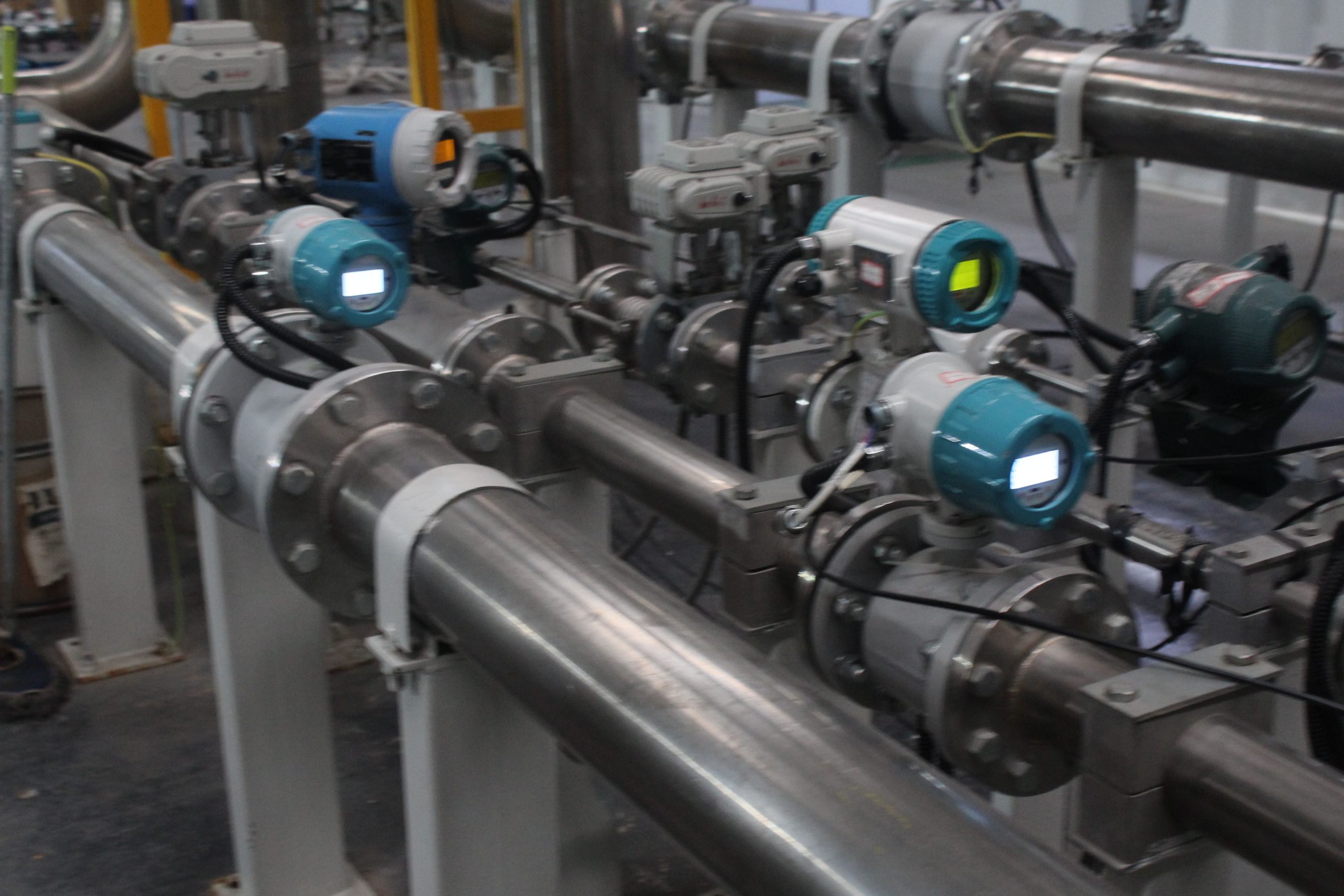
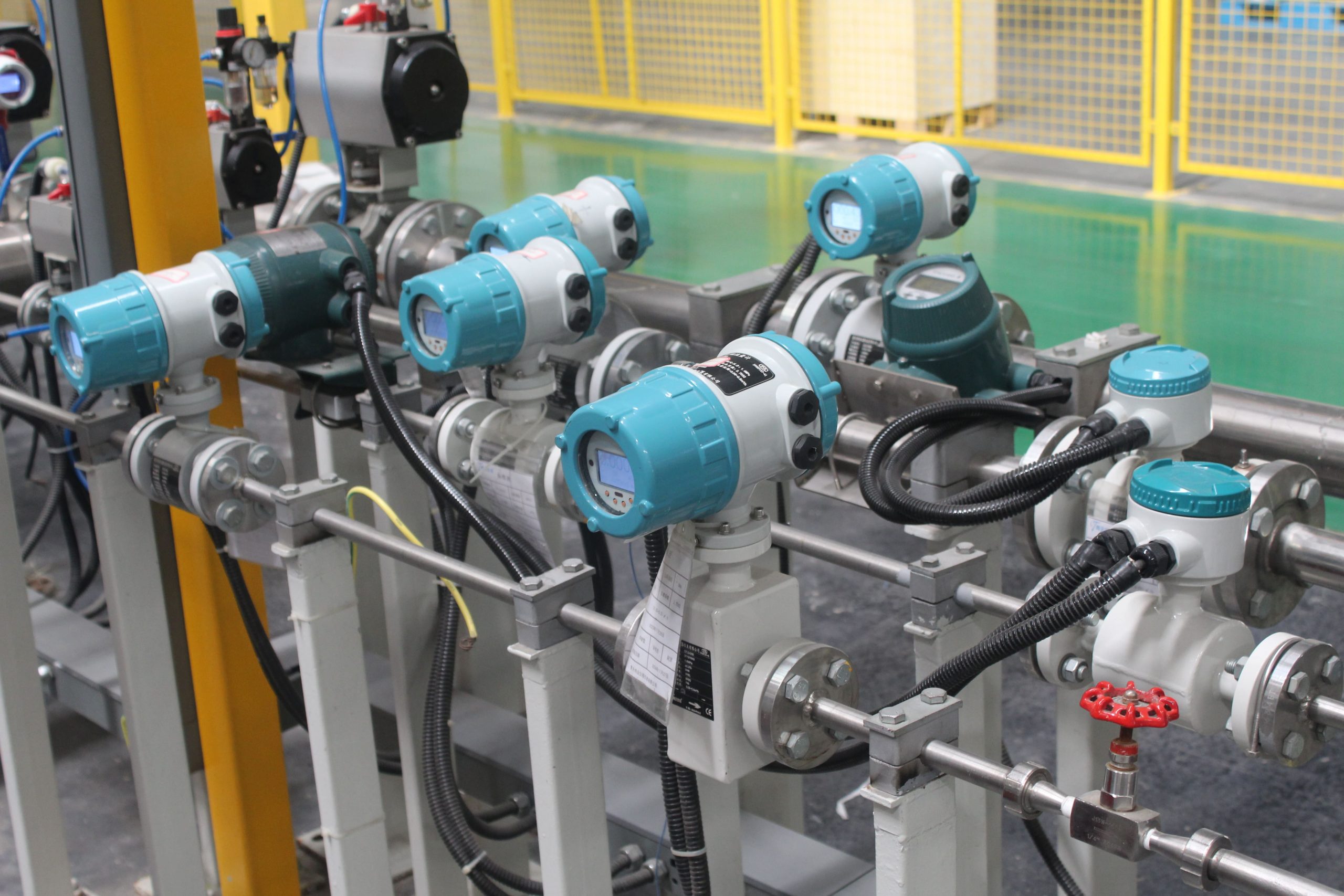
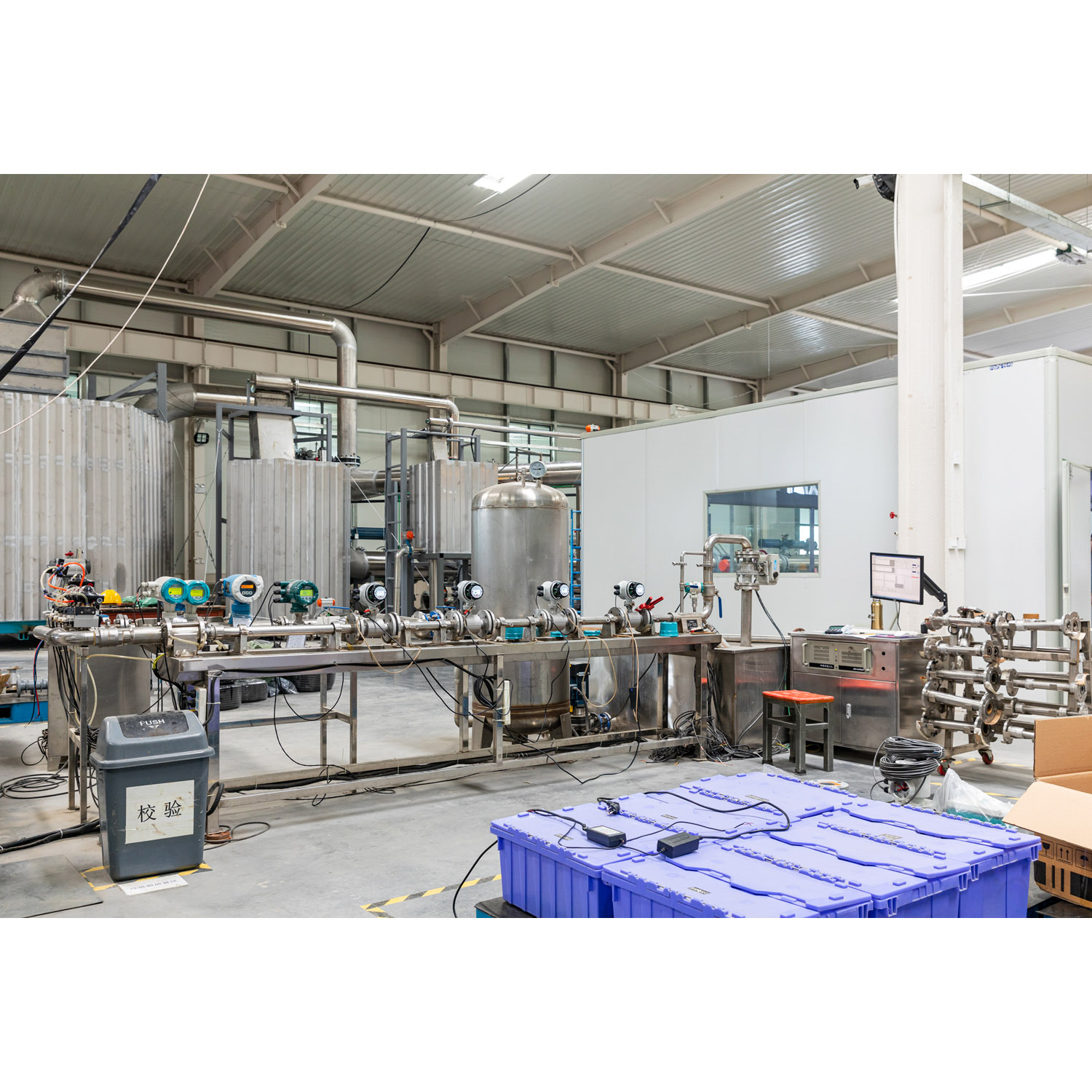
Application conditions and brief introductions of several commonly used flowmeters
Application conditions and brief introductions of several commonly used flowmeters
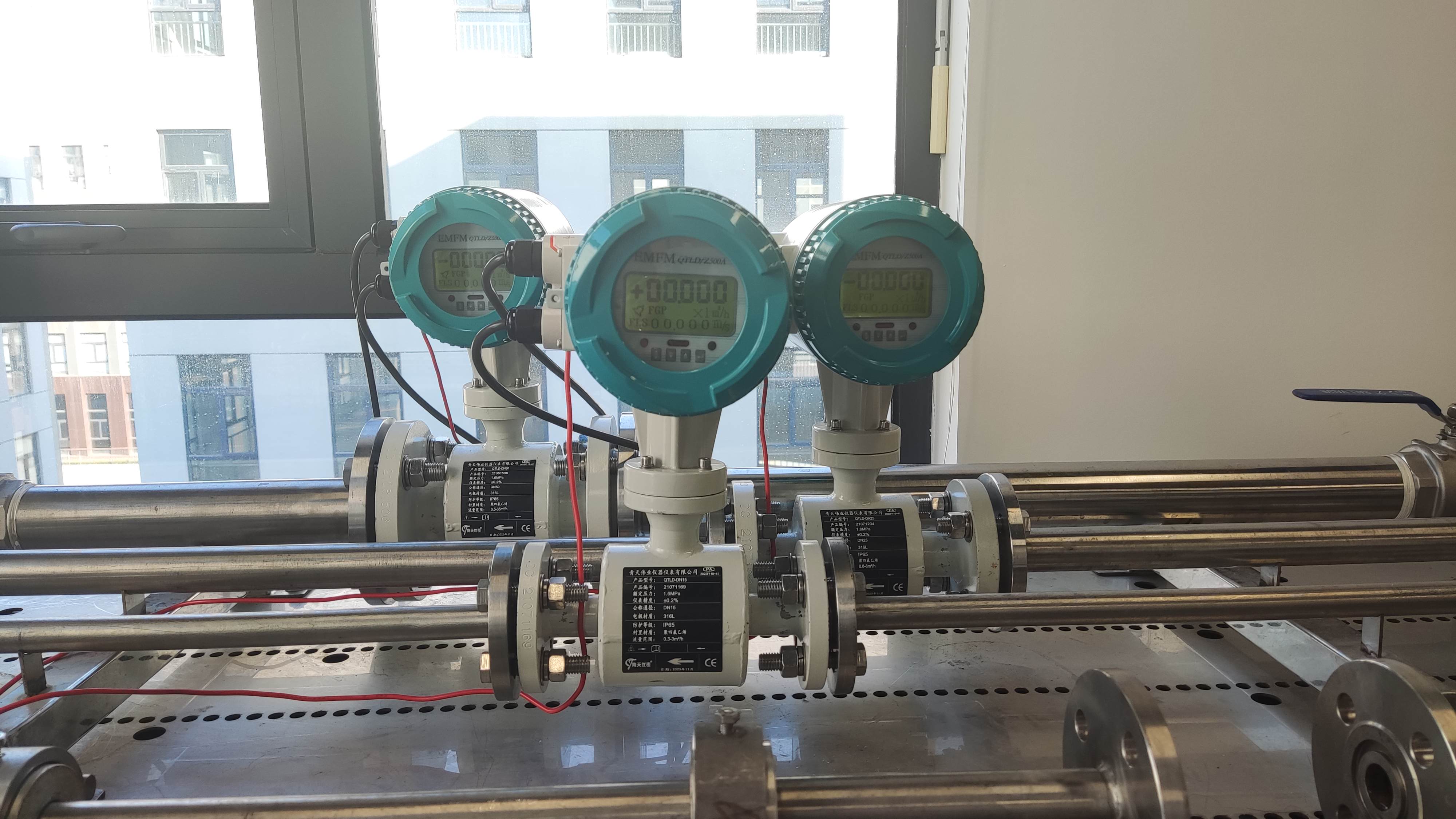
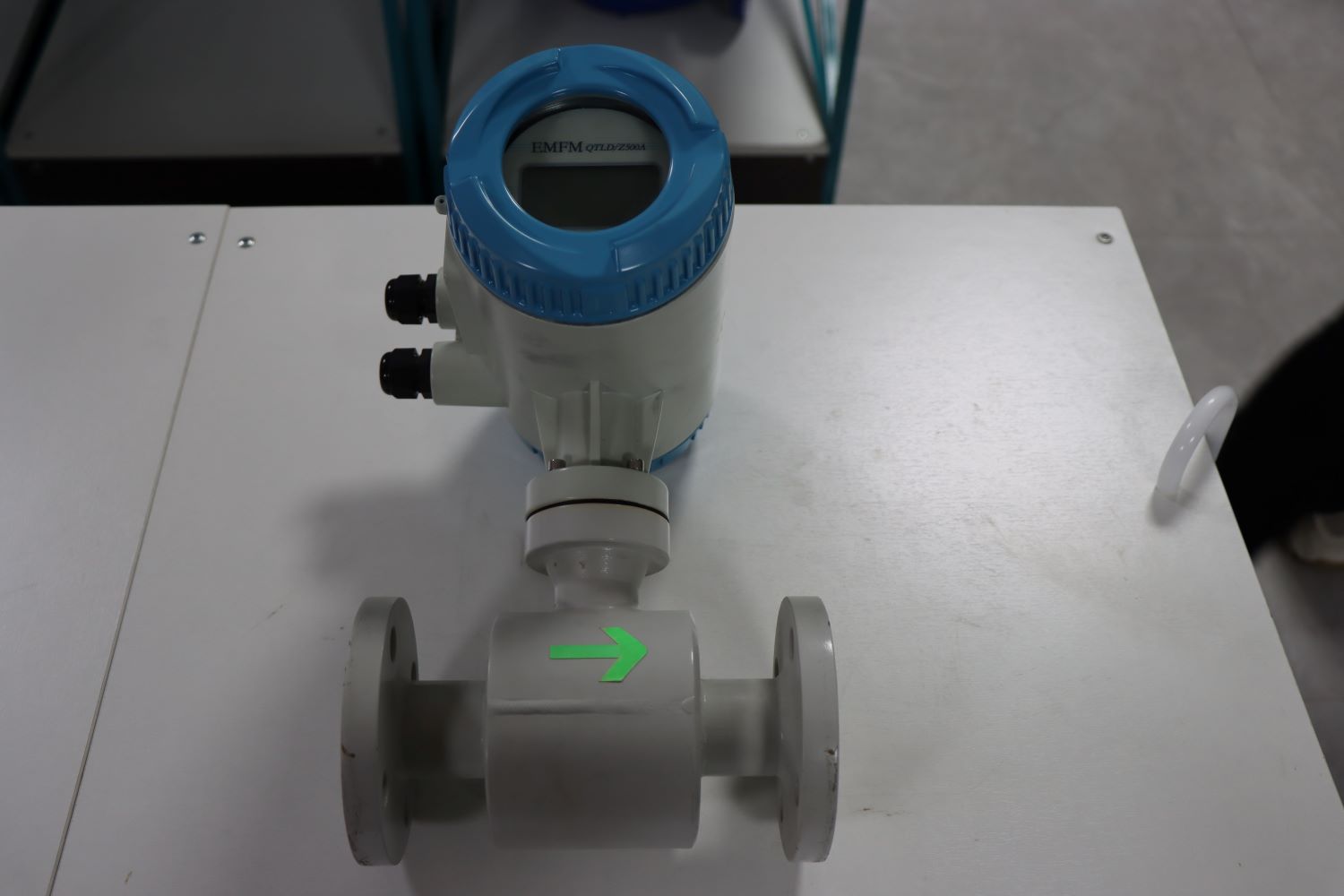
