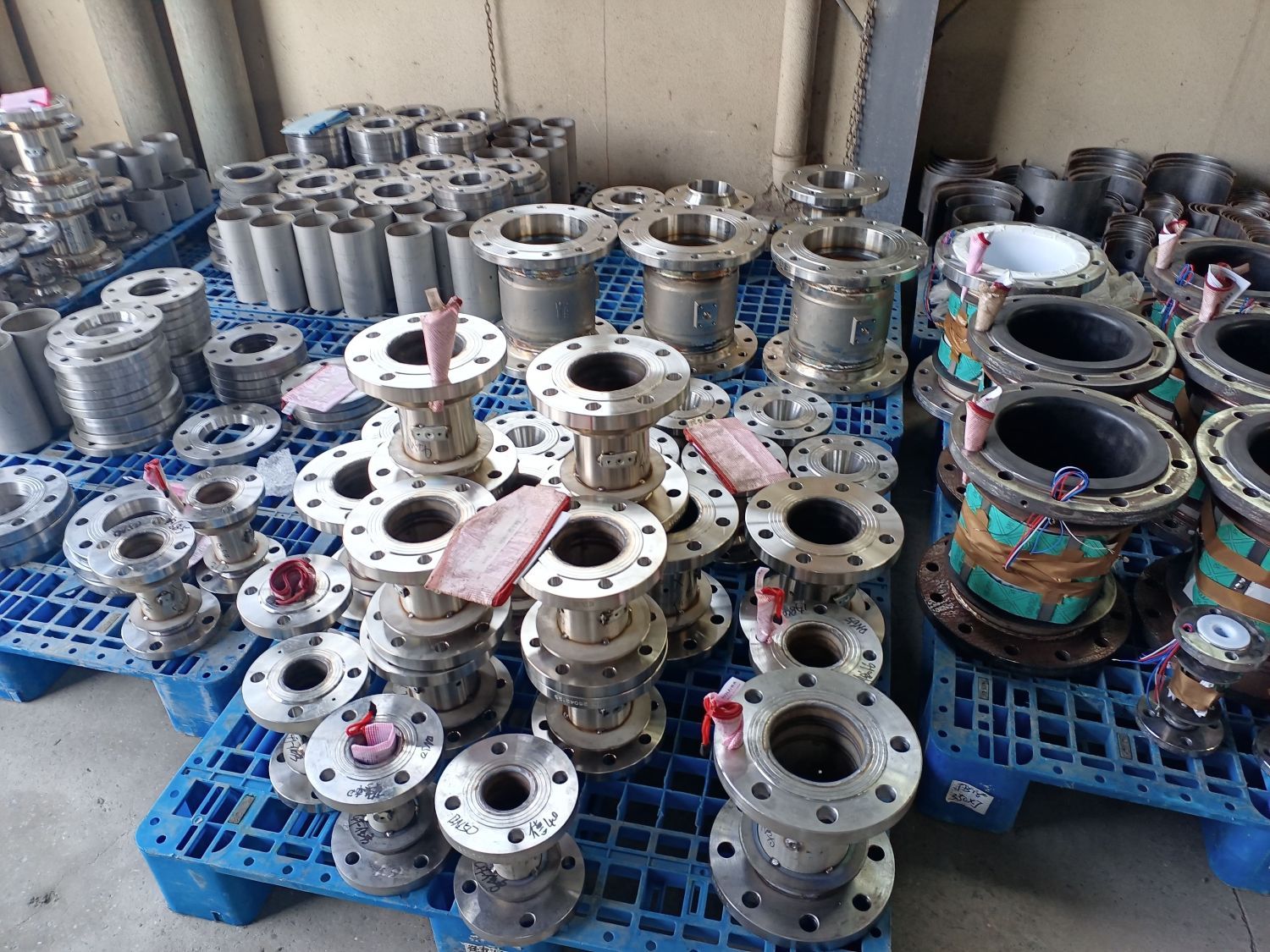
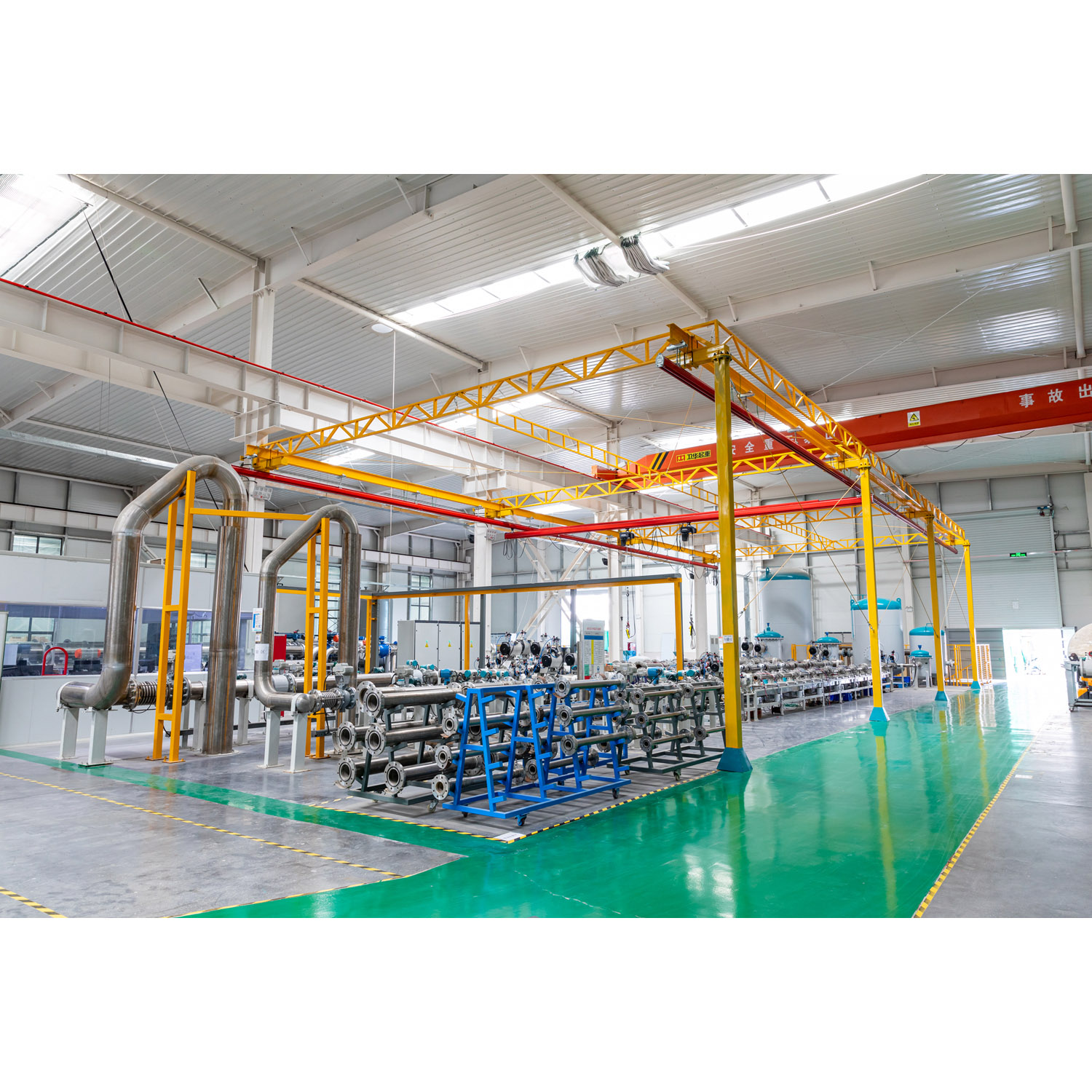
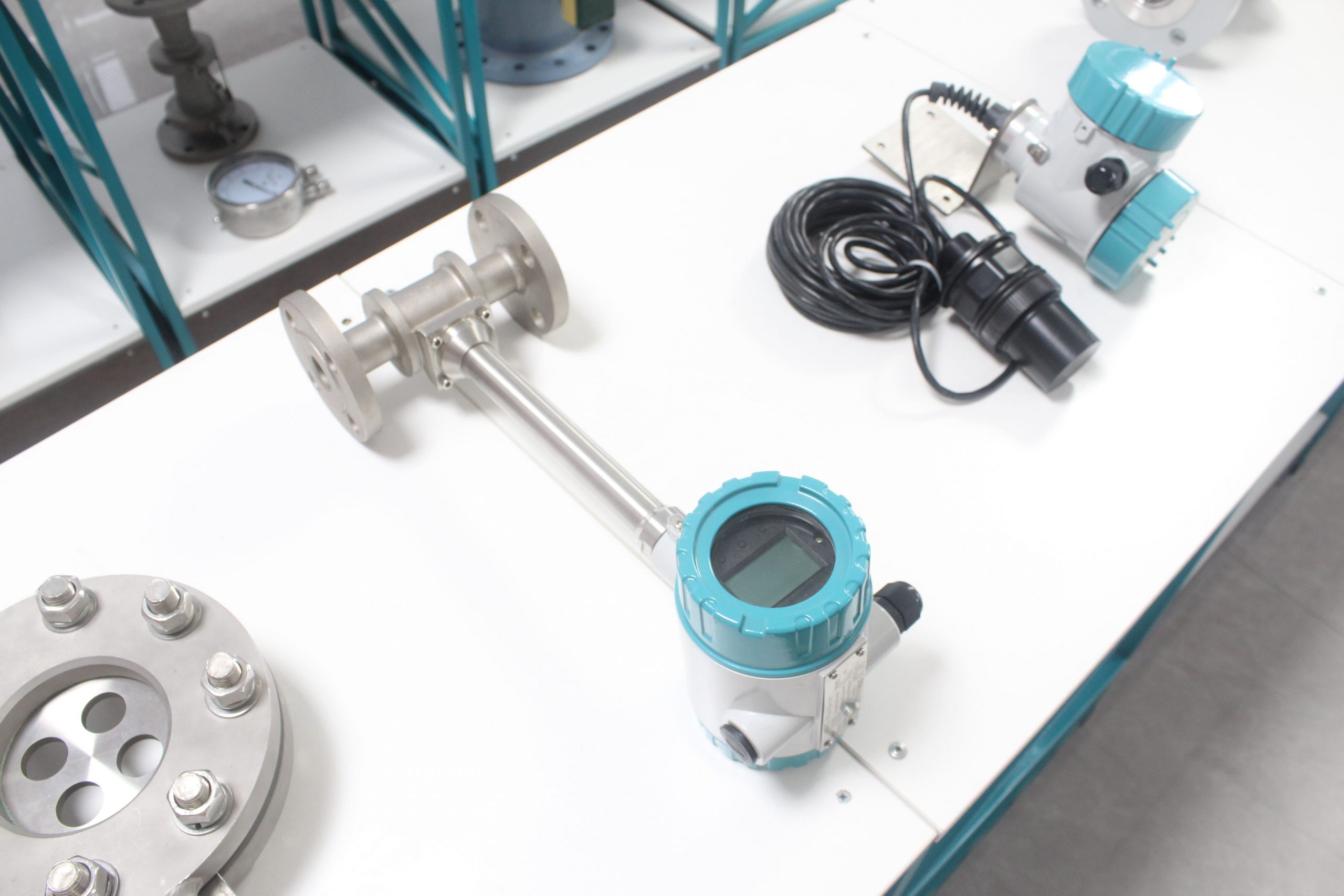
Common fault solutions for compressed air vortex flowmeters
The common fault analysis and solutions of compressed air vortex flowmeters are as follows:
When the compressed air vortex flowmeter has no signal output or no instantaneous flow display, the common fault analysis and solution measures are as follows:
1) it is necessary to check whether the power supply voltage is correct and reasonable.
2) If the power supply voltage is correct and reasonable, turn the sensitivity potentiometer and the amplification factor potentiometer counterclockwise to the maximum.
3) If there is a signal output, check whether the pipeline flow exceeds the measurable flow range of the vortex street.
4) If the flow rate is within the measurable range, it indicates that the sensitivity of the vortex street flow sensor head is already low and needs to be readjusted.
2. When there is no flow in the pipeline of the compressed air vortex flowmeter and there is signal output or instantaneous flow display, the common fault analysis and solutions are as follows:
First, it is necessary to inspect and verify that there is indeed no fluid flow or disturbance in the pipeline and whether the vibration intensity of the pipeline is too high.
2) Adjust the sensitivity potentiometer clockwise until there is no signal output or the instantaneous flow returns to zero. When adjusting the potentiometer, it should be done as slowly as possible. Every time a 5-degree Angle is adjusted, pause for more than 10 seconds to observe whether the output returns to zero.
3. When the signal output of the vortex flowmeter is unstable or the instantaneous flow rate is unstable, the common fault analysis and solutions are as follows:
1) it is necessary to check whether the pipeline flow exceeds the measurable flow range of the vortex street.
2) If the flow rate is within the measurable range, check whether the straight pipe sections before and after meet the requirements. If it is not up to standard, the straight pipe section needs to be refitted.
3) Check whether the process flow rate is a stable flow rate.
4) Check whether the vibration intensity of the pipeline is too high. If it is too large, shock-absorbing joints need to be installed.