Regarding the principles of circular gear flowmeters and elliptical gear flowmeters
The elliptical gear flowmeter, also known as the displacement flowmeter, is a type of volumetric flowmeter. It is one of the flowmeters with relatively high accuracy among all types. It uses mechanical measuring elements to continuously divide the fluid into individual known volume portions. The total volume of the flow is measured by the number of times the measurement chamber fills and discharges the volume portion of the fluid successively and repeatedly. The elliptical gear flowmeter can be manufactured using different materials (cast steel, stainless steel, and 316), and is suitable for flow measurement work in industries such as chemical engineering, petroleum, medicine, power, metallurgy, and food.
The elliptical gear flowmeter has high measurement accuracy and is suitable for measuring the flow of high-viscosity media. However, it is not suitable for fluids containing solid particles. If the measured liquid medium contains gas, it will also cause measurement errors. Generally, the accuracy of the elliptical gear flowmeter can reach 0.5 grade, and it is a relatively accurate flow measurement instrument. However, if the flow of the measured medium is too small when using it, the influence of the leakage error of the elliptical gear flowmeter will be prominent, and the sufficient measurement accuracy cannot be guaranteed.
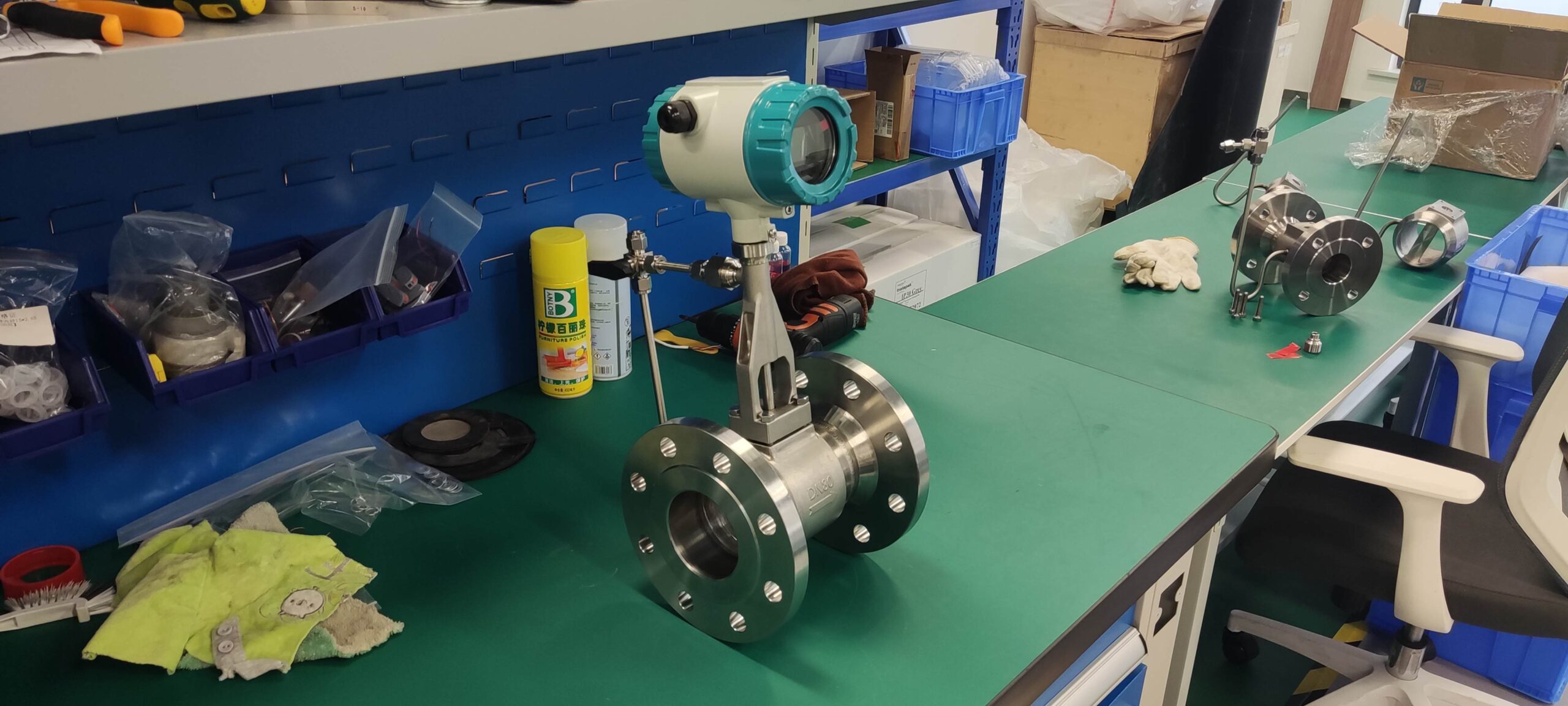
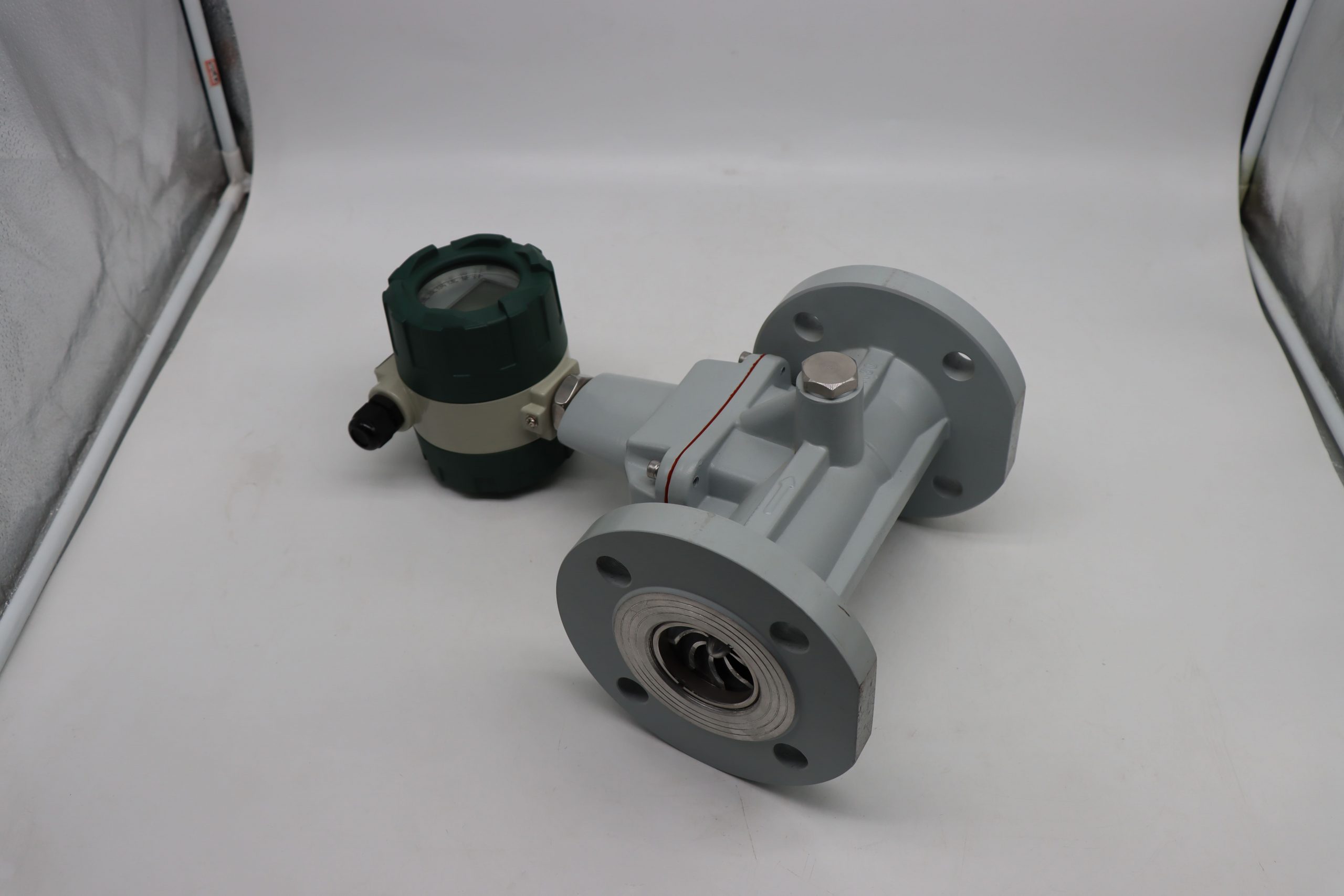
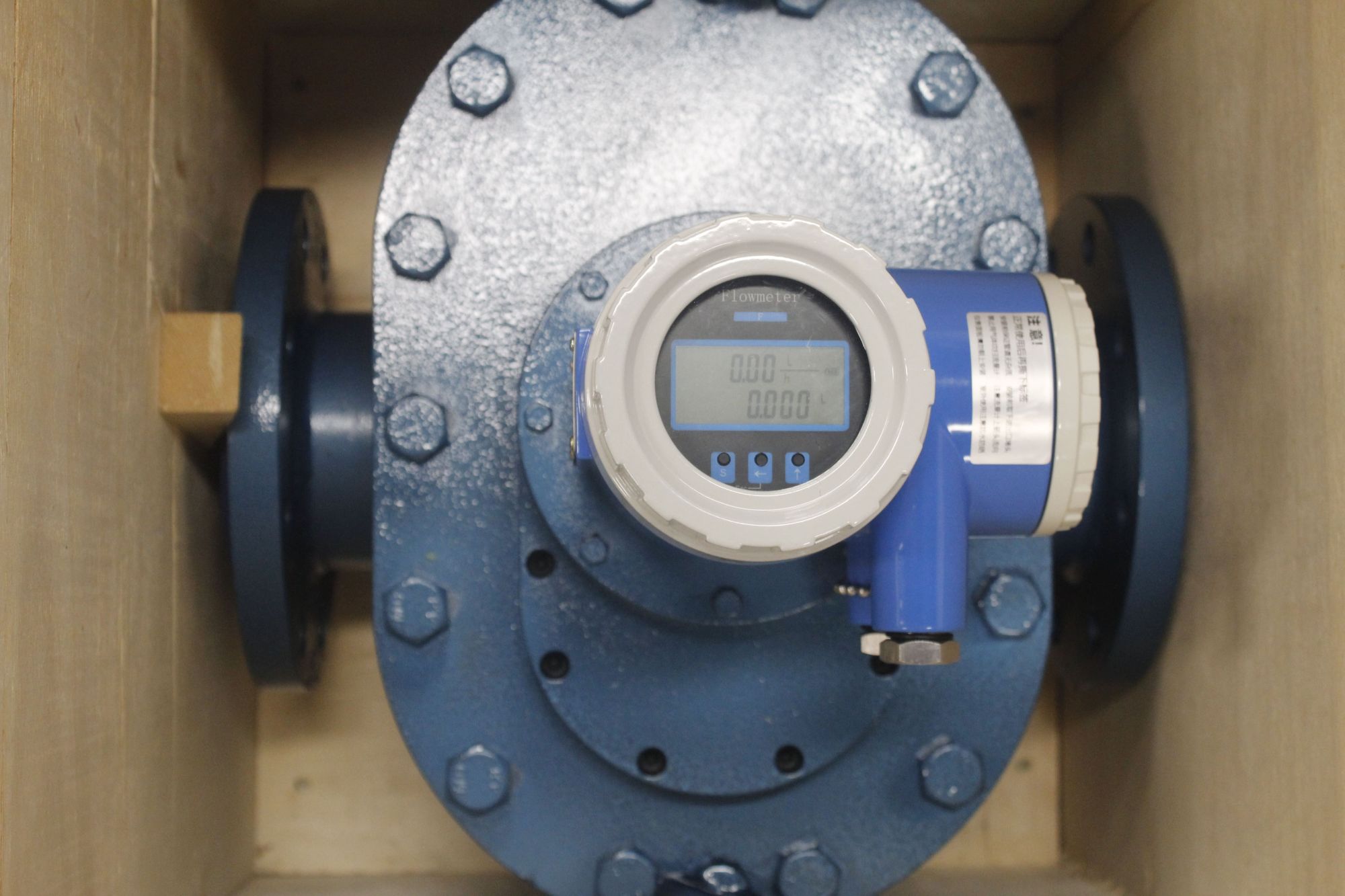
The structure of the elliptical gear flowmeter consists of a measuring chamber and a pair of elliptical gears installed inside the chamber, along with the upper and lower cover plates, forming a sealed crescent-shaped cavity (due to the rotation of the gears, it is not an absolutely sealed structure) as the calculation unit for the initial flow volume. When the measured liquid enters the flowmeter through the pipeline, the pressure difference at the inlet and outlet drives the pair of gears to rotate continuously, constantly transporting the liquid measured by the crescent-shaped cavity to the outlet. The product of the number of rotations of the elliptical gears and four times the flow volume per time is the total flow volume of the measured liquid (see the principle in the figure). The flowmeter is mainly composed of the housing, the counter, the elliptical gears, and the coupling (including magnetic coupling and axial coupling).
Like the elliptical gear flowmeter, the circular gear flowmeter is also a type of volumetric flowmeter, used for precise continuous or intermittent measurement of the flow or instantaneous flow of liquids in pipelines. It can be used for low-viscosity media and also for cryogenic liquids (such as liquid nitrogen, liquid oxygen, LNG, etc.), and is particularly suitable for the flow measurement of media with high viscosity such as heavy oil and resin. The circular gear flowmeter uses mechanical measuring elements to continuously divide the fluid into individual known volume portions. It measures the total volume of the fluid based on the number of times the measurement chamber fills and discharges the volume portion of the fluid successively and repeatedly.
The working principle of the circular gear flowmeter is to detect through the sensing coil installed on the sensor amplifier inside the housing. The signal amplifier does not come into contact with the measured medium. When the transformer gear cuts through the magnetic lines of force generated by the magnet inside the housing, it will cause a change in the magnetic flux in the sensing coil. The sensing coil transmits the periodic change signal of the detected magnetic flux to the preamplifier, which amplifies and shapes the signal, generating a pulse signal proportional to the flow rate, which is sent to the unit conversion and flow accumulation circuit to obtain and display the cumulative flow value. At the same time, the pulse signal is sent to the frequency current conversion circuit, converting the pulse signal into an analog electrical current, thereby indicating the instantaneous flow value.







-.jpg)




