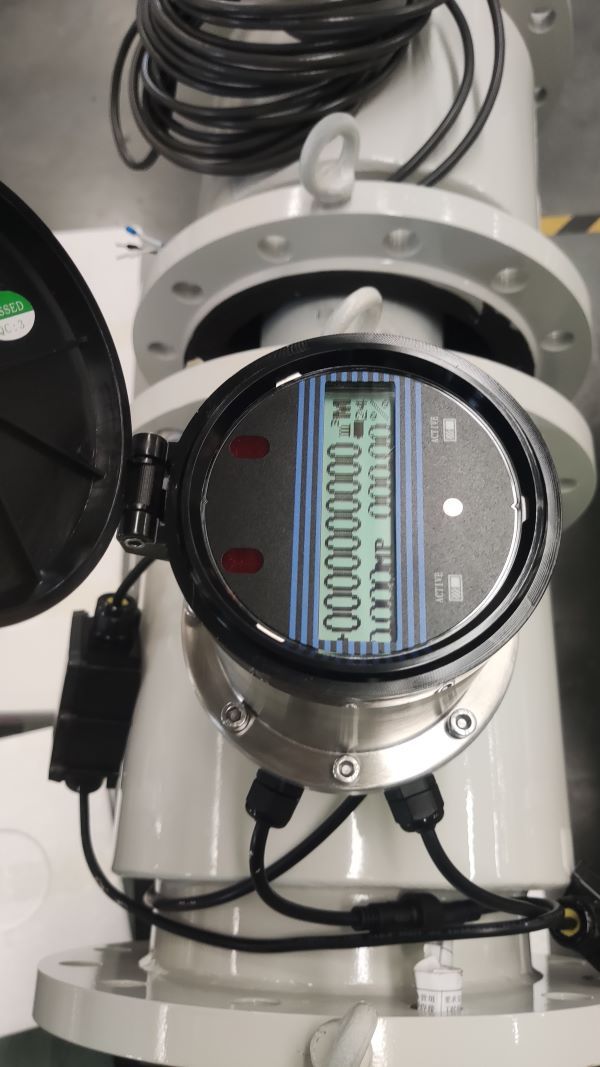
1. Electromagnetic flowmeter: Measurement principle: Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction proves that when a conductor moves in a magnetic field, an electric potential will be induced. Based on the principle of electromagnetic measurement, the fluid is a conductor in motion. The induced electromotive force is proportional to the flow velocity and is detected by two measuring electrodes. Then, the transmitter amplifies it and calculates the flow rate based on the cross-sectional area of the pipe. When a conductive fluid flows through an electromagnetic field, its velocity can be obtained by measuring the voltage. Electromagnetic flowmeters have no moving parts and are not affected by fluids. The measurement accuracy of conductive liquids is very high when the pipe is full. Electromagnetic flowmeters can be used to measure the flow velocity of slurry fluids.
2. Turbine flowmeter: When the fluid flows through the turbine flowmeter, the fluid causes the rotor to rotate. The rotational speed of the rotor is related to the speed of the fluid. The flow rate or total volume is derived from the average flow velocity of the fluid sensed by the rotor. Turbine flowmeters can accurately measure clean liquids and gases.
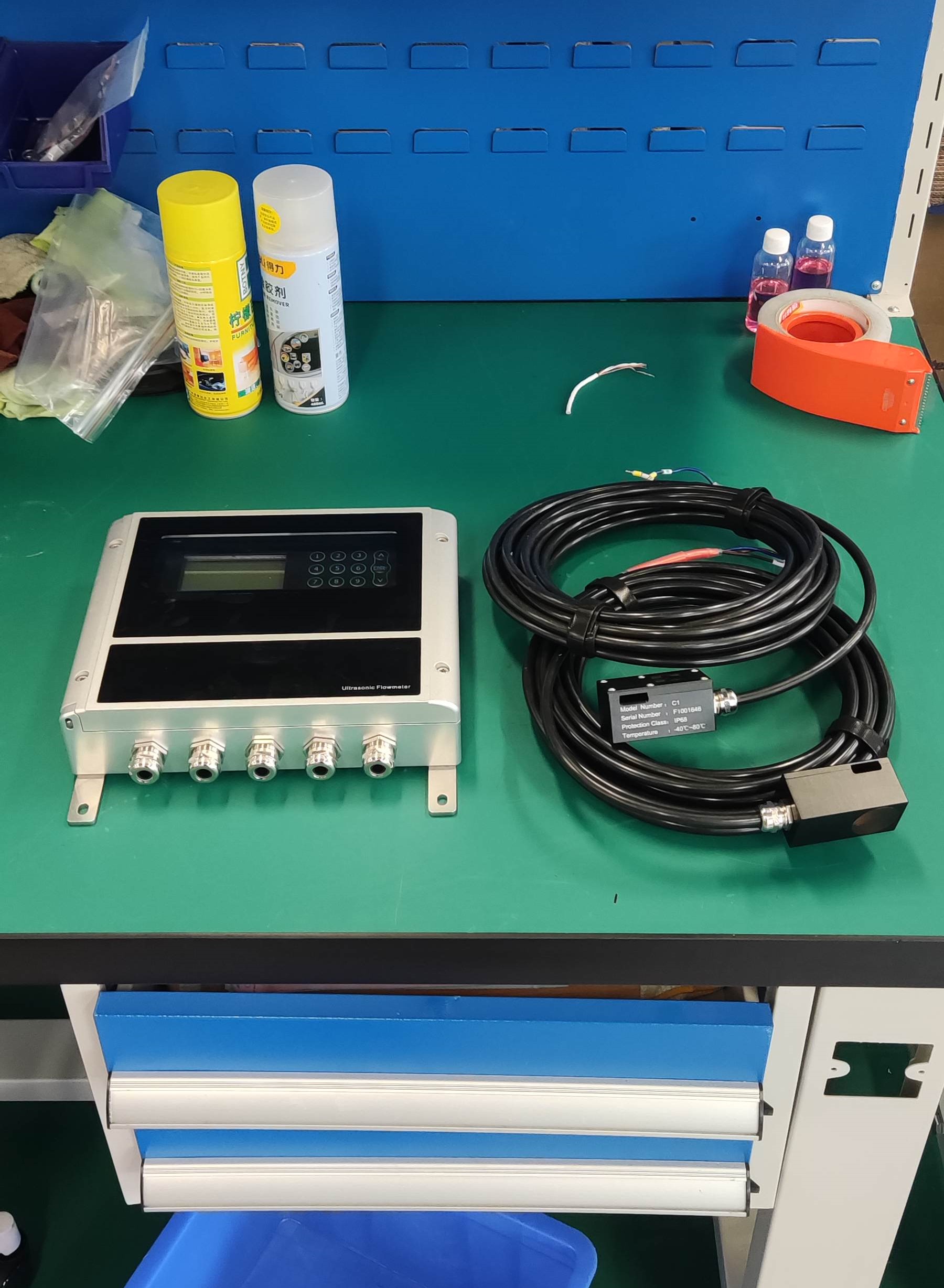
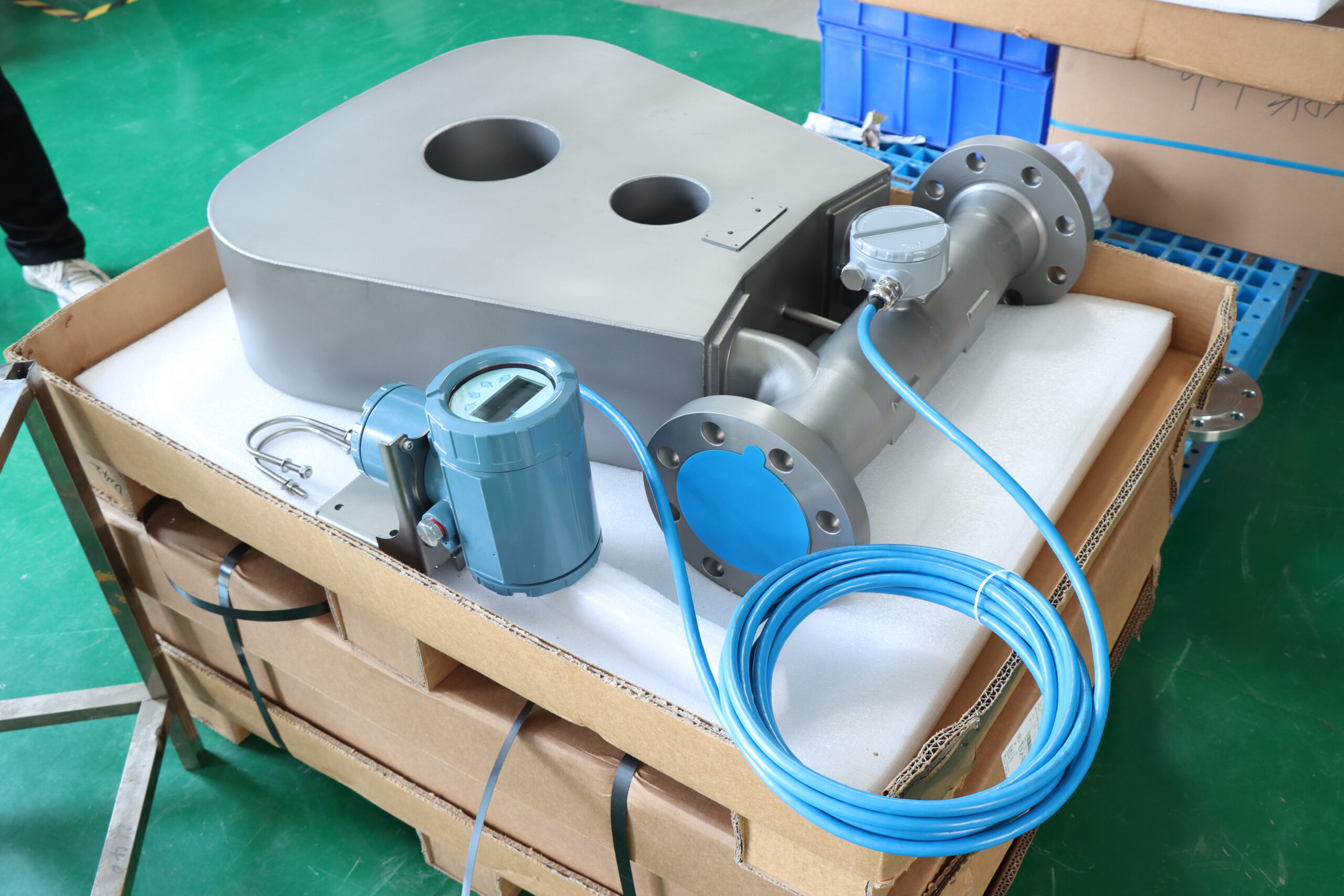
3. Ultrasonic flowmeters: The propagation time method and Doppler effect method are commonly used in ultrasonic flowmeters to measure the average velocity of fluids. Like other speed gauges, it is an instrument for measuring volumetric flow. It is an unobstructed flowmeter. If the ultrasonic probe is installed outside the pipeline for measurement, there is no need to insert it. It is applicable to almost all liquids, including slurries, with high precision. However, the dirtiness of the pipes will affect the accuracy.
4. Vortex flowmeter: A vortex flowmeter places a non-streamlined vortex generator in the fluid. The velocity of the vortex is proportional to the velocity of the fluid, thereby calculating the volumetric flow rate. Vortex flowmeters are suitable for measuring liquids, gases or steam. It has no moving parts and no dirt problems. Vortex flowmeters generate noise and require the fluid to have a relatively high flow rate to produce vortices.
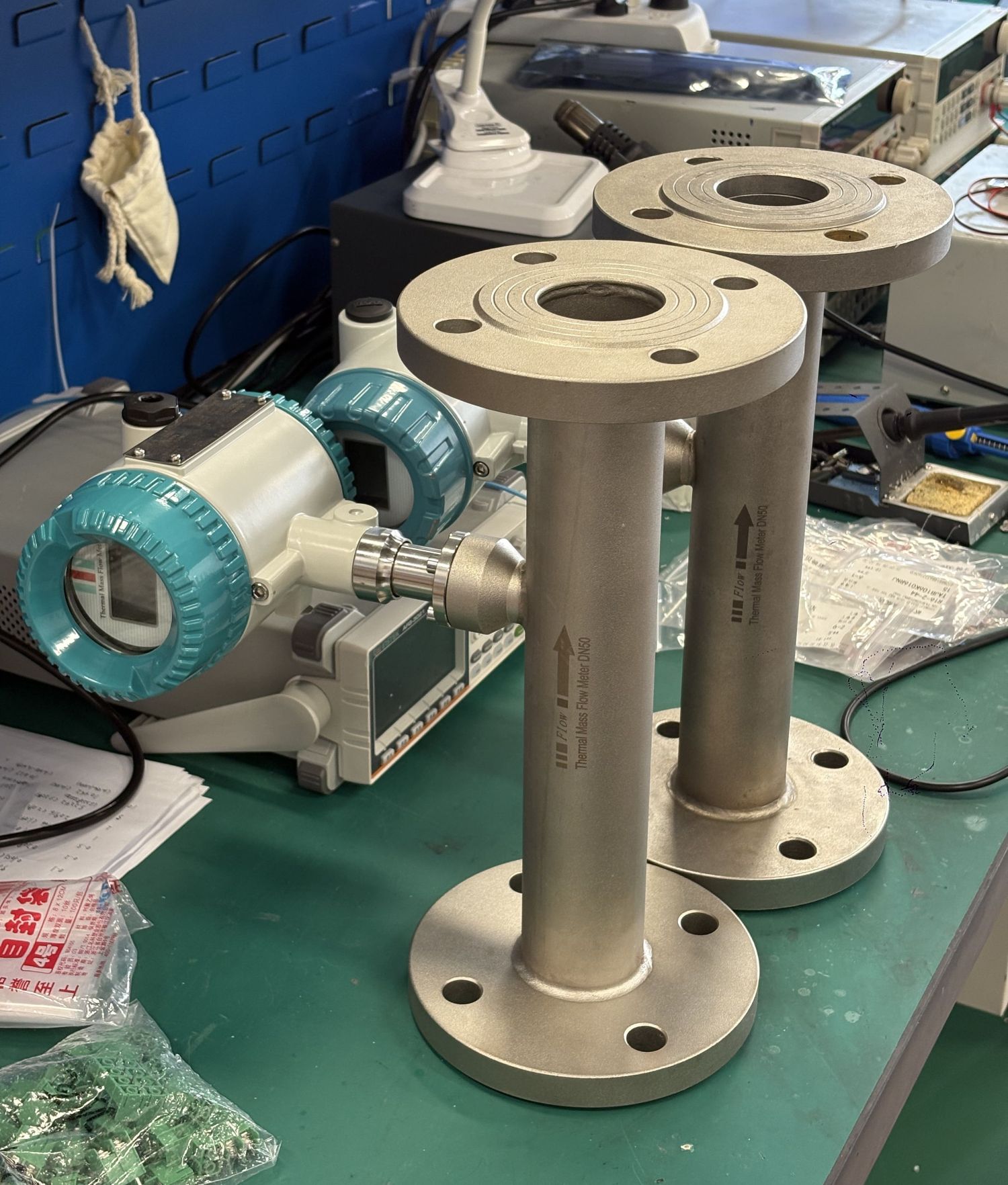
5. Thermal gas mass flowmeter: It measures the fluid velocity by measuring the increase in fluid temperature or the decrease in the thermal sensor. Thermal mass flowmeters have no moving parts or holes and can accurately measure the flow of gases. Thermal gas mass flowmeters are one of the few technologies capable of measuring mass flow and also one of the few used for measuring the flow of large-diameter gases.
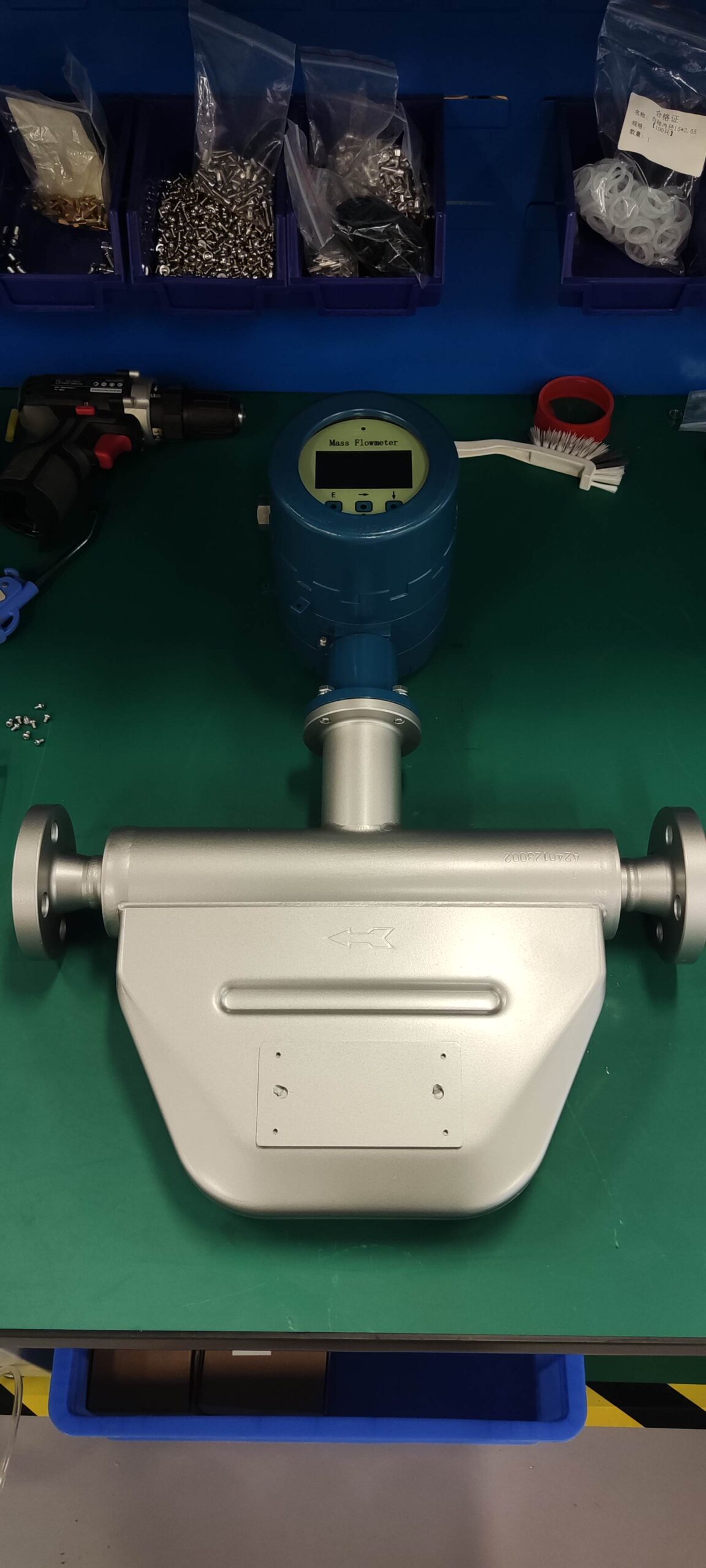
6. Coriolis flowmeter: This type of flowmeter measures by generating deflection corresponding to the mass flow rate in a vibrating fluid tube. Coriolis flowmeters can be used to measure the mass flow of liquids, slurries, gases or steam. High precision. However, regular maintenance of the pipe walls should be carried out to prevent corrosion.