pipeline network and also to control the non-heating use by heat users.
4. Accurate upper limit flow measurement: For steam measurement, due to the different characteristics of the medium itself and the form of the heat exchange unit, if the steam flow rate exceeds 90 meters per second, the vortex flowmeter will lose pulses and the measurement will be inaccurate. When measuring hot water, due to the characteristics of the medium and the limitations of the device, it is difficult to exceed 9 meters per second.
5. Calibration and usage are closer: When calibrating vortex flowmeters to measure steam, air is generally used. Due to the different calibration and usage media, there are still measurement differences. When measuring hot water and water, the calibration medium is the same, and the calibration and actual measurement error is smaller.
6. Factors affecting the accurate measurement of vortex flowmeters: Unlike steam measurement, due to the very small compression coefficient of water, factors such as pressure, temperature, and medium that affect steam measurement have a relatively small impact on hot water measurement. However, attention should still be paid to the influence of vibration on vortex flow.
7. Installation of vortex flowmeters: Unlike measuring steam, when measuring hot water, the installation of vortex flowmeters should be full pipe without air. Horizontal installation is suitable for low positions, and vertical installation should ensure that hot water flows from bottom to top.